PROJEK MEMELIHARA IKAN AIR TAWAR/
UDANG GALAH DI TANJONG TUALANG,
PERAK
PRELIMINARY REPORT ON THE
ENGINEERING ASPECTS OF PLANNING,
DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION
March, 1979
WAN MOHAMED & KHOO SDN. BHD.
Jurutera Perunding,
No. 14A Lorong 8/1E,
Petaling Jaya,
Selangor,
MALAYSIA.
Tel: 03-53683/772854/563760/775158
CONTENTS
1.3 ALTERNATIVE SITES FOR THE AQUACULTURE CENTRE
III PLANNING, DESIGN AND OPERATION OF FISH/SHRIMP CULTURING PONDS
3.8 OPERATION OF NURSERY & CULTURING PONDS
IV BUILDING, INFRASTRUCTURE, PLANT & EQUIPMENT
4.5 PLANT/EQUIPMENT AND HARD FURNISHING
5.4 ANNUAL RECURRENT MAINTENANCE EXPENDITURE FOR PUMPING PLANT/EQUIPMENT
LIST OF FIGURES
3/1 LAYOUT OF PONDS, OFFICE AND QUARTERS
3/2 TYPICAL DETAILS OF TERTIARY, SECONDARY AND PERIMETER DYKES
3/3 TYPICAL DETAIL OF SUPPLY CHANNEL
3/4 TYPICAL DRAINAGE CHANNEL DETAILS
3/5 TYPICAL DETAIL OF WATER INLET CONTROL STRUCTURE
3/6 DETAIL OF OVERFLOW & OUTLET CONTROL STRUCTURE
3/7 DETAIL OF DRAINAGE OUTLET STRUCTURE
LIST OF APPENDICES
B RESULTS OF WATER ANALYSIS OF SUNGEI TUMBOH
D ANNUAL RECURRENT OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE EXPENDITURE FOR PUMPING INSTALLATION AT POND COMPLEX
PROJEK MEMELIHARA IKAN AIR TAWAR/UDANG GALAH DI TANJONG TUALANG, PERAK
PRELIMINARY REPORT ON THE ENGINEERING ASPECTS OF PLANNING, DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION
1.1.1 Lembaga Kemajuan Ikan Malaysia (Majuikan) propose to establish a Fresh Water Aquaculture Centre at Tanjong Tualang, Perak primarily to undertake works of a commercial nature. The Centre would also be actively involved in research and training of Majuikan personnel in aquaculture development. Initially the Centre intends to commence work on a commercial scale for culturing of fish and shrimp.
1.1.2 Preliminary aquaculture studies undertaken by Majuikan in conjunction with Fisheries Department have identified three (3) sites in the State of Perak suitable for fresh water aquaculture, however, from the engineering point of view the site at Tanjong Tualang was selected. The site chosen is part of an existing low/swamp ground bordering a major river Sungei Tumboh and at present Sungei Tumboh is known to support a large stock of wild shrimps.
1.1.3 Discussions have been held with Majuikan officials and other officials from different agencies to ascertain their requirement and criteria for the design of the shrimp and fish culturing ponds and other facilities in the Centre and this forms the basis for planning and layout of the Centre.
1.1.4 This report covers the engineering aspects of planning, design and construction of fish and shrimp culturing ponds, buildings, and infrastructure for the Centre.
The Terms of Reference require the Consultants to conduct preliminary investigation, design and construction of the Centre and details of these are set out in letter of invitation for consultancy services enclosed in Appendix ‘A’.
1.3.1 Three (3) sites, i.e. in slim, Kampar and Tanjong Tualang areas have been identified by Majuikan Official in conjunction with the Fisheries Department as being suitable for freshwater fish and prawn culture. The sites were visited to ascertain the suitability from the engineering point of view and details are listed in the below mentioned paragraphs.
1.3.2 Site No.1, Daerah Batang Padang, Mukim of Slim is located in a region where tin mining activity is currently in progress and this is a source of pollution of Sungei Slim from which we propose to obtain water for the culture ponds. The land available is only 50 acres and this is insufficient for expansion purposes. Also the site is located on both banks of Sungei Slim and access and control of the works would be difficult and would involve substantial initial cost for the bridge crossings. As such this site was generally not suitable nor selected for the construction of the pond complex.
1.3.3 Site No.2 at Kampar is situated about 16 miles from the town of Ipoh and located on the right bank of Sungei Kampar slightly inland and extends to the foothills. Most portions of the site is disused tin mining areas with large sections of it being stagnant ponds. The land avaialble is only about 100 acres and not sufficient for expansion purposes. Tin mining activity is noted in adjacent areas of the proposed site.
More than half the site is covered by existing disused mining pools and these have now been used by local farmers to rear fish on a TOL basis. The ponds are more than 20 feet deep with large amounts of rock outcrops in the pond areas. In the remaining areas some vegetable farming is being carried out.
The soil at site appears to be sandy clay with large sand content and appears not capable of retaining water above the water table. Five hand augers to a maximum depth of 3 feet have been conducted by Majuikan and the test results confirms to an extent the sandy nature of soil.
The water in Sungei Kampar is quite clear but at times the effleunt from tin mines are discharged into Sungei Kampar. The water level in Sungei Kampar is quite low in comparison to proposed site and pumping to lift water to the ponds would be necessary.
In view of the following facts this site is also not suitable for construction of the pond complex :
Insufficient land for expansion purposes;
Difficulty in acquiring land already given out on a TOL basis;
Expensive earthworks due to sandy nature of soils, presence of rock, existence of deep ponds;
Pumping is essential due to elevation of site in relation to water level;
Possible pollution of Sungei Kampar, the only water source.
1.3.4 Site No.3 at Tanjong Tualang is located along the 32nd milestone along the Tanjong Tualang-Kampung Gajah road near Sungei Tumboh bridge. Most of the areas is open grassland with patches of belukar and forms part of an extensive swamp/water logged areas. An existing earth track constructed by loggers forms the main access to the site from the main road. Some isolated tapioca growing was observed at site. Most of the site is state land and an extensive area is available for development purpose. It was also noted that this area was ear-marked for aquaculture development in the Trans-Perak Development.
The soil at site seems to be sandy clay with fair amount of clay and appears able to retain water. Stagnant patches of water were observed in many places in the other areas and the water table was quite high.
The main source of water at this site would be Sungei Tumboh, however, the normal water level is low in relation to site. Sungei Tumboh is fairly wide and deep and the water is turbid as logging and minor tin mining activity is still going on upstream. However, it is known that prawns and fish are abundant in this natural condition.
Among the 3 sites available it was generally noted that this site at Tanjong Tualang is more suitable for construction of Aquaculture Centre and the site was selected for further studies and investigation.
1.4.1 Topography surveys were carried out at the Tanjong Tualang site and works included spot levelling within the site, detailing and cross-sectioning of Sungei Tumboh within the area.
1.4.2 The proposed site (for the initial phase) comprising approximately 100 acres is located in fringes of Hutan Simpan Parit and is situated on the right bank of Sungei Tumboh (see Fig. 1/1). The ground level varies from +18.00 M.S.L. to +25.00 M.S.L. and is presently under open grassland and belukar. Certain portion of the site are subject to inundation when the river water level rises in Sungei Tumboh. Sungei Tumboh is not subject to tidal effects or saline intrusion.
1.5.1 The climate in this region is on the whole equable and continuously humid. The site is affected by the SouthWest Monsoons and rainfall records from neighbouring station indicate the average rainfall ranges from 84.99" to 119.98" (year 1965 – 1970) and 68.8" to 92.97" (1970 – 1975) annually. The mean raingall ranges from 106.41" to 81.55" and the greater part of the rainfall is during October through December.
1.5.2 The site is free from the effects of tropical cyclones or severe winds.
1.6.1 The soil in the proposed site is of recent alluvial deposits and during the time of writing this report field and laboratory information from a recently initiated soil investigation programme indicate a layer of sandy clay 3 feet to 20 feet thick over-lying a coarse to medium sandy layer (refer soil profile Fig. 1/2)
1.6.2 Examination of the soil samples and laboratory test results indicate the soil is characterised by reasonable shear strength and bearing capacity generally capable of retaining water.
1.7.1 Discussion with other government agencies indicated that there would be substantial development activity in the Tumboh Block in time to come and most of these have been enumerated in the Trans-Perak Study. The upper catchment area of Sungei Tumboh has been ear-marked for cattle farming, cash crop cultivation and forest reserves.
1.7.2 For immediate development it is known that Jabatan Parit dan Taliair Perak (JPT) propose to improve the complete drainage system in the Tumboh area and topographical surveys for these have already commenced and this has to be taken into account in the design of the Aquaculture Centre.
1.7.3 The Jabatan Kerja Raya Perak (JKR) have already appointed engineering consultants to upgrade the existing logging track adjacent to the site and this is being done under the Accelerated Rural Roads Programme and JKR envisage construction works to be completed around late 1980.
1.8.1 The data initially available and obtained from various Government Department include :
Topographical Map Sheet No.64 (Series L7010)
) Standard 8 chain revenue sheets
Rainfall record for period 1965 to 1975 at station No. 3094, Kampung Gajah.
Water levels at Sungei Tumboh.
2.1.1 The only source of surface water at site is Sungei Tumboh, a fairly large river, however, its catchment is not well defined as it flows through swamp and water logged areas. Approximating the catchment area at 33.7 acres the flood flows and dry weather flows is estimated at 3135 cusecs and 12.6 cusecs respectively for a once in ten year frequency.
2.1.2 The once in ten year flood level is estimated to reach a level of +23.00 M.S.L. and at a similar frequency low flows is estimated at +10.00 M.S.L. The normal average water level record is +15.00 M.S.L.
2.1.3 The water in the Sungei is quite turbid with a high sediment load and a form of retention is necessary to settle a major portion of silt in suspension. Results of water sample analysis obtained from the Sungei is indicated in Appendix ‘B’.
2.2.1 No information regarding groundwater is available at or around the vicinity of the site. Groundwater studies were not undertaken at site as these are generally expensive and pilot drilling for test wells, observation wells and testing would have to be carried to ascertain the availability and quality of groundwater. Also with the presence of large surface source of water, investigation for groundwater was set aside.
