Last updated: December 2006
Plant Protection Organization Chart
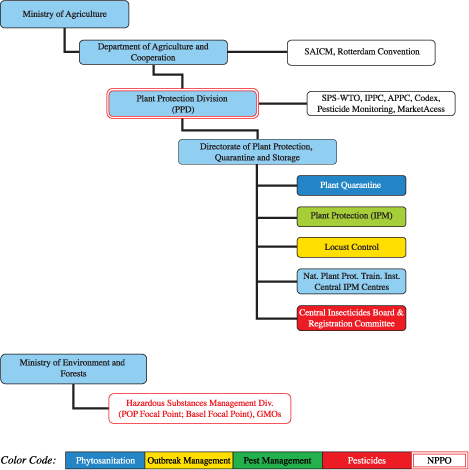
Important Contact Addresses
Responsible Ministry/Ministries
–
Responsible Department
–
Plant Protection (Policy, Regulations, Pesticide Registration, Overall Management)
Directorate
of Plant Protection, Quarantine and Storage
Dr W.R. Reddy, Joint Secretary
(Plant Protection)
Mr Amit Jha, Director (Plant Protection)
Department of
Agriculture & Cooperation, Ministry of Agriculture
Room No. 147, Krishi Bhavan, Rajendra Prasad Road
New
Delhi 110001, India
Tel:
(+91) 11-23073384 / (+91) 11-23381385
Fax: (+91) 11-23384468
E-mail: [email protected]
Websites: http://www.dacnet.ppin.nic.in; http://www.plantquarantineindia.org/; http://agricoop.nic.in.
Address for nominations
–
Operational Offices:
Plant Protection
Plant Quarantine
Surveillance, Pest Outbreaks and Invasive Species Management
Directorate
of Plant Protection, Quarantine & Storage
Dr P.S. Chandurkar, Plant Protection Advisor
Department of
Agriculture & Cooperation, Ministry of Agriculture
N.H-IV,
Faridabad – 121 001 (Haryana), India
Tel:
(+91) 129-2413985; 129-2410056
Fax: (+91) 129-2412125
E-mail: [email protected]
Website: www.plantquarantineindia.org/www.cibrc.nic.in/dacnet.nic.in/ppin
Pesticide Registration
Registration
Committee, Directorate of Plant Protection, Quarantine and Storage
Dr (Mrs) S. Kulshrestha, Secretary
Department of
Agriculture & Cooperation, Ministry of Agriculture
N.H-IV,
CGO Complex
Faridabad-121001 (Haryana), India
E-mail: [email protected]
Website: http://www.cibrc.nic.in
Official International Contact Points
National Plant Protection Organization (NPPO) Contact Point (for IPPC/APPPC)
Directorate of Plant
Protection, Quarantine and Storage
Dr
W.R. Reddy, Joint Secretary (Plant Protection)
Mr
Amit Jha, Director (Plant Protection)
Dr
P.S. Chandurkar, Plant Protection Advisor (Information officer for IPP)
Department of
Agriculture & Cooperation, Ministry of Agriculture
Room No. 147, Krishi Bhavan, Dr Rajendra Prasad Road
New
Delhi 110001, India
Tel:
(+91) 129 2413985 / (+91) 11 23385026
Fax: (+91) 129 2412125
/ (+91) 11 23384182
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Website: http://www.dacnet.ppin.nic.in; http://www.plantquarantineindia.org/
WTO-SPS Contact Point
Department
of Agriculture & Cooperation
Amit Jha, Director (Plant Protection)
Ministry
of Agriculture
Krishi Bhavan
New
Delhi 110001, India
Tel/Fax:
(+91) 11 2338 1385
E-mails: [email protected]/[email protected]
Rotterdam Convention (PIC) DNA Pesticides (P)
Plant
Protection Division
Mr Amit Jha, Director
Department of
Agriculture and Cooperation, Ministry of Agriculture
Room No. 228-A, Krishi Bhavan, Dr Rajendra Prasad Road
New
Delhi 110 001, India
Fax: (+91) 11 233
81385
E-mail: [email protected]
Stockholm Convention (POP) National Focal Point (P)
| Ministry of Environment & Forests | Plant Protection Division | ||
| Mr Shri R.K. Vaish, Joint Secretary | Mr Amit Jha, Director | ||
| Paryavaran Bhavan | Department of Agriculture and | ||
| CGO Complex, Lodhi Road | Cooperation, Ministry of Agriculture | ||
| New Delhi – 110 003, India | Room No. 228-A, Krishi Bhavan | ||
| Tel: (+91) 11 2436 0634 | Dr Rajendra Prasad Road | ||
| Fax: (+91) 11 2436 3577 | New Delhi 110 001, India | ||
| E-mail: [email protected] | Fax: (+91) 11 233 81385 | ||
| E-mail: [email protected] | |||
Basel Convention Competent Authority (CA) and Focal Point
Ministry
of Environment and Forests
Secretary to the Government of India
CGO Complex, Lodi Road
New Delhi 110 003, India
Tel: (+91) 11 24 36 07 21 or 24 36 18 96
Fax: (+91) 11 24 36 27 46
E-mail: [email protected]
Hazardous
Substances Management Division
Mr Shri R.K. Vaish, Joint Secretary
Ministry of
Environment and Forests
Paryavaran Bhavan
CGO Complex, Lodi Road
New
Delhi 110 003, India
Tel:
(+91) 11 24 36 06 34
Fax: (+91) 11 24 36 35
77
E-mail: [email protected]
Selected Country Statistics
|
Agricultural Population |
553 million |
Agricultural Land |