2.3.1 At the moment the only form of pollution noticeable at site is the logging and minor mining activity being carried out in the upstream catchment. Further pollution is generally not expected if the development of the upstream catchment will be as outlined in Masterplan of the Trans-Perak Study.
3.1.1 Siting of Ponds
In order to take advantage of the easy access from the main road, minimum earthworks and to site the ponds in soils which substantially retain water, the area bounded by the existing main road, existing logging track and Sungei Tumboh has been considered ideal for siting of ponds. (See Fig. 3/1)
The ponds are located 2 chains away from the existing river reserve to allow for any drainage improvements. Also the ponds have been sited at a minimum distance of 1 chain from the existing logging track which would be soon upgraded.
3.1.2 Layout of Ponds
Discussion with Majuikan Officials revealed that for the initial phase 15 No. Nursery Ponds of ¼ acre size and 25 No. Culturing Ponds of 1 acre size each would be the minimum required at the Centre. A retention pond has been provided with a capacity of minimum 24 hours settling time to reduce the turbidity of water being supplied to the nursery and culturing ponds.
Nursery and culturing ponds are rectangular in shape with opposite corners rounded-off to facilitate uniform dispersal of water during times of supply and draining. The ratio of the height to breadth of ponds varies from 1:1 to 1:2.
The depth of the nursery and culturing ponds is 3 feet with central collecting channel about a foot deeper than the general level of the pond to enable draining and harvesting. Generally the collecting channel would normally be unstable and requires regular maintenance possible after each harvest.
3.1.3 The general elevation of the nursery and culturing pond bottom has been proposed at +17.00 M.S.L. and this has been derived by using normal operating conditions with average water level at Sungei Tumboh being +15.00 M.S.L.
Dykes are constructed of material excavated from ponds. In this particular case there is insufficient spoil from excavation of ponds and selected imported borrow material would be necessary to supplement the excavated earth for dyke construction. Typical details of dykes are shown in Fig. 3/2. The side slopes of the dykes are maintained at 1 ½ : 1 slope. The top width of dyke are 4 ft. minimum and for dykes accommodating light vehicular traffic 10 ft. width is provided. Turfing would be essential to prevent erosion of exposed surface. However, suitable cover crop which could also serve as fish feed could also be substituted.
3.2.1 Perimeter Dykes
Perimeter dykes are provided as a flood protection bund around the pond complex. The height of dyke after settlement and shrinkage is maintained at +25.00 M.S.L. and is 2 ft. above the once in 10 year flood level.
3.2.2 Secondary Dykes
Secondary dykes are provided on both sides of the supply and drainage channels. The secondary dykes are designed to a consolidated height of +22.00 M.S.L. which is 2 ft. above the maximum water level maintained in the ponds.
3.2.3 Tertiary Dykes
Tertiary dykes form partitions between ponds. The consolidated height is maintained at 1 ft. higher than the maximum pond water level.
A network of interconnected supply channel conveying water from spillweir at the outlet of the Retention Pond to individual ponds. The size of the channel are designed to carry water at the rate of 30 gallons per minute flow for each pond or to fill one of the culturing pond over a period of a day. In order to minimise losses in water and gradient the supply channels are lined. Details of supply channels are indicated in Fig. 3/3.
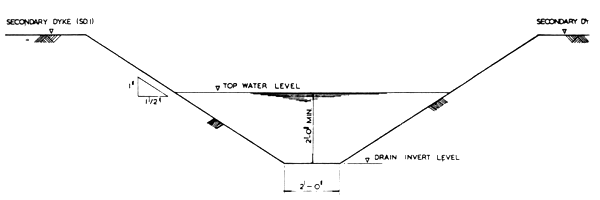
Earth interconnecting drainage channels (see Fig. 3/4) are provided to completely drain the ponds or drain away excess and or waste-water from ponds. Lining of drainage channels have been omitted to keep the initial financial outlay to the minimum, however, later these could be incorporated. The free drainage level is set +15.00 M.S.L. which is the average normal water level in Sungei Tumboh. Drainage channel are designed to cater for the draining of any one of the culturing ponds within a period of 3 hours or a continuous spill of 30 gallons per minute of circulation or waste-water per pond.
Spillweir, inlet and water control structures and drainage structures are provided in the group of ponds to regulate and efficiently control the flow of water in ponds.
3.5.1 Spillweir
A concrete spillweir to drain off the top layers of the settled water in Retention pond is provided before the supply channel network. Water passes through a graded course filter which is integrated with the spillweir. This serves as a predator control device. Frequent washing of filter media and replacement of filter media would be necessary to ensure quality and quantity of water.
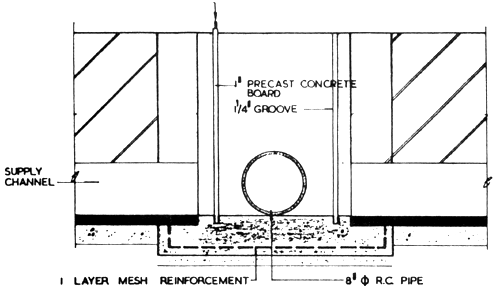
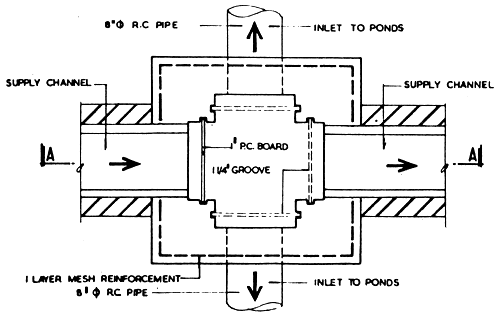
3.5.2 Inlet Water Control Structure
Inlet water control structures are provided at points where water from the supply channel are introduced into individual ponds. This structure is a simple concrete/ masonry division box with precast concrete drop boards to allow water from supply channel to be diverted into concrete pipes which lead the water to the ponds. Typical details are indicated in Fig. 3/5. The structure has been designed to fill the pond within a period of a day.
3.5.3 Overflow-cum-Outlet Water Control Structure
Each nursery and culturing pond is provided with an overflow-cum-outlet water control structure. This structure is of masonry and reinforced concrete pipe construction (see Fig. 3/6). Excess water above the top water level flows over the side spill arrangement into a sump and is lead away by concrete pipe to the drainage channels. At the bottom of the sump a timber gate is provided to drain the entire pond. The outlet structure is designed to empty the pond within a period of 3 hours or to cater for spill of 30 gallons per minute.
3.5.4 Drainage Control Structures
Where drainage channel meets the perimeter dykes, drainage control structure (see Fig. 3/7) are provided to keep flood waters from entering the drainage system in the pond complex. Drainage control structures are constructed of reinforced concrete with inlet and outlet wingwalls and concrete pipe barrel with flap gates fitted on the external side of perimeter dyke.
3.6.1 The elevation of the pond bottom in relation to the normal water level is such that economic water management is possible only with a pumped sypply system. Heading up Sungei Tumboh with an enormous weir structure and the construction of leeves on both banks to contain the raised water level to maintain a complete gravity system through the nursery and culturing ponds is estimated at $1 million. This initial outlay is considered high and therefore this alternative of having a complete gravity scheme is not considered any further.
3.6.2 Water is lifted from the inlet channel leading from Sungei Tumboh into the retention pond for settlement filteration and distribution to the ponds.
3.7.1 It is envisaged that the construction of ponds and dykes would be mechanised. Stumps under dykes are not cleared as it stabilises the dykes, however roots and stumps in the pond areas would have to be removed.
3.7.2 Draglines would have to be used for general excavation and dyke building, and low ground pressure (1gp) dozers for levelling and trimming.
3.8.1 The operation of nursery and culturing ponds necessitates filling of ponds and regular circulation of water. Draining and drying the ponds is also necessary to eradicate pests and predators, re-condition the pond bed, harvesting of fish/shrimps and also for routine maintenance. For the filling and regular circulation operations water management is totally dependant on pumped supply. Draining and wastewater flows is by gravity and the free drainage is +15.00 M.S.L. after which drainage is restricted due to high water level conditions in Sungei Tumboh.
3.8.2 Water is pumped from the channel into the Retention Pond wherein it is allowed to settle and the top layer of the settled water is taken over a spillweir through a coarse filter and from here it is distributed through a network of supply channels into individual ponds. The inlet control board for any particular pond to be completely filled shall be fully open. For allowing normal regular circulation of water the drop board is left partially open only. Circulation or excess water from individual ponds spill over the outlet structure into the system of drainage channel and eventually are led out of the perimeter dykes. When any particular pond is to be drained the timber gate at the outlet control structure is fully opened and the water in the pond is released into the drainage channel. Fine screens are permanently provided in the overflow area of the outlet control structure whereas a set of fine screens would have to be introduced while completely draining the ponds.
The office and laboratories would be housed in the same building and is located close to the Nursery Ponds. A lean-to area for external work purposes is also provided at the office to receive fish and shrimp fry or fingerlings and for subsequent transfer to the Nursery Ponds, also this place serves for harvested fish/prawns waiting for collection. The structure shall be a single storey building of a combination masonry and timber construction and having a floow area of approximately 3,700 sq.ft. The office has been strategically located so as to be centrally located when further phase of the pond complexes are constructed.
4.2.1 Staff quarters are located along the main road and access road and also near to the pond complex. The following number of staff quarters are proposed :
| - | Class ‘D’ Quarters | - | 1 No. |
| - | Class ‘F’ Quarters | - | 4 No. |
| - | Class ‘H’ Quarters | - | 8 No. |
4.2.2 The quarters are single-storey buildings of a combination of masonry and timber construction and having the following floor areas :
| - | Class ‘D’ quarters | - | Approximately 2,430 sq.ft. each |
| - | Class ‘F’ quarters | - | Approximately 1,930 sq.ft. each |
| - | Class ‘H’ quarters | - | Approximately 810 sq.ft. each |
4.3.1 Other buildings to be provided in the complex would include the following :
1 No. Store of masonry and timber construction (approximately 1,600 sq.ft.) for stocking chemicals, feed and etc.
1 No. Guard House of a masonry and timber construction (approximately 100 sq.ft.)
1 No. Timber Garage.
These buildings are to be located in the office compound.