170 million ha |
|
GDP $598 966 million |
Agric. GDP: 22.7% |
GDP $598 966 million |
Undernourishment: 20% |
|
Main crops grown: |
|||
| GDP = Gross Domestic Product; GNI = Gross National Income; Hunger = Population below minimum energy requirement | |||
Last updated: December 2006
List of Key Legislation/Regulations/Rules
|
1914 |
Destructive Insects & Pests Act. |
|
2003 |
Plant Quarantine Order (effective: 1.1.2004) and amendments therto (under consideration) Plant Quarantine Bill to replace “Destructive Insects and Pest Act” of 1914 |
| Web sources for further information: |
http://www.plantquarantineindia.org/law.htm; |
|
Policies (regarding plant quarantine) |
Yes |
No |
|
Does phytosanitary legislation cover domestic quarantine? |
x |
|
|
Does phytosanitary legislation cover import quarantine? |
||
|
Does phytosanitary legislation cover export quarantine? |
||
|
Does phytosanitary legislation cover living modified organisms? |
x | |
|
Is plant quarantine a separate organization from animal quarantine? |
x |
|
|
Other policy initiatives (under review/progress): The DIP Act is in the process of being amended but is not likely to result in altered import phytosanitary conditions. |
||
|
Web source for further information: http://www.plantquarantineindia.org/abpqo.htm |
||
|
Organization of Plant |
Responsible
Organizational Unit |
|
Pest Risk Analysis |
MOA/DAC/PPD/PPQ&S/NBPGR |
|
National standards development |
MOA/DAC/PPD/PPQ&S |
|
International notifications |
MOA/DAC/PPD |
|
Import: |
|
|
Import permits |
MOA/DAC/PPD/PPQ&S/ NBPGR/DBT/State Agricultural Universities |
|
Import inspections |
MOA/DAC/PPD |
|
Emergency action |
MOA/DAC/PPD |
|
Export: |
|
|
Phytosanitary certificates |
MOA/DAC/PPD/PPQ&S/Notified State government authorities/ ICAR/SAUs |
|
Treatment of commodities |
MOA/DAC/PPD/PPQ&S/NBPGR/DBT/State Agricultural Universities |
|
Infrastructure |
Year: 2006 |
|
|
Number of plant quarantine officers authorized to inspect/certify |
292 |
|
|
Total qualified personnel for plant pest risk analysis |
100 |
|
|
Number of quarantine offices |
||
|
entry points (sea/air/land/mail = total) |
34/12/13/ = 59 |
|
|
post-entry plant quarantine containment facilities |
140 |
|
| other offices |
5 N/RPQS +22 PQS |
|
|
Number of quarantine service diagnosis laboratories |
45 |
|
|
In-country recognized pest diagnostics capabilities (incl. universities, etc.) |
||
|
Number of laboratories for insect/mite (arthropod) samples |
40 | |
|
Number of laboratories for bacteria samples |
||
|
Number of laboratories for virus samples |
||
|
Number of laboratories for fungus samples |
55 | |
|
Number of laboratories for mycoplasma samples |
||
|
Number of laboratories for nematode samples |
||
|
Number of laboratories for plant/weed samples |
40 | |
|
Number of laboratories for other pests (snail, slug, rodents, etc.) |
||
|
Pest-Free Areas |
Responsible Organizational Unit (Ministry/Department/Unit) |
||
| Overall management | MOA/DAC | ||
| – | surveillance | MOA/DAC/PPQ&S/ICAR/State Agricultural Universities | |
| – | management | MOA/DAC assisted by PPQ&S | |
|
– |
certification | MOA/DAC/PPQ&S/ICAR | |
| List of target pest species and crops ISPM 4 | Number of sites in [year] | ||
| Fruit fly | |||
| Brown rot on potato | |||
| Stone weevil and pulp weevil on mango | |||
| List of target pest species and crops ISPM 10 | Number of sites in [year] | ||
Key Situation Indicators
|
International Trade |
Year: |
|
|
Main Import Plant Commodities |
Main countries/areas of origin |
Quantity (tons) |
|
Pulses and Peas |
USA/Canada/France/Australia/ Myanmar |
|
| Timber |
Canada/ Malaysia/South America/ New Zealand/Ghana |
|
|
Fresh fruits-pome/stone/citrus |
Australia/New Zealand, Thailand |
|
|
Main Export Plant Commodities |
Main destination countries |
|
| Mango |
EC/Japan/Canada/Africa/China |
|
| Grapes |
EC/Canada/China/Middle East |
|
| Basmati Rice |
Across the Globe – Majority of the Countries |
|
Cooperation Projects |
|||