4.3.2 Field Shelters
Timber field shelters are provided at the shrimp breeding ponds, to serve as rest areas for the field workers and also to serve as guard posts. These shelters of light timber construction could be easily dismantled and re-assembled at any desired location.
4.4.1 Roads
The internal road network in the office area and quarters area is constructed of selected imported earth fill materials and shall be paved for roads in the buildings and office compound and laterite surfaced for the other areas. The total top width of the road is 12 feet and side slopes are maintained at 1 ½ : 1 and turfed to prevent erosion. Road culverts and drains are provided where necessary for the proper and efficient drainage of the area.
4.4.2 Water Supply
Water supply could be tapped from the Jabatan Kerja Raya Main along the Tanjong Tualang/Telok Anson Road with the approval of Jabatan Kerja Raya.
4.4.3 Electricity
Electricity supply could be obtained from the LLN supply mains with the appropriate contributions and prior approval from LLN. Power would be supplied to all the buildings and lamp posts would also be erected at the pond complex, road junctions, office compound and quarters. A space has been allocated for the provision of an LLN sub-station.
4.4.4 Sewerage
Individual septic tanks with filter beds are proposed for each of the above-mentioned buildings.
4.5.1 Pumping Equipment
For reasons mentioned in Section III, pumping equipment would be required and this would be housed in a building for better protection. These pumpsets would be mixed flow type with high capacities and low head lift. Pumpsets would be electrically operated with all necessary protection systems in conforming with Lembaga Letrik Negara and chief Electrical Inspector regulations. Three pumps are proposed to be installed; two of these pumpsets would be duty pumpsets while the third unit is standby, providing 50% of standby capacity.
4.5.2 The duty pumpsets have been designed to cater for a regular circulation flow of 30 gallons per minute for each pond or complete filling of a culturing pond within a period of a day under maximum head conditions, i.e. during low flows.
4.5.3 Hard Furnishing
A provisional sum is included in the cost estimates for hard furnishing for the office and quarters and these would have to be defined at a later stage.
Cost Estimates have been based on 1979 current prices and adjusted to suit works of this nature.
It is assumed that the existing logging track adjacent to the site, which is also used as a means of access to the complex would be upgraded in the Trans-Perak Development and therefore these costs have not been included in the cost estimates.
The total capital cost of works including the capital cost for installation of pumping equipment is estimated at $1 million and details of these estimates are given in Appendix ‘C’.
The annual recurrence maintenance expenditure for operating the pumping plant have been estimated at $8,000.00 and details are shown in Appendix ‘D’. In estimates, allowance has been made for pump attendant operating the pumpsets, however, no other labour or administration costs for other aquaculture needs have been included at this stage.
FIGURES
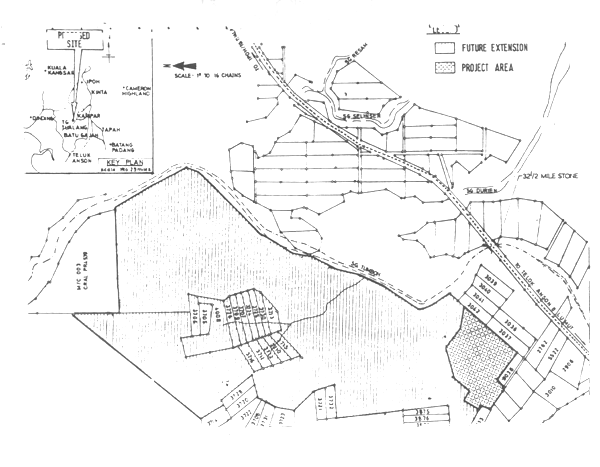
FIGURE 1/1
LOCATION PLAN
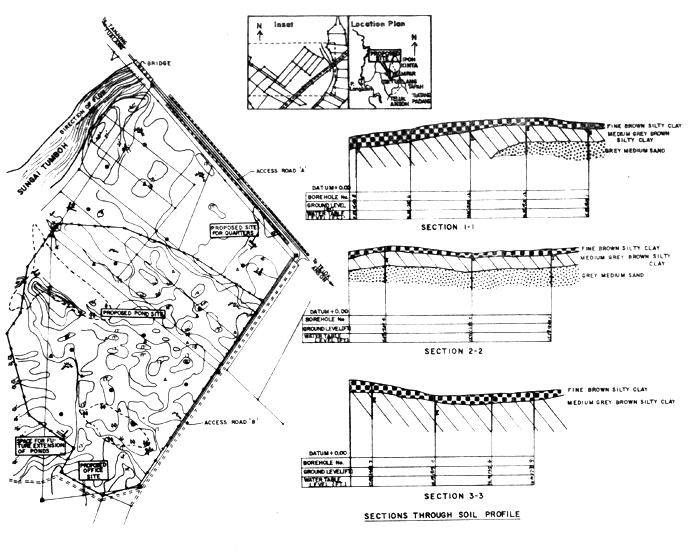
Figure 1/2. Soil profile
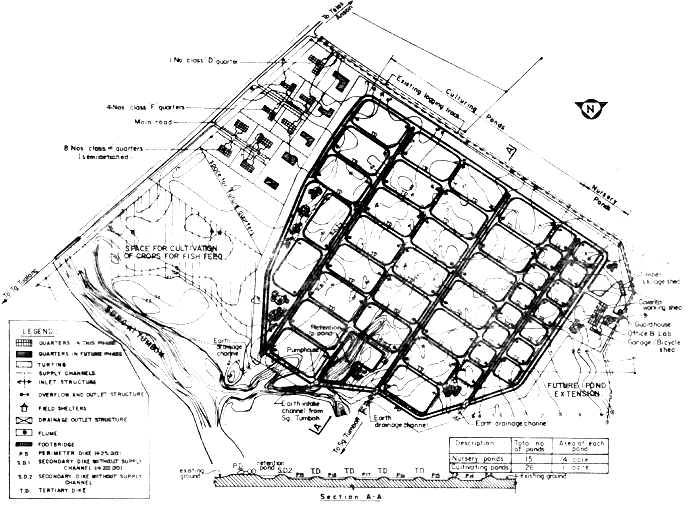
Figure 3/1. Layout of ponds, office & quarters
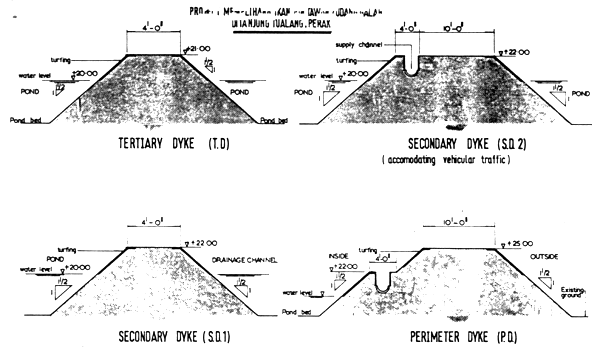
FIGURE 3/2
TYPICAL DETAILS OF TERTIARY,
SECONDARY & PERIMETER DYKES
| SUPPLY CHANNEL | W (inches) | D (inches) | GRADIENT |
| A-B | 15 | 18 | 1:2000 |
| B-D | 15 | 15 | |
| A-K-M | 12 | 18 | |
| D-E, D-F, M-P, M-N | 12 | 15 | |
| B-C, F-H, F-6 | 12 | 12 | |
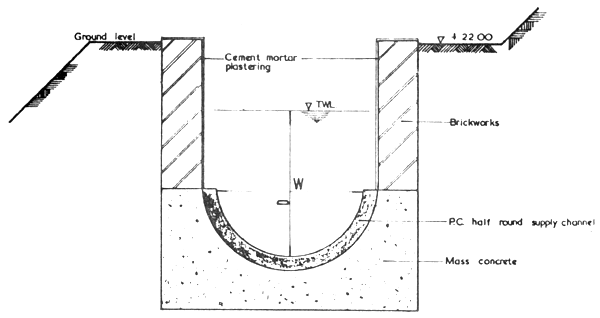
FIGURE 3/3
TYPICAL DETAIL OF
SUPPLY CHANNEL
TYPICAL DRAINAGE CHANNEL DETAILS
FIGURE 3/4
TYPICAL DRAINAGE
CHANNEL DETAILS
SECTION A-A
PLAN
FIGURE 3/5
TYPICAL DETAIL OF WATER
INLET CONTROL STRUCTURE
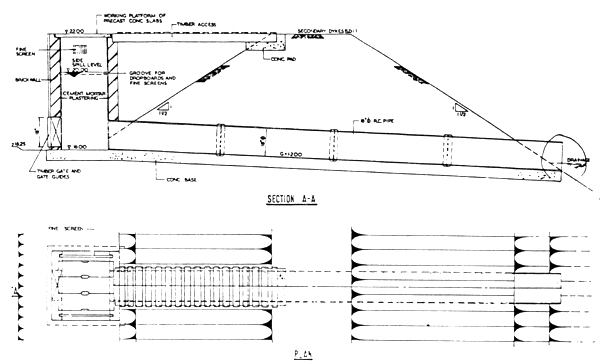
FIGURE 3/6
DETAIL OF OVERFLOW AN
OUTLET CONTROL STRUCTURE
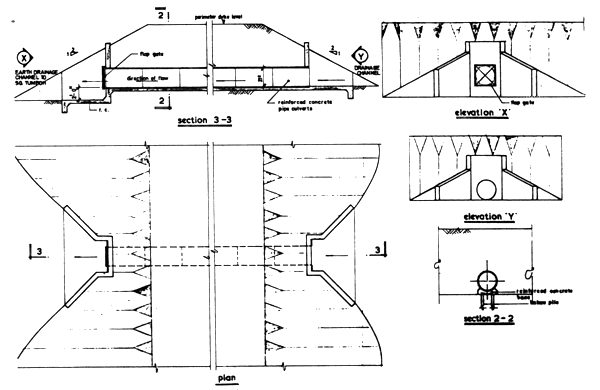
FIGURE 3/7
DETAIL OF DRAINAGE
OUTLET STRUCTURE
 | TERMS OF REFERENCE | APPENDIX ‘A’ |
| MAJUIKAN |  | |
| BIL KAMI: | LKIM(T)4/19/9 (56) | LEMBAGA KEMAJUAN IKAN MALAYSIA |
| BIL TUAN: | TINGKAT 7, WISMA PKNS, JALAN RAJA LAUT, KUALA LUMPUR 01–06 TAL: 924044, KABEL: “MAJUIKAN KUALA LUMPUR”, TELEKS: IKAN MA 30054 |
29hb. Julai, 1978
Wan Mohamed & Khoo Sdn. Bhd.,
Jurutera Perunding,
14A, Lorong B/1E,
P.O. Box 290,
Jalan Sultan,
Petaling Jaya,
Selangor.