|
Title (Purpose/Target) |
Donor | Amount |
Years (start-end) |
|
Need assessment and project formulation for the development of an Integrated National Quarantine |
UNDP | ||
|
Title of government follow-up programmes |
Amount |
Years (start-end) |
|
Key Operation Indicators
|
Institutional Functions |
Year: 2005-2006 |
|
Number of import permits issued |
20 877 |
|
Number of import inspections carried out |
|
|
Number of emergency phytosanitary treatments taken on imports |
|
|
Number notifications of non-compliance |
|
|
Number of conventional phytosanitary certificates issued |
100 152 |
|
Number of electronic phytosanitary certificates issued |
|
Number of quarantine pests intercepted |
Year: |
|
|
Top three commodity |
Top three pest/commodity |
# of interceptions |
|
Lists of Regulated Pests |
Year of last update |
Insects |
Pathogens |
Plants |
|
Number of quarantine pests |
2006 |
31 |
||
|
Number of regulated non-quarantine pests |
2006 | |||
|
Number of regulated import articles |
||||
|
372 Commodities with Import Risk Analyses Web source for further
information: – |
||||
|
Pest Risk Analysis |
Insects |
Pathogens |
Plants |
|
No. of PRA completed and documented (according to ISPM) |
(1 682) |
||
|
Web source for further information: 1682 Commodities can be imported into India as per the Pest Risk Analysis. Details are available in website: www.plantquarantineindia.org |
|||
Progress and Constraints
|
Main Progress in Recent Years (legislation, policies, infrastructure, investments, training, etc.) |
|
|
Main Constraints (personnel, infrastructure, administrative, operational, training, etc.) |
|
|
Implementation of ISPM |
Relevance |
Implementation |
Planned/Actual Year of full implementation |
||||||
|
International Measures |
low | medium | high | none | partial | most | full | ||
|
ISPM 01 |
Principles of plant quarantine as related to international trade | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 02 |
Guidelines for pest risk analysis | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 03 |
Code of conduct for the import and release of exotic biological control agents | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 04 |
Requirements for the establishment of pest free areas | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 05 |
Glossary of phytosanitary terms | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 06 |
Guidelines for surveillance | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 07 |
Export certification system | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 08 |
Determination of pest status in an area | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 09 |
Guidelines for pest eradication programmes | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 10 |
Requirements for the establishment of pest free places of production and pest free production sites | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 11 |
Pest risk analysis for quarantine pests | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 12 |
Guidelines for phytosanitary certificates | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 13 |
Guidelines for the notification of noncompliance and emergency action | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 14 |
The use of integrated measures in a systems approach for pest risk management | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 15 |
Guidelines for regulating wood packaging material in international trade | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 16 |
Regulated non-quarantine pests: concept and application | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 17 |
Pest reporting | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 18 |
Guidelines for the use of irradiation as a phytosanitary measure | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 19 |
Guidelines on lists of regulated pests | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 20 |