Tuan,
Perkhidmatan Perunding Untuk “Freshwater Fish and Prawn Projek” di Perak
Adalah says diarah merujuk kepada perkara tersebut diatas dan sukacits dimaklumkan bahawa Jawatankuasa pemilikan telah bersetuju supaya firma tuan dilantik sebagai perunding untuk projek memelihara ikan air tawar/ udang galah di Perak. Kami mengucapkan tahniah keatas kejayaan tuan.
Satu perjanjian akan ditandatangani tidak lama lagi mengikut model form of Agreement ‘A’.
Sementara itu, kami berharap bahawa kerja-kerja permulaan bolah dijalankan.
Bersama-sama ini disertakan cadangan jadual kerja untuk makluman dan komen tuan.
Sakian terima kasih.
Yang benar, b/p LEMBAGA KEMAJUAN IKAN MALAYSIA

BR/smp.
Scope of work of Consulting Engineers
1. Preliminary Stage
1.1 Water Source
1.1.1 To test the physical and chemical quality of water, such as pH, dissolved oxygen, dissolved carbon dioxide, alkalinity, phosphate content, nitrate content, trace elements, transparency, biological oxygen demand, chemical oxygen demand etc.
1.1.2 To determine the volume and velocity of water source during dry and wet seasons.
1.2 Soil
1.2.1 To determine the types of soil, its organic content and chemical properties.
1.3 Survey
1.3.1 To undertake a topographical survey of the site.
2. Design stage
2.1 To prepare:
2.1.1 Designs and tender drawings.
2.1.2 Specifications, schedules and bills of quantity.
2.2 To advice on appropriate conditions of contract, forms of tender and invitations to tender.
3. Construction Stage
The administration of the contract and the technical control of the construction of works.
APPENDIX ‘B’
RESULTS OF WATER ANALYSIS OF SUNGEI TUMBOH
(Kimia 12)
(Pin. 1/69)
JABATAN KIMIA
MALAYSIA

A cas cerukinan, keputusan beriloit telah didapati : -
| Maknal No. (Ip.) | 5315/78 | 5836/78 | 6144/78 | 6392/78 |
| Tarikh mencontoh | 2.10.78 dry | 23.10.78 dry | 6.11.78 | 20.11.78 |
| Keputusan disebutkan dlm. mg/lit accuali disebutran | ||||
| Colour in dazen units. | 40 | 400 | 400 | 600 |
| Turoidity in Fullor's earth | 15 | 95 | 60 | 60 |
| Conductivity whos on-1 | 340 | 230 | 106 | 91 |
| Total hardness as Caco3 | 122 | 79 | 27 | 25 |
| Total solids dried @ 105°C | 290 | 340 | 180 | 130 |
| Suspended solids dried @ 105°C | 35 | 115 | 25 | 10 |
| Dissolved solids dried @ 105°C | 255 | 225 | 155 | 120 |
| pd value | 7.9 | 7.2 | 5.1 | 6.3 |
| Total alkalinity | 41 | 15 | 3 | 3 |
| Calcium | 41.2 | 25.2 | 6 | 4.8 |
| Chloride | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Potassium | 3.3 | 3.0 | 2.9 | 2.5 |
| Magnesium | 4.6 | 3.9 | 2.9 | 3.2 |
| Sodium | 2.4 | 5.0 | 3.6 | 2.7 |
| Sulphate | 33.5 | 37.0 | 40.0 | 16.0 |
| C.O.D. | 56 | 20 | 56 | 56 |
| B.O.D. 5 Days @ 20°C | 1.9 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 1.0 |
| Nitrate | 1.53 | 0.76 | 2.83 | 0.44 |
| Ammonia | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
| Phosphate | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 |
| Silicon | 10 | 8 | 8 | 10 |
| Iron | 2.0 | 3.0 | 5.5 | 2.6 |
| Maganese | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.13 |
| Chloride | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
| Dissolved oxygen | 7.0 | 4.1 | 0.4 | 0.7 |
| Temperature insitu | 29°C | 28°C | 27.5°C | 26°C |
| Pegawai Hajuikan Negeri, Lembaga Kamajuan Ikan Malaysia, PEARK |  |
| (U.P. 1 |
| No. Makmol: | JABATAN KIMIA, MALAYSIA | (Kims 5a) | ||
| LAPURAN BERKENAAN ANALISA CONTOH-CONTOH AIR BEKTERIA | Jabatan Kimia, | |||
| Bekulan Air Sungei Tumboh | Jalan Sultan P. Jaya | |||
| Dibawa Oleh | Jam Pukul | Pada | 19 | L—JCK.K L |
| PLAIMAL CONTOH | PEMERTKSAAN KAJIKUMAN | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Tempal Contoh | Diambil Pukul | Tarikh | Baki keloran (Bahagian reda Sejuta) (Spri yg disebutkan dim. Borang Kajikuman oleh Pengambil Contoh) | Hitungan de mangkok agar dim. 1 ml. 37°C 1 hari | Kumpulan Coli-Aerogenes (Ujian Sangkaan) Bilangan Bangkali timp-timp 100 ml | E. Coli 1. Bilangan Bangkali timp-timp 100 ml. |
| 1. | Sungei Tumboh | 9.45pg. | 23.10.78 | 18 | 0 | ||
| 2. | Sungei Tumboh | 9.35pg. | 6.11.78 | 24 | 490 | 490 | |
| 3. | Sungei Tumboh | 9.45pg. | 20.11.78 | Countless | 330 | 330 | |
| 4. | Sungei Tumboh | 9.45pg. | 2.10.78 | Countless | 4900 | 3300 | |
APPENDIX ‘C’
COST ESTIMATES
| Item No. | Description | Quantity | Unit | Rate($) | Amount($) | Total($) | |
| I. | PONDS | ||||||
| 1.1 | Site clearance and destumping | 50 | Acre | 100.00 | 5,000.00 | ||
| 1.2 | Excavation for ponds and bund | formation | 74,200 | Cu.yd. | 0.80 | 59,360.00 | |
| 1.3 | Imported earthfill for bunds | 30,000 | Cu.yd. | 3.00 | 90,000.00 | ||
| 1.4 | Strip turfing | 28,100 | Sq.yd. | 0.70 | 19,670.00 | ||
| 1.5 | Precast concrete supply channels | 6,000 | Lin.ft. | 6.00 | 36,000.00 | ||
| 1.6 | Spillweir | - | Sum | - | 3,000.00 | ||
| 1.7 | Inlet control structure | 41 | No. | 350.00 | 14,350.00 | ||
| 1.8 | Overflow and outlet structure | 41 | No. | 1,000.00 | 41,000.00 | ||
| 1.9 | Drainage outlet gate | 3 | No. | 3,000.00 | 9,000.00 | ||
| 1.10 | Foot bridges | 3 | No. | 1,200.00 | 3,600.00 | ||
| 1.11 | Flume | 2 | No. | 2,000.00 | 4,000.00 | 284,980.00 | |
| II. | PUMPING INSTALLATION | ||||||
| 2.1 | Civil works | ||||||
| 2.1.1 | Intake channel and sump | - | Sum | - | 10,000.00 | ||
| 2.1.2 | Pumphouse | - | Sum | - | 3,000.00 | ||
| 2.2 | Equipment | ||||||
| 2.2.1 | Pumps and motors | 3 | Set | 7,000.00 | 21,000.00 | ||
| 2.2.2 | Electrical installation | - | Sum | - | 7,000.00 | ||
| 2.3 | Pipeworks and specials | - | Sum | - | 2,000.00 | 43,000.00 | |
| III. | QUARTERS | ||||||
| 3.1 | Class ‘D’ Quarters (1 No.) | ||||||
| 3.1.1 | Earthworks | 2,550 | Cu.yd. | 3.00 | 7,650.00 | ||
| 3.1.2 | Building | 2,430 | Sq.ft. | 15.00 | 36,450.00 | ||
| 3.1.3 | Turfing | 1,220 | Sq.yd. | 0.60 | 732.00 | 44,832.00 | |
| 3.2 | Class ‘F’ Quarters (4 No.) | ||||||
| 3.2.1 | Earthworks | 7,000 | Cu.yd. | 3.00 | 21,000.00 | ||
| 3.2.2 | Building (1930 × 4 = 7720 sq.ft.) | 7,720 | Sq.ft. | 13.00 | 100,360.00 | ||
| 3.2.3 | Turfing | 4,000 | Sq.yd. | 0.60 | 2,400.00 | 123,760.00 | |
| 3.3 | Class ‘H’ Quarters (8 No.) | ||||||
| 3.3.1 | Earthworks | 5,000 | Cu.yd. | 3.00 | 15,000.00 | ||
| 3.3.2 | Building (850 × 8 = 6800 sq.ft.) | 6,800 | Sq.ft. | 11.00 | 74,800.00 | ||
| 3.3.3 | Turfing | 2,500 | Sq.yd. | 0.60 | 1,500.00 | 91,300.00 | |
| 259,892.00 | |||||||
| IV. | OFFICE | ||||||
| 4.1 | Earthworks | 12,000 | Cu.yd. | 3.00 | 36,000.00 | ||
| 4.2 | Building | 3,670 | Sq.ft. | 12.00 | 44,040.00 | ||
| 4.3 | Turfing | 5,000 | Sq.yd. | 0.60 | 3,000.00 | 83,040.00 | |
| V. | ANCILLARY BUIDLING | ||||||
| 5.1 | Guard house | 100 | Sq.ft. | 8.00 | 800.00 | ||
| 5.2 | Garage | 720 | Sq.ft. | 5.00 | 3,600.00 | ||
| 5.3 | Covered working shed | 3,400 | Sq.ft. | 5.00 | 17,000.00 | ||
| 5.4 | Timber storage shed | 1,600 | Sq.ft. | 8.00 | 12,800.00 | ||
| 5.5 | Timber field shelter | 5 | No. | 1,000.00 | 5,000.00 | 39,200.00 | |
| VI. | SERVICES | ||||||
| 6.1 | Access road | 1,400 | Lin.ft. | 24.00 | 33,600.00 | ||
| 6.2 | Electricity supply including contribution to LLN (allow) | - | Sum | - | 30,000.00 | ||
| 6.3 | Water supply | - | Sum | - | 25,000.00 | ||
| 6.4 | Sewerage and drainage | - | Sum | - | 10,000.00 | 98,600.00 | |
| VII. | MISCELLANEOUS | ||||||
| 7.1 | Fencing | 6,300 | L.F. | 4.00 | 25,200.00 | ||
| 7.2 | Hard furnishings for office and quarters (allow) | - | Sum | - | 40,000.00 | 65,200.00 | |
| Total capital cost | 873,912.00 | ||||||
| Allow for contingencies (say) | 126,088.00 | ||||||
| TOTAL COST | 1,000,000.00 | ||||||
APPENDIX ‘D’
ANNUAL RECURRENT OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE EXPENDITURE FOR PUMPING INSTALLATION AT POND COMPLEX
# Annual recurrent operating and maintenance expenditure for pumping installation at pond complex has been computed on the assumption that the ponds would be filled twice a year and daily circulation water of 30 gal/minute for each of the ponds.
- SALARY OF PUMP ATTENDANT
| • | Basic salary | $ 240.00 per month |
| • | EPF, Medical Benefits, etc. @ 16% | $ 38.40 per month |
| • | Total salary per month | $ 278.40 per month |
| • | Total salary per year | $3,340.80 per ;year |
- COST FOR PROVIDING CONTINUOUS CIRCULATION WATER FOR PONDS
| • | Discharge for culturing ponds (26 No.) @ 30 gpm = 30 × 26 | 780 gpm | |
| • | Discharge for nursery ponds (15 No.) @ 30 gpm = 30 × 15 | 450 gpm | |
| • | Total amount of water to be circulated for ponds | 1,230 gpm or 3.28 cusecs | |
| • | Maximum pumping head | 12 ft. | |
| • | Horse power of pump required 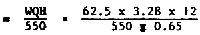 | 6.88 h.p. say 7 h.p. | |
| • | Power required for pumpset (allowing 15% excess) = 0.746 × 7 × 1.15 | 6 Kwh | |
| • | Cost of power consumed @ $0.08 per unit (Kwh) per month = 6 × 24 × 30 × 0.08 | $ 345.60 | |
| • | Cost of power consumption per year = $345.60 × 12 | $4,147.20 |
• COST FOR FILLING PONDS TWICE A YEAR
| • | Quantity of water required for culturing ponds @ 894,000 gallons per pond | |
| = 894,000 × 26 | 23,244,000 gallons | |
| • | Quantity of water required for nursery ponds @ 223,500 gallons per pond | |
| = 223,500 × 15 | 3,352,500 gallons | |
| • | Total quantity of water required | |
| = 23,244,000 + 3,352,500 | 26,596,500 gallons | |
| • | Time required to fill ponds | |
| = 26,596,500 ÷ 1230 | 21,623 min. = 360 hrs. | |
| • | Cost of power consumption (for filling once) | |
| = 360 × 6 × 0.08 | $ 172.80 | |
| • | Cost of power consumption for filling ponds twice | |
| = 172.80 × 2 | $ 345.60 per year |
- ANNUAL RECURRENT OPERATING & MAINTENANCE EXPENDITURE
| • | Total operating cost | ||
| Pump Attendant | $3,340.80 | ||
| Continuous circulation | |||
| of water for ponds | $4,147.20 | ||
| Filling of ponds | $ 345.60 | ||
| $7,833.60 | $ 7,833.60 | ||
| • | Repairs and renewals of | ||
| pumpsets @ 2% of capital cost | |||
| = 0.02 × $21,000.00 | $ 420.00 | ||
| • | Annual recurrent operating and | ||
| maintenance expenditure | |||
| = $7,833.60 + $420.00 | $ 8,253.60 | ||
| say | $ 8,000.00 |
PUBLICATIONS OF THE
SOUTH CHINA SEA FISHERIES DEVELOPMENT AND COORDINATING PROGRAMME
WORKING PAPERS
| SCS/74/WP/1 | Rabanal, H.R. The potentials of aquaculture development in the Indo-Pacific Region. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1974. 34p. |
| SCS/74/WP/2 | Crutchfield, J.A., D.A. Lawson and G.K. Moore. Malaysia - Legal and institutional aspects of fisheries development. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1974. 27p. |
| SCS/74/WP/3 | Marr, J.C. Republic of Vietnam - Legal and institutional aspects of fisheries development. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1974. 20p. |
| SCS/74/WP/4 | Larsson, S.O.R., G.C.A. Van Noort and E.O. Oswald. Malaysia - A report on artisanal fisheries of Peninsular Malaysia with particular reference to Kuala Besut. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 58p. |
| SCS/75/WP/5 | Rabanal, H.R. Irian Jaya, Indonesia - Survey of possibilities and recommendations for development of brackishwater fish production. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 27p. |
| SCS/75/WP/6 | Tussing, A.R. Fishery development perspectives. Sub-Region V: South China Sea. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. (IPFC/74/Sym/7). 23p. |
| SCS/75/WP/7 | Murdoch, W.R. and M.A. Myers. Republic of Singapore - An assessment of the Jurong Fishing Harbour complex and expansion site on the east bank of the Jurong River. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 46p. |
| SCS/75/WP/8 | Peterson, C.L., K.J. Rosenberg and A.C. Simpson. Regional - Trip reports of chartered purse seine vessels Royal Venture and Southward Ho covering voyages I and II. Dec. 1–13, 1974 and Jan. 5 - Feb. 3, 1975. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 37p. |
| SCS/75/WP/9 | Oswald, E.O. and R.E.K.D. Lee. Regional - A proposal for a live bait pole-and-line tuna fishing survey in the South China Sea and adjacent waters. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 38p. |
| SCS/75/WP/10 | Rosenberg, K.J. and A.C. Simpson. Regional Trip reports of chartered purse seine vessels Royal Venture and Southward Ho covering voyage 3. 9 February to 26 March 1975. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 28p. |
NOTE: Copies of these papers can be obtained by writing to the Programme in Manila, Philippines
| SCS/75/WP/11 | Peterson, C.L. Regional - Resource survey of larger pelagic fish. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 32p. |
| SCS/75/WP/12 | Rosenberg, K.J., A.C. Simpson and C.M. Renwick. Regional - Trip reports of chartered purse seine vessels Royal Venture and Southward Ho covering voyage 4. 9 April to 24 May 1975. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 36p. |
| SCS/75/WP/13 | Baum, G.A. Kuala Besut II - A supplementary report on selected socio-economic aspects and problems in a fishermen's community on the East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 43p. |
| SCS/75/WP/14 | Cuerden, C. Library services for the South China Sea Fisheries Programme and its participating countries. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 48p. |
| SCS/75/WP/15 | Lawson, R.M. Malaysia - An interim report on socio-economic aspects of the development of artisanal fisheries on the East Coast of Malaysia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 29p. |
| SCS/75/WP/16 | Jamandre, T.J. and H.R. Rabanal. Engineering aspects of brackish water aquaculture in the South China Sea region. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 96p. |
| SCS/75/WP/17 | Murdoch, W.R. Malaysia - Assessment of the viability and potential of the joint venture, Majuikan Mideast Sdn Bhd, Kuching, Sarawak, as requested by Lembaga Majuikan, Malaysia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 16p. (Restricted) |
| SCS/75/WP/18 | Cleaver, W.D. Malaysia - A preliminary design and general arrangement for an offshore purse seine vessel for the East Coast of West Malaysia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 35p. |
| SCS/75/WP/19 | Pischedda, J.L. Republic of the Philippines - Legal and institutional aspects in the development of the fishing industry. Preliminary observations and identification of the main obstacles. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 35p. |
| SCS/75/WP/20 | Simpson, A.C. Regional - Acoustic surveys of pelagic resources. Report No. 1. Gulf of Thailand, July 1975. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 28p. |
| SCS/75/WP/21 | Cintas, D. and C.M. Renwick. Regional - Report of aerial survey for schooling pelagic fish. 1. Philippine waters, 12–29 June 1975. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 28p. |
| SCS/76/WP/22 | Baum, G.A. and J.A. Maynard. Tobuan/Sual, Pangasinan Province Central Luzon - A socio-economic study on a rural fishing population in Central Luzon in connection with the Municipal Fisheries Pilot Programme. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 44p. |
| SCS/76/WP/23 | Baum, G.A. and J.A. Maynard. Panigayan, Lampinigan, Baluk-Baluk and Manangal, Basilan Province. A socio-economic study on four fishermen's communities affiliated to the Basilan Fishing Association (BFA/Isabela in connection with the Municipal Fisheries Pilot Programme). Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 62p. |
| SCS/76/WP/24 | Barica, J. Nutrient-dynamics in eutrophic inland waters and for aquaculture in some countries bordering the South China Sea with particular reference to mass fish mortalities. Proposal for monitoring programmes, Philippines, Thailand and Hong Kong. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 43p. |
| SCS/76/WP/25 | Rosenberg, K.J., A.C. Simpson and J.A. Maynard. Regional - Trip reports of chartered purse seine vessels Royal Venture and Southward Ho covering voyages 5 and 6. 13 June to 10 September 1975. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 52p. |
| SCS/76/WP/26 | Moore, G.K. Malaysia - Legal and institutional aspects of fisheries development. (2nd working paper). Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 38p. |
| SCS/76/WP/27 | Wheeland, H.A. Malaysia - Preliminary observations and recommendations concerning the fisheries statistics programme of Peninsular Malaysia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 22p. |
| SCS/76/WP/28 | Maynard, J.A. Regional - Report of aerial survey for schooling pelagic fish. II. Thailand - 20 November to 1 December 1975. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 20p. |
| SCS/76/WP/29 | Baum, G.A. and J.A. Maynard. Salay, Misamis Oriental Province - A socio-economic study on the fishing population of the seven coastal barrios of Salay Municipality in connection with the Municipal Fisheries Pilot Programme. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 47p. (Country - Philippines) |
| SCS/76/WP/30 | Murdoch, W.R. Hong Kong - A preliminary feasibility study to prosecute offshore pelagic stocks from Hong Kong. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 27p. |
| SCS/76/WP/31 | Johnson, R.F. Preliminary report on aquatic pollution in the South China Sea Region. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 34p. |
| SCS/76/WP/32 | Wheeland, H.A. Preliminary observations and recommendations concerning the fisheries statistics programme of Singapore. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 21p. |
| SCS/76/WP/33 | Baum, G.A. and J.A. Maynard. Coron/Tagumpay - Busuanga Island/ Calamianes Group (Palawan Province). A socio-economic study of two rural fishing populations in northern Palawan in connection with the Municipal Fisheries Pilot Programme. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 112p. |
| SCS/76/WP/34 | Jones, R. Mesh regulations in the demersal fisheries of the South China Sea area. Regional. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 79p. |
| SCS/76/WP/35 | Simpson, A.C. and S. Chikuni. Progress report on fishing for tuna in Philippine waters by FAO chartered purse seiners. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 38p. |
| SCS/76/WP/36 | Bonga, O.B. Vessel specifications and drawings for two 10 m multipurpose fishing vessels for the small scale fisheries project - Kuala Besut. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 36p. |
| SCS/76/WP/37 | Shang, Y.C. Economics of various management techniques for pond culture of finfish. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 36p. |
| SCS/76/WP/38 | Johnson, H.N. Malaysia - A preliminary study of investment opportunities for the development of small-scale fisheries on east coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 21p. |
| SCS/76/WP/39 | Shang, Y.C. Follow-up programmes on economics of aquaculture in the South China Sea Region. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 19p. |
| SCS/76/WP/40 | Cook, H.L. Problems in shrimp culture in the South China Sea Region. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 50p. |
| SCS/76/WP/41 | Johnson, H., J. Dibbs and R. Nasoetion. Indonesia - A preliminary assessment for small-scale fisheries development in Riau, North Sumatra and West Kalimantan Provinces. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 51p. |