Guidelines for a phytosanitary import regulatory system | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 21 |
Pest risk analysis for regulated non-quarantine pests | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 22 |
Requirements for the establishment of areas of low pest prevalence | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 23 |
Guidelines for inspection | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 24 |
Guidelines for the determination and recognition of equivalence of phytosanitary measures | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 25 |
Consignments in transit | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 26 |
Establishment of pest free areas for fruit flies (Tephritidae) | x | x | ||||||
|
ISPM 27 |
Diagnostic protocols for regulated pests | x | x | ||||||
|
Comments/Constraints |
|||||||||
Last updated: December 2006
List of Key Legislation/Regulations/Rules for Surveillance, Pest Reporting and Emergency Actions
List of legislation/regulations/rules for surveillance, pest reporting and emergency actions: DIP Act/Plant Quarantine (Regulation of Import into India) Order, 2003 (DIP Act proposed to be amended and replaced by Plant Quarantine Act
Web source for further information: www.agricoop.nic.in
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
National strategy to control serious field pest outbreaks? |
x |
|
|
National strategy to control migratory or periodically occurring pests? |
x |
|
|
National strategy to eradicate serious newly invaded exotic pests? |
x |
|
|
Other policies: (e.g. subsidies, etc.): IPM/GAP/Survey and Surveillance Project/NRM |
||
|
Web source for further information: www.agricoop.nic.in |
||
|
Organization of Outbreak |
|
|
Field/Storage Pest Outbreaks |
(e.g. BPH, bollworm, etc.) |
|
Response strategy/plans |
MOA/DAC/PPQ&S/CIPMC/LWO/State Government/ICAR and SAUs |
| Surveillance |
MOA/DAC/PPQ&S/CIPMC/State Governments |
| Control |
MOA/DAC/State Government/PPQ&S/LWO/CIPMCs/ICAR/ SAUs/Pesticide Industry |
|
Migratory Pest Outbreaks |
(e.g. locusts, birds, armyworm) |
|
Response strategy/plans |
MOA/DAC/PPQ&S/Locust Warning Organization (LWO) |
| Surveillance |
MOA/DAC/PPQ&S/CIPMC/State Governments |
| Control |
MOA/DAC/State Government/PPQ&S/LWO/CIPMCs/ICAR/ SAUs/Pesticide Industry |
|
New Exotic Pest Eradication |
(e.g. coconut beetle) |
|
Response strategy/plans |
MOA/DAC/PPQ&S/CIPMC/LWO/State Government/ICAR and SAUs |
| Surveillance |
MOA/DAC/PPQ&S/CIPMC/State Governments |
|
Control/eradication |
MOA/DAC/State Government/PPQ&S/LWO/CIPMCs/ICAR/ SAUs/Pesticide Industry |
|
Reporting to bilateral or international organizations |
MOA/DAC/PPD |
|
Infrastructure |
Year: |
|
Number of designated staff for surveillance of field pests of national importance |
>150 000 |
|
Number of designated staff for surveillance of migratory and periodically occurring pests |
11 Locust
and |
|
Number of designated staff for surveillance of invasive species |
>150 000 |
|
Number of designated staff for control of field pests of national importance |
|
|
Number of designated staff for control of migratory and periodically occurring pests |
11 Locust
and |
|
Number of designated staff for eradication of invasive species |
Key Situation and Operation Indicators
(Outbreaks and invasions in the
past 2 years)
|
New exotic species found established in country |
Insects |
Pathogens |
Weeds |
|
Total number for year: |
|||
|
Total number for year: |
|||
|
Total number on record |
|
Eradication or internal quarantine actions taken against economically important species |
|||
|
Name of species |
White Woolly Aphid |
Migratory Locust |
|
|
Year of first discovery |
2005 |
2006 |
|
| Passway | |||
|
Location of first discovery |
Tamil Nadu |
J&K-Ladakh Himalayas |
|
|
Area affected [ha] |
6 000 |
5 000 |
|
|
Area treated [ha] |
6 000 |
5 000 |
|
|
Control method |
State Government was facilitated with financial and technical support |
Inspection/Air Spray/ Pesticide based control in 13 000 feet altitude terrain |