| SCS/76/WP/42 | Baum, G.A. and J.A. Maynard. Bayawan Municipality, Negros Oriental Province/Negros. A socio-economic study on the rural fishing population of Bayawan municipality in connection with the Municipal Fisheries Pilot Programme. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 33p. (Country - Philippines) |
| SCS/76/WP/43 | Maynard, J.A. Philippines - Report on aerial survey for schooling pelagic fish in waters of the South China Sea and Sulu Sea adjacent to Palawan Island, 9–12 March 1976. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 17p. |
| SCS/76/WP/44 | Chakraborty, D. Fisheries statistics in the Philippines - A plan for a new and expanded data collection programme. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 70p. |
| SCS/76/WP/45 | Marr, J.C., G. Campleman and W.R. Murdoch. Thailand - An analysis of the present and recommendations for future fishery development and management policies, programmes and institutional arrangements. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 185p. (Restricted) |
| SCS/76/WP/46 | Cleaver, W. and O.B. Bonga. Thailand - Preliminary design, general arrangement and lines plans for two pelagic purse- seine/midwater trawl research vessel, 27.5 m and 24 m lengths. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. |
| SCS/76/WP/47 | Cleaver, W. Hong Kong - A preliminary design, general arrangement and specifications for a combination pelagic/demersal research vessel. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. |
| SCS/76/WP/48 | Simpson, A.C. and W.R. Murdoch. Regional - Trip reports of chartered purse seine vessel Royal Venture - Trips Nos. 7 ε 8. 1 October to February 1976. Area - Moro Gulf. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 17p. |
| SCS/76/WP/49 | Simpson, A.C. Regional - Trip reports of chartered vessel Southward Ho - Trips 7 ε 8. 11 September 1975 to March 1976. Areas - Malaysia and Thailand. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 33p. |
| SCS/76/WP/50 | Simpson, A.C. Regional - Trip reports of chartered purse seine vessel Royal Venture and Southward Ho - Trip No. 9. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 22p. |
| SCS/76/WP/51 | Simpson, A.C. Regional - Trip reports of chartered purse seine vessel Southward Ho - Trips 10 and 11. 15 April to 8 August 1976. Area - East, North and West Coasts Luzon Island, Bohol Sea, Sulu Sea, Moro Gulf. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 20p. |
| SCS/76/WP/52 | Wheeland, H.A. Statistics for fisheries development. Regional. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 11p. |
| SCS/76/WP/53 | Christy, L.C. Republic of the Philippines - Legal and institutional aspects of fisheries development. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 65p. (Restricted) |
| SCS/76/WP/54 | Maynard, J.A. Philippines - Province of Tawi-Tawi project identification and semi-detailed feasibility study relative to improving the status of small-scale fishermen and creating an integrated fishing industry in the Province of Tawi-Tawi. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 110p. |
| SCS/77/WP/55 | Oswald, E.O. ε J.A. Maynard. Thailand - Proposed small-scale fisheries pilot project for Ban Ao Makam Pom, Rayong Province. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1977. 38p. |
| SCS/77/WP/56 | Murdoch, W.R. ε P.S. Walczak. Regional - Trip reports of chartered purse seine vessel. Southward Ho covering voyage 12. Area - waters of the Sulu Sea. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1977. 11p. |
| SCS/77/WP/57 | Murdoch, W.R. and P.S. Walczak. Regional - Trip reports of chartered purse seine vessels Southward Ho and Royal Venture covering voyage 13. Area - mainly Moro Gulf, Philippines. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1977. 18p. |
| SCS/77/WP/58 | Simpson, A.C., W.R. Murdoch. Regional - Trip reports of chartered purse seine vessel Southward Ho covering voyages nos. 14 and 15. Area - Moro Gulf. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1977. 15p. |
| SCS/77/WP/59 | Murdoch, W.R. and P.S. Walczak. Regional - Trip reports of chartered purse seine vessel Southward Ho covering voyages nos. 16 and 17. Area - Waters of the Moro Gulf. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1977. 23p. |
| SCS/77/WP/60 | Doty, M.S. Seaweed resources and their culture in the countries of the South China Sea Region. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1977. 19p. |
| SCS/77/WP/61 | Rabanal, H.R. et al. Shellfisheries of Thailand: Background and proposal for development. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1977. 14p. |
| SCS/77/WP/62 | Chakraborty, D. Observations and recommendations concerning the fisheries statistics programme of Hong Kong. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1977. 14p. |
| SCS/77/WP/63 | Chakraborty, D. Observations and recommendations concerning the inland fisheries statistics programme of Thailand. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1977. 15p. |
| SCS/77/WP/64 | Hansen, K.A., P. Lovseth and A.C. Simpson. Acoustic surveys of pelagic resources. Report No. 2. Hong Kong, Nov. 1976. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1977. 24p. |
| SCS/77/WP/65 | Christy, L.C. Republic of the Philippines - Legal and institutional aspects of fisheries development. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1977. 55p. |
| SCS/77/WP/66 | Murdoch, W.R. et al. A proposal for a small-scale fisheries pilot project in the Pulau Tujuh (Seven Islands) area, Riau Archipelago District, Riau Province, Indonesia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1977. 69p. |
| SCS/77/WP/67 | Moore, G. Malaysia - A new fisheries bill. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1977. 56p. |
| SCS/77/WP/68 | Gedney, R.H. Water supply of the fishery development centre in freshwater aquaculture at Sukabumi, West Java, Indonesia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1977. 20p. |
| SCS/78/WP/69 | Chan, W.L. et al. Cage culture of marine fish in East Coast Peninsular Malaysia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 66p. |
| SCS/78/WP/70 | Lee, R.E.K.D. Results of small-scale live bait pole-and-line fishing explorations for tuna in the Philippines. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 41p. |
| SCS/78/WP/71 | Moore, G. Legal and institutional aspects of fisheries management and development - a new licensing system, Thailand. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 23p. (Restricted) |
| SCS/78/WP/72 | Angeles, H.G. Preliminary fish and resources survey along the coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. |
| SCS/78/WP/73 | De la Cruz, Y.T. Malaysia - Small-scale fishermen credit and subsidy programmes - Implementing guideline recommendations (with particular reference to the Kuala Besut Fishermen's Association). Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 50p. |
| SCS/78/WP/74 | Chikuni, S. Report on fishing for tuna in Philippine waters by FAO chartered purse seiners. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. (Published as SCS/DEV/78/18) |
| SCS/78/WP/75 | Fyson, J.E. Fishing vessel design proposals for small-scale artisanal fisheries in the Philippines. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 23p. |
| SCS/78/WP/76 | Lau, F. and Cheng Chor Luk. Recent innovations in the cage culture activity at Kuala Besut small-scale fisheries pilot project, Malaysia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 16p. |
| SCS/78/WP/77 | Wheeland, H.A. Proposal for further development of fishery statistics programmes in developing countries with particular reference to the South China Sea region. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 6p. |
| SCS/78/WP/78 | Moore, G. Legal and institutional aspects of fisheries management and development - A second Interim Report (Thailand). Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 37p. (Restricted) |
| SCS/79/WP/79 | Jonasson, G. and Paisal Katanyuwong. Review of fishing activities of the small-scale fisheries project in Kuala Besut, Malaysia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 23p. |
| SCS/79/WP/80 | Cansdale, G.S. Low-cost water filtration system. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 73p. |
| SCS/79/WP/81 | Lisac, H. Some technical aspects of small-scale fish landing facilities. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 32p. |
| SCS/79/WP/82 | Chakraborty, D. Catch analysis of fishermen in Kuala Besut, Peninsular Malaysia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 59p. |
| SCS/79/WP/83 | Thompson, B.G. Thailand - Management of fisheries data - feasibility of computerization. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 24p. |
| SCS/79/WP/84 | Cansdale, G.S. Report on second regional consultancy low-cost water filtration. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 48p. |
| SCS/79/WP/85 | New, M. Report of consultancy on the fish nutrition programme at Changi Marine Fisheries Research Centre, Primary Production Department, Singapore. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 8p. |
| SCS/79/WP/86 | Woynarovich, E. and W.W. Kuhnhold. Report of consultancy to Penang, Malaysia, regarding animal waste management problem. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 59p. |
| SCS/79/WP/87 | Thomson, D.B. Intermediate technology and alternative energy systems for small-scale fisheries. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 69p. |
| SCS/80/WP/88 | Hechanova, R.G. and B. Tiensongrusmee. Report of assistance on selection of site, design, construction and management of the Ban Merbok, Kedah, Malaysia Brackishwater Aquaculture Demonstration Project. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 154p. |
| SCS/80/WP/89 | Tiensongrusmee, B. and R.G. Hechanova. Malaysia - Evaluation of the site selected, design of project and proposed construction and operations of the Majuikan Tanjong Tualang Freshwater Aquaculture Centre. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 52p. |
| SCS/80/WP/90 | Skillman, R.A. Tuna statistics Indo-Pacific and Indian Ocean. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 45p. |
| SCS/80/WP/91 | Trono, G.C., Jr., H.R. Rabanal and I. Santika. Report of technical assistance on seaweed farming in Indonesia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 56p. |
| SCS/80/WP/92 | Bilal, J. and W.W. Kuhnhold. Marine oil pollution in Southeast Asia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 85p. |
| SCS/80/WP/93 | Evans, E.D. Legal and policy consideration for use of the chartered fishing vessels in Philippine waters. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 35p. |
| SCS/80/WP/94 | Gomez, E.D. The present state of mangrove ecosystems in Southeast Asia and the impact of pollution. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 102p. |
| SCS/80/WP/94a | Soegiarto, A. The present status of mangrove ecosystems in Southeast Asia and the impact of aquatic pollution - Indonesia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 65p. |
| SCS/80/WP/94b | Sasekumar, A. The present state of mangrove ecosystems in Southeast Asia and the impact of pollution - Malaysia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 80p. |
| SCS/80/WP/94c | Gomez, E.D. The present state of mangrove ecosystems in Southeast Asia and the impact of pollution - Philippines. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 88p. |
| SCS/80/WP/94d | Zoology Department, University of Singapore. The present state of mangrove ecosystems in Southeast Asia and the impact of pollution - Singapore. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 76p. |
| SCS/80/WP/94e | Twesukdi, P. The present state of mangrove ecosystems in Southeast Asia and the impact of pollution - Thailand. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 108p. |
| SCS/80/WP/95 | Wheeland, H.A. and P.J. Hooker. Organizational implications of a fisheries information system for the Philippines; specific recommendations regarding BFAR's statistics program; and a plan for implementation. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 33p. |
| SCS/80/WP/96 | Hechanova, R.G. Technical assistance on the design of government coastal aquaculture projects in Peninsular Malaysia (A pattern for planning and design of aquaculture facility). Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 78p. |
COORDINATING COMMITTEE REPORTS
| SCSP: | 74/1 | REP | Report of the Ad Hoc Coordinating Committee Meeting of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. Manila, 18–19 June 1974. 27p. |
| SCSP: | 74/2 | REP | Report of the first session of the Coordinating Committee of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. Jakarta, Indonesia, 6 November 1974. Rome, FAO, 1974. 22p. |
| SCSP: | 76/3 | REP | Report of the second session of the Coordinating Committee of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. Manila, 9 April 1976. 16p. |
| SCSP: | 77/4 | REP | Report of the third session of the Coordinating Committee of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. Manila, 24–25 February 1977. 19p. |
| SCSP: | 77/5 | REP | Report of the fourth session of the Coordinating Committee of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. Manila, 11–12 October 1977. 21p. |
| SCSP: | 78/6 | REP | Report of the fifth session of the Coordinating Committee of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. Manila, 11 March 1978. 16p. |
| SCSP: | 78/7 | REP | Report of the sixth session of the Coordinating Committee of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. Manila, 28–29 September 1978. |
| SCSP: | 79/8 | REP | Report of the seventh session of the Coordinating Committee of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. Rome, 11–16 October 1979. |
WORKSHOP REPORTS
| SCS/GEN/74/1 | Report of the workshop on planning and coordinating of resources survey and evaluation in the South China Sea. 28 August to 4 September 1974. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1974. 197p. |
| SCS/GEN/76/2 | Report of the workshop on the fishery resources of the Malacca Strait. Part I. Jakarta, 29 March to 2 April 1976. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 89p. |
| SCS/GEN/76/3 | Report of workshop on legal and institutional aspects of fishery resources management and development. 5–8 April 1976. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 95p. |
| SCS/GEN/76/4 | Report on the training workshop for field enumerators of the Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources - Philippines. 22–31 March 1976 by D. Chakraborty and H. Wheeland. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 32p. |
| SCS/GEN/76/5 | UNDP/FAO Training Course on the management of small-scale fishery enterprises. Kuala Trengganu, Malaysia. 25 August to 26 September 1975. Rome, FAO, 1976. 14p. |
| SCS/GEN/77/6 | Report of the workshop on the fishery resources of the Malacca Strait - Part II. Jakarta, 29 March to 2 April 1976. South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 85p. |
| SCS/GEN/76/7 | Report of the BFAR/SCSP workshop on the fishery resources of the Visayan and Sibuyan area. Tigbauan, Iloilo, Philippines. 18–22 October 1976. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 26p. |
| SCS/GEN/76/8 | Philippines - Report seminar on the fisheries statistics survey of the Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources. 23 July 1976. DNR/BFAR/SCAP, Manila, 1976. 17p. |
| SCS/GEN/76/9 | Report of the consultative group meeting on small-scale fisheries development in the South China Sea region. 13–15 December 1976. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 140p. |
| SCS/GEN/77/10 | Report on the training workshop on fisheries statistics, Malaysia, 12–21 October 1976. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1977. 27p. |
| SCS/GEN/77/11 | Report on the BFAR/SCSP workshop on fishery resources of the Sulu Sea and Moro Gulf areas, 25–29 April 1977, Cagayan de Oro. Manila, 1977. 58p. |
| SCS/GEN/77/12 | Report of the workshop on the demersal resources, Sunda Shelf. Part I. Nov. 7–11, 1977. Penang, Malaysia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 58p. |
| SCS/GEN/77/13 | Report of the workshop on the demersal resources, Sunda Shelf. Part II. Nov. 7–11, 1977. Penang, Malaysia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 120p. |
| SCS/GEN/77/14 | Joint SCSP/SEAFDEC workshop on aquaculture engineering with emphasis on small-scale aquaculture projects) Vol. I - General Report. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. v.p. |
| SCS/GEN/77/15 | Joint SCSP/SEAFDEC workshop on aquaculture engineering (with emphasis on small-scale aquaculture projects) Vol. 2 - Technical Report. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 463p. |
| SCS/GEN/77/16 | A layout of standard tables of fishery statistics in the Philippines. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 162p. |
| SCS/GEN/77/17 | Report of the workshop on the biology and resources of mackerels (Rastrelliger spp.) and round scads (Decapterus spp.) in the South China Sea. Part I. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 70p. |
| SCS/GEN/78/18 | Report of the workshop on management of resources of the Sunda Shelf, Malacca Strait and related areas. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 14p. |
| SCS/GEN/78/19 | Report of the BFAR/SCSP workshop on the fishery resources of the Pacific Coast of the Philippines. 18–22 September 1978. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 48p. |
| SCS/GEN/79/20 | Report of the workshop on demersal and pelagic fish resources of the Java Sea. 5–9 December 1978. Semarang, Indonesia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 60p. |
| SCS/GEN/79/21 | Report of the workshop on the tuna resources of Indonesia and Philippine waters. Jakarta, 20–23 March 1979. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 35p. |
| SCS/GEN/79/22 | Report of the BFAR/SCSP workshop on the fishery resources of the north Luzon and Western Coasts of Luzon. 18–20 April 1979, Manila, Philippines. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 57p. |
| SCS/GEN/79/23 | Report on training course in fishery statistics. 2 October- 10 November 1978, Manila, Philippines. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. v.p. |
| SCS/GEN/79/24 | Report of the consultation meeting on management of tuna resources of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. 26–29 June 1979, Manila, Philippines. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 155p. |
| SCS/GEN/80/25 | Report of the workshop on application and results of acoustic methods for resource appraisal surveys in the South China Sea. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 19p. + Annexes 1 to 4 |
| SCS/GEN/80/26 | Report of the workshop on the biology and resources of penaeid shrimps in the South China Sea area. Part I. 30 June - 5 July 1980. Kota Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. |
| SCS/GEN/80/27 | Report of the workshop on application and results of acoustic methods for resource appraisal surveys in the South China Sea. Part II. 19–22 November 1979. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. |
SCS MANUALS
| SCS Manuals No. 1 | Handbook on field identification of fishes, crustaceans, molluscs, shells, and important aquatic plants. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 60p. |
PERIODIC PROGRESS REPORTS
| SCS/PR/74/1 | Woodland, A.G. Project progress report of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. 1 July to 31 December 1974. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1974. 19p. |
| SCS/PR/75/2 | Woodland, A.G. Project progress report of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. 1 January to 30 June 1975. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 40p. |
| SCS/PR/75/3 | Woodland, A.G. Project progress report of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. 1 July to 31 December 1975. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 38p. |
| SCS/PR/76/4 | Woodland, A.G. Project progress report of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. 1 January to 31 December 1976. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 47p. |
| SCS/PR/77/5 | Woodland, A.G. Project progress report of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. 1 January to 30 June 1977. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1977. 37p. |
| SCS/PR/77/66 | Woodland, A.G. Project progress report of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. 1 July to 31 December 1977. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1977. 19p. |
| SCS/PR/78/7 | Woodland, A.G. Project progress report of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. 1 January to 30 June 1978. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 12p. |
| SCS/PR/78/8 | Woodland, A.G. Project progress report of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. 1 July to 31 December 1978. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 11p. |
| SCS/PR/79/9 | Woodland, A.G. Project progress report of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. 1 January to 30 June 1979. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 12p. |
| SCS/PR/79/10 | Woodland, A.G. Project progress report of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. 1 July to 31 December 1979. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 65p. |
| SCS/PR/80/11 | Woodland, A.G. Project progress report of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. 1 January to 30 June 1980. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 28p. |
| SCS/PR/80/12 | Woodland, A.G. Project progress report of the South China Sea Fisheries Development and Coordinating Programme. 1 July to 31 December 1980. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 25p. |
FISHERIES TECHNICAL PAPERS
| SCS/DEV/73/1 | Woodland, A.G. et al. The South China Sea Fisheries: A proposal for accelerated development. Rome, FAO, 1974. 162p. |
| SCS/DEV/73/2 | Yamamoto, T. Review of marine fishery statistical system in countries bordering the South China Sea, and proposals for their improvement. Rome, FAO, 1973. 46p. (Cover title: The South China Sea Fisheries Statistical Systems) |