|
| Expenditures | |||
|
Pest outbreak actions |
Outbreak 1 |
Outbreak 2 |
Outbreak 3 |
|
Name of species |
Tobacco caterpillar |
||
|
Year of outbreak |
2004/05 | ||
|
Area affected [ha] |
674 867 | ||
|
Estimated damage $ |
|||
|
Area treated by government [ha] |
522 051 | ||
|
Expenditures by government [$] |
|||
|
Control method |
|||
|
More information |
on soybean in |
Progress and Constraints
|
Main Progress in Recent Years (legislation, policies, infrastructure, investments, training, etc.) |
|
Main Constraints (personnel, infrastructure, administrative, operational, training, etc.) |
Last updated: December 2006
List of Key Legislation/Regulations/Rules for Pest Management
Insecticides Act, 1968, Insecticides Rules, 1971
Web source for further information: –
|
Policies (regarding pest management) |
Yes |
No |
|
Do you have policies encouraging organic or low-pesticide use production |
x |
|
|
Is IPM specifically mentioned in laws or policy documents? |
x | |
|
Do you have official Good Agricultural Practice (GAP) or any other relevant food safety (ecofood, etc.) standards for pest management? |
x |
|
|
Is pest management extension separate from general extension? |
x |
|
|
Other policies: (subsidies, production inputs, etc.) |
||
|
||
|
Web source for further information: www.dacnet.ppim.nic.in |
|
Organization of
Plant |
Responsible Organizational Unit |
|
Policy development |
MOA/DAC |
|
Pest management research |
MOA/DAC/ICAR & PPQ&S |
|
Control recommendations |
MOA/DAC/ICAR & PPQ&S |
|
Pest management extension |
States/PPQ&S |
| IPM training | States/PPQ&S |
| GAP training |
|
Infrastructure |
Year: |
|
Number of technical officers for pest management |
|
|
Number of central, regional, provincial or state offices |
35 Central IPM centres |
|
Number of district and village level field offices |
|
|
Number of field/extension agents for pest management advice |
|
|
Number of field/extension agents trained in IPM-FFS facilitation |
1 400 |
|
Number of government biocontrol production/distribution facilities |
31 |
|
Number of government biopesticide production/distribution facilities |
|
|
Number of general extension staff involved in pest management |
|
|
Number of designated plant protection technical officers for extension |
Key Situation and Operation Indicators
|
Pest Management |
Yes |
No |
|
Does
the country have a National IPM Programme? |
x |
|
|
Does
the country have specific IPM extension programmes? |
||
|
Does
the country have specific IPM research programmes? |
||
|
Does
the country have specific GAP extension programmes? |
||
|
Does
the country have specific GAP research programmes? |
|
Market shares (estimated value, volume or area under control) |
Year: 2004-2005 |
|
Size of chemical pest control market |
39 000 MT |
|
Size of biopesticides market |
3 000 MT |
|
Size of biological control agents market |
|
Major pest control
requiring crops |
1st |
2nd |
3rd |
|
Affected crop |
Cotton | Paddy | Vegetables |
|
Name(s) of pest(s) |
|||
|
Estimated crop loss |
|||
|
Affected area |
|||
|
Number
of pesticide applications or |
40% | 20% | 15% |
|
Government action taken |
|
Cooperation Projects |
|||
| Purpose/Target | Donor | Amount |
Years (start-end) |
|
Purpose/Target of government follow-up programmes |
Amount |
Years (start-end) |
|
|
Pest Management Extension |
Year: 2004/05 |
|
Number of farmers trained in IPM during the year |
|
|
Number of IPM-FFS conducted during the year |
|
|
Number of farmers trained in GAP standards during the year |
|
|
Area under IPM/low pesticide management [ha] |
|
|
Area under organic/pesticide-free management [ha] |
|
|
Crops
in which IPM or other ecology friendly programmes are successfully
implemented: |
|
|
Crops grown organic/pesticide-free: |
|
Progress and Constraints
|
Main Progress in Recent Years (legislation, policies, infrastructure, investments, training, etc.) |
|
Main Constraints (personnel, infrastructure, administrative, operational, training, etc.) |