| SCS/DEV/73/3 | Aoyama, T. The demersal fish stocks and fisheries of the South China Sea. Rome, FAO, 1973. 80p. (Cover title: The South China Sea Fisheries Demersal Resources) |
| SCS/DEV/73/4 | Kume, S. Tuna resources in the South China Sea. Rome, FAO, 1973. 18p. |
| SCS/DEV/73/5 | Ling, S. Status, potential and development of coastal aquaculture in the countries bordering the South China Sea. Rome, FAO, 1973. 51p. (Cover title: The South China Sea Fisheries Aquaculture Development) |
| SCS/DEV/73/6 | Menasveta, D. et al. Pelagic fishery resources of the South China Sea and prospects for their development. Rome, FAO, 1973. (Cover title: The South China Sea Fisheries Pelagic Resources) |
| SCS/DEV/73/7 | Mistakidis, M.N. The crustacean resources and related fisheries in the countries bordering the South China Sea. (Cover title: The South China Sea Fisheries Crustacean Resources) |
| SCS/DEV/73/8 | Ruckes, E. Fish utilization, marketing and trade in countries bordering the South China Sea - status and programme proposals. Rome, FAO, 1973. 33p. (Cover title: The South China Sea Fisheries Marketing and Trade) |
| SCS/DEV/73/9 | Doucet, F.J. et al. Institutional and legal aspects affecting fishery development in selected countries bordering the South China Sea. Rome, FAO, 1973. 32p. (Cover title: The South China Sea Fisheries Institutional Legal Aspects) |
| FAO species identification sheets for fishery purposes. Eastern Indian Ocean (Fishing area 57) and Western Central Pacific (Fishing area 71) Rome, FAO, 1974. 4 vols. | |
| SCS/DEV/76/11 | Development potentials of selected fishery products in the regional member countries of the Asian Development Bank. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 107p. (ADB/FAO Market Studies) |
| SCS/DEV/76/11 (Appendix 1) | Fishery country profiles. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 173p. (ADB/FAO Market Studies) |
| SCS/DEV/76/12 | The international market for shrimp. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 105p. (ADB/FAO Market Studies) |
| SCS/DEV/76/13 | The international market for tuna. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 69p. (ADB/FAO Market Studies) |
| SCS/DEV/76/14 | The international market for crab. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 49p. (ADB/FAO Market Studies) |
| SCS/DEV/76/15 | The international market for lobster. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 46p. (ADB/FAO Market Studies) |
| SCS/DEV/76/16 | The international market for cephalopods. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 95p. (ADB/FAO Market Studies) |
| SCS/DEV/76/17 | The European canned fish market: Prospects for Rastrelliger spp. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1976. 56p. (ADB/FAO Market Studies) |
| SCS/DEV/78/18 | Chikuni, S., A.C. Simpson and W.R. Murdoch. Test fishing for tuna and small pelagic species: Reports on the operation of FAO chartered purse seiners in Philippines and South China Sea waters, 1974–1977. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. v.p. |
| SCS/DEV/79/19 | Pope, J. Stock assessment in multispecies fisheries with special reference to the trawl fishery in the Gulf of Thailand. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 106p. |
| SCS/DEV/80/20 | Implications of the extension of national jurisdiction for fisheries management and development. Report of an FAO Mission to the Government of Indonesia. 7 January - 2 February 1980. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme and Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 1980. 90p. |
TECHNICAL REPORTS CONTRIBUTED TO SYMPOSIA/MEETINGS, ETC.
Rabanal, H.R. 1975 FAO activities in inland fisheries and aquaculture with particular reference to Asia and the Far East. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme. 17p. (Contributed to the First Fisheries Research Congress, Philippine Council for Agriculture and Resources Research, 7–10 March 1975, Legaspi City, Philippines).
Rabanal, H.R. 1975 Preliminary report on the Macrobrachium fishery in the Indo-Pacific region. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme. 20p. (Contributed to the International Conference on Prawn Farming, Vung Rau, Vietnam, 31 March – 4 April 1975).
Rabanal, H.R. 1975 Distribution and occurrence of milkfish Chanos chanos (Forskal). Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1975. 18p. (Contributed to the National Bangus Symposium. Manila, 25–26 July 1975).
Rabanal, H.R. 1976 Mangrove and their utilization for aquaculture. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme. 20p. (Contributed to the National Workshop on Mangrove Ecology held in Phuket, Thailand, 10–16 January 1976).
Rabanal, H.R. 1976 Report of project identification mission to Bangladesh on inland fisheries and aquaculture. Manila, Asian Development Bank. 56p.
Rabanal, H.R. 1976 Aquaculture 1976: Focus Southeast Asia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme. 12p. (Talkdelivered at the National Convention of the Federation of Fish Producers of the Philippines, Iloilo City, 26 August 1976).
Simpson, A.C. 1976 Some proposals for research related to the understanding of mangrove ecology and the utilization of mangrove areas. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme. 10p. (Contributed to the National Workshop on Mangrove Ecology held in Phuket, Thailand, 10–16 January 1976).
Cook, H.L. 1976 Some aspects of shrimp culture research with particular reference to Philippine species. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme. 7p. (Contributed to the Philippine Council for Agriculture and Resources Research (PCARR) Fisheries Workshop, Subic, Zambales, Philippines, 15–17 January 1976).
Rabanal, H.R. 1976 The resources in inland waters: their utilization and management. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme. 21p. (Talk delivered before the Phi Sigma Biological Society as a contribution to the Deogracias V. Villadolid Memorial lecture series. Manila, Philippines, 26 November 1976).
Rabanal, H.R. 1977 Aquaculture in the Philippines. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme. 15p. (Talk delivered before the United States Peace Corps Volunteers, Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines - 11 January 1977).
Rabanal, H.R. 1977 Aquaculture in Southeast Asia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme. 10p. (Paper contributed to the Fifth FAO/ SIDA Workshop on Aquatic Pollution in relation to Protection of Living Resources. Manila, Philippines, 17–27 February 1977)
Simpson, A.C. 1977 Fisheries research and development in the Philippines: Some recommendations with special reference to resource assessment. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme. 16p.
Rabanal, H.R. 1977 Aquaculture management. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme. 12p. (Contribution to the BFAR/FAO-UNDP Training of Regional Trainors in Aquaculture. Lucena, Quezon, Philippines, 19 September to 27 October 1977)
Rabanal, H.R. 1977 Recent trends in aquaculture. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme. 13p. (Paper contributed to the Seminar/ Workshop for Fishery Schools' Administrators, conducted by the Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources. Manila, Philippines, 24–28 October 1977)
Rabanal, H.R. 1977 Forest conservation and aquaculture development of mangroves. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme. 15p. (Paper contributed to the International Workshop on Mangrove and Estuarine Area Development for the Indo-Pacific region. 14–19 November 1977, Manila, Philippines)
Thomson, D.B. 1978 Lecture notes on fishing methods, equipment and deck layout of fishing vessels. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 151p. (Paper presented at the FAO NORAD Course on Fishing Vessel Design, Bangkok, Thailand, October-November 1978)
Rabanal, H.R. 1978 International traffic of live and fish eggs and control of the spread of fish diseases. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1978. 21p. (Contribution to the Workshop on Tropical Fish Diseases - Their causes and control in Southeast Asia, Puncak, West Java, Indonesia, 28 November to 1 December 1978)
Rabanal, H.R. and R.O. Juliano 1979 Aquaculture extension: How it could be a potent force in fisheries development in the ASEAN region. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. (Paper contributed to the First ASEAN Seminar/Workshop on Fisheries Extension, Manila 18–25 February 1979)
Thomson, D. B. 1979 Marine fisheries extension. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 41p. (Paper contributed to the First ASEAN Seminar/Workshop on Fisheries Extension, Manila, 18–25 February 1979)
Thomson, D. B. 1979 Training requirements of the fisheries of Southeast Asia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 11p. (Paper presented at the SEAFDEC Consultative Meeting on Fisheries Training, Bangkok, 14–18 May 1979)
Kuhnhold, W. W. 1979 Aquatic pollution: Classes of pollutants, their occurrence, transport and dispersion. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 22p. (Lecture given at the Seventh FAO/SIDA Workshop on Aquatic Pollution in Relation to Protection of Living Resources - Analyses of Metals and Organochlorines in Biota. Manila, Philippines, 7 May to 9 June 1979)
Kuhnhold, W. W. 1979 Effects of aquatic pollution on fish and fisheries. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. (Lecture given at the Seventh FAO/SIDA Workshop on Aquatic Pollution in Relation to Protection of Living Resources - Analyses of Metals and Organochlorines in Biota. Manila, Philippines, 7 May – 9 June 1979)
Rabanal, H. R. 1979 The design of research in brackishwater aquaculture. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 7p. (Paper contributed to the Seminar/Workshop on Research Methodology and Technical Report Writing, conducted by the Fisheries Training Division, Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources, Fisheries Training Center, Cavite City, Philippines, 10–29 June 1979)
Kuhnhold, W. W. 1979 Some aspects of the impact of aquatic oil pollution on fishery resources. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. (Seminar held at Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources, Quezon City, Metro Manila, Philippines, 31 July 1979)
Rabanal, H. R. 1979 Production and recent innovation in design and management in aquaculture industry in Southeast Asia. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 7p. (Paper contributed to the Asian Seminar and Tour sponsored by the Bank of America, Manila, 6–9 November 1979)
Thomson, D. B. 1979 The challenge of the 1980's for fisheries education, training and extension. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1979. 11p. (Paper presented at the First International Symposium on Fishery Education, Fishing Processing and Marketing Systems. Mexico, December 1979)
Kuhnhold, W. W. 1980 Some aspects of the impact of aquatic oil pollution on fishery resources. Manila, South China Sea Fisheries Programme, 1980. 25p. (Paper contributed to the International Workshop on the Prevention, Abatement and Combating of Pollution from Ships in East Asian Waters. 3–8 November 1980, Manila, Philippines)
Feb. 1981