Last updated: December 2006
List of Key Legislation/Regulations/Rules
Ministry of Agriculture Department of Agriculture & Cooperation
1968 Insecticide Act
1971 Insecticide Rules.
Ministry of Environment & Forest
1986 Environment Protection Act.
Ministry of Health & Family Welfare
1954 Prevention of Food Adulteration Act (residue monitoring, MRLs).
Ministry of Labour
1948 Factories Act.
Web source for further information: –
|
Policies (regarding pesticide management) |
Yes |
No |
|
|
Do you
have national pesticide reduction targets? |
|||
|
Have you ratified the Rotterdam (PIC) Convention? |
x |
||
|
Have you ratified the Stockholm (POP) Convention? |
x |
||
|
Have your ratified the Basel Convention? (hazardous wastes) |
x |
||
|
Have your ratified the Montreal Protocol? (MeBr phasing-out) |
|||
|
Have you reported the
observance of the Code of Conduct to FAO according to |
x |
||
|
Have you adopted Good Laboratory Practices (GLP)? |
x |
||
|
Pesticide Registration |
|||
|
Do you require pesticides to conform to relevant FAO or WHO specifications? |
x |
||
|
Do you allow the “me-too” registration and sale of generic pesticides? |
x |
||
|
Do you require data on product equivalence for generic registration? |
x |
||
|
Do you conduct country-specific risk assessments for… |
|||
|
occupational risks? |
x |
||
|
consumer risks? |
x |
||
|
environmental risks? |
x |
||
|
Have you adopted the Global Harmonized System (GHS) for pesticides hazards evaluation and labelling? |
x |
||
|
Do you accept evaluation results from other countries? |
x |
||
|
Do you accept field studies conducted in other countries? |
x |
||
|
Do you require environmental fate studies? |
x |
||
|
Incentives/Disincentives |
|||
|
Do you have a special tax on pesticides to cover externality costs? |
x |
||
|
Do you subsidize or provide low-cost pesticides? |
x |
||
|
Do you subsidize or provide low-cost biopesticides? |
x |
||
|
Other policies: Other policies: Insecticides Act, 1968 being amended. |
|||
|
Web source for further information: http://agricoop.nic.in |
|||
|
Organization of Plant |
|
| Legislation | MOA/DAC |
| Registration | MOA/DAC/CIB&RC |
|
Licensing of shops |
State Governments |
|
Licensing of field applicators |
State Governments |
|
Enforcement/inspections |
States, Central Task Force |
|
Testing of pesticide efficacy |
RC, IARI, PLT, ICAR |
|
Development of pesticide use recommendations |
RC |
|
Safe use training/extension |
MOA/DAC/PPQ&S/NPPTI |
|
Food residue monitoring |
MOA/DAC/PPD & DOH |
|
Environmental monitoring |
DOC/DBT |
|
Health monitoring |
DOH |
|
Other Stakeholders: |
|
|
Pesticide Industry Association |
Crop Life India, Indian Pest Control Assoc., Crop Care Fed. of India, Pestic. Manuf. & Formulation Assoc. of India |
|
Civil Society Organizations (NGO, etc.) |
Center for Science and Environment (CSE), Voluntary Health Assoc. of India |
|
Infrastructure |
Year: |
|
Number of registration officers |
|
|
Number of enforcement officers |
>10 000 |
|
Number of department quality control laboratories |
35 |
|
Number of quality control laboratory personnel |
>500 |
|
Number of department residue analysis laboratories |
21 Central Gov’t, 56 States; |
|
Number of residue laboratory personnel |
>1 500 |
Key Situation Indicators
|
Pesticide Trade: |
Tons |
$ ’000 Value |
|
| Imports | 11 050 | 89 796 | |
| Manufacture | |||
| Export | 89 052 | 896 360 | |
|
Domestic Use/Sales |
|||
|
Pesticide Use Profile: |
Tons |
$ ’000 Value |
|
| Agriculture | 39 000 | ||
|
Chem. Insecticides |
56% |
||
|
Chem. Fungicides |
15% |
||
|
Chem. Herbicides |
15% |
||
|
Chem. Others: e.g. molluscicide, acaricide |
14% |
||
|
Other e.g. Avamectrin, Bt, Neem |
|||
|
Other purposes |
|||
| TOTAL | |||
Post Registration Monitoring
|
Testing, Quality Control and Effects in the Field |
Yes |
No |
|
Do you have significant problems with low-quality pesticides in the market? |
x |
|
|
Do you have significant problems with pesticide resistance? |
x |
|
|
Do you have a list of pesticides under close observation for problems |
||
|
Source for more information: – |
|
Health and Environmental Information |
Yes |
No |
|
Do you maintain data on pesticide poisoning cases? |
x |
|
|
Do you have a system to monitor pesticide residues in food? |
x |
|
|
Do you have a system to monitor pesticide residues in the environment? |
x |
|
|
Do you have significant problems of environmental contamination from pesticides? |
x |
|
|
Do you have data on pesticides effects on wildlife and ecosystems? |
x |
|
|
Source for more information: – |
|
Pesticide Disposal |
Yes |
No |
|
Do you have system to collect and safely dispose of used containers and small quantities of left-over pesticides? |
x |
|
|
Do
you have an inventory of outdated and obsolete pesticides in the country? |
x |
|
|
Do you have illegal trade in pesticides? |
||
|
if yes: what is the estimated
amount: ______ |
Note |
|
|
Source for more information: – |
Key Operation Indicators
|
Registration/Regulation/Monitoring |
Year: |
|
|
a.i.* |
Trade Name |
|
|
Number of registered pesticide products |
194 | |
|
Number of registered biopesticides (Avamectrin, Bt, Neem, etc.) |
15 prov. | |
|
Number of restricted-use pesticides/formulations |
10 | 4 |
|
Number of banned pesticides |
26 | |
|
Number of licensed outlets |
>5 000 |
|
|
Number of licensed field applicators (professional and/or farmers) |
250 |
|
|
Number of licensing violations reported during year |
24 |
|
|
Number of quality control analyses conducted during year |
42 900 |
|
|
Number of food samples analyzed for pesticide residues during year |
7 800 |
|
|
Number of samples exceeding MRL |
47 |
|
|
Number of environmental samples analyzed for pesticide residues |
48 0 |
|
| * active ingredient | ||
|
Pesticides Restricted in Recent Years |
|
|
Year |
Name of active ingredient or hazardous formulation |
|
Pesticides Banned in Recent Years |
|
|
Year |
|
| Cooperation Projects | |||
| Purpose/Target | Donor | Amount |
Years (start-end) |
| Purpose/Target of government follow-up programmes | Amount |
Years (start-end) |
|
Progress and Constraints
|
Main Progress in Recent Years (legislation, policies, infrastructure, investments, training, etc.) |
|
Monitoring of pesticide residues at national level, a new national initiative has been started by the Plant Protection Division of the Ministry of Agriculture to synthesize the efforts and data/results of more that 100 laboratories across the country with view to synthesize and collate their results and prepare the basis for future food safety decision-making and as a tool for policy formulation. This scheme is being handled through existing and dedicated laboratories which have been made updated and state of the art in the current year. The Nodal officers for this new major initiative are Mr Ashish Bahuguna, Joint Secretary and Amand Shah Director, Plant Protection Division in the Ministry of Agriculture along with Dr T.P. Rajendran, Assistant Director General, ICAR, New Delhi. The scheme has started functioning only in the year 2005. |
|
Main Constraints (personnel, infrastructure, administrative, operational, training, etc.) |
Last updated: December 2006
|
Genetically Modified Crops |
|
|
Name of GMO Crop |
Area under Cultivation [ha] |