


The woodfuel types and flows that compose the “items” of the i-WESTAT database refer to the definitions formulated in the Unified Bioenergy Terminology and summarized in the following figure.
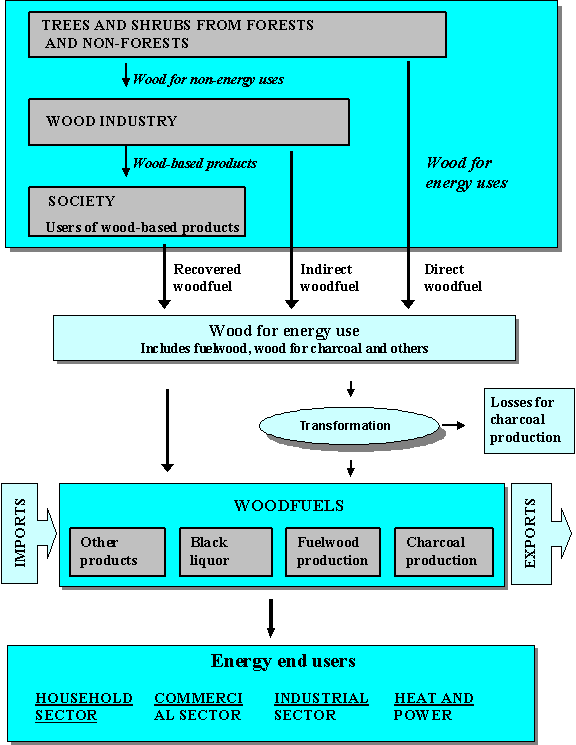
Woodfuel balance scheme, from supply source to end user
The following is a selection of the more relevant terms from the Unified Bioenergy Terminology.
black liquor
alkaline spent liquor obtained from digesters in the production of sulphate or soda pulp during the process of paper production, in which the energy content mainly originates from the content of lignin removed from the wood in the pulping process
charcoal
solid residue derived from carbonization distillation, pyrolysis and torrefaction of fuelwood
energy density
ratio of net energy content and bulk volume
NOTE The energy density is calculated using the net calorific value determined and the bulk density
cut and split oven-ready fuelwood used in household wood-burning appliances such as stoves, fireplaces and central heating systems. Firewood usually has a uniform length, typically in the range 150 to 500 mm.
fuel
energy carrier intended for energy conversion
fuelwood
woodfuel where the original composition of the wood is preserved
absolute value of the specific energy of combustion, in joules, for unit mass of a solid fuel burned in oxygen in a calorimetric bomb under the conditions specified. The results of combustion are assumed to consist of gaseous oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide, of liquid water (in equilibrium with its vapour) saturated with carbon dioxide under conditions of the bomb reaction, and of solid ash, all at the reference temperature and at constant volume. The old term is higher heating value
NOTE Adopted by ISO1928:1995
net calorific value (qnet)
under such conditions that all the water of the reaction products remains as water vapour (at 0.1 MPa), the other products being as for the gross calorific value, all at the reference temperature. The net calorific value can be determined at constant pressure or at constant volume. The old term is lower heating value. Net calorific value as received (qnet,ar) is calculated by the net calorific value from dry matter (qnet,d) and the total moisture as received
wood free of moisture, produced by drying to constant weight under specific conditions
recovered construction wood
used wood arising from construction of buildings or from civil engineering works
sawdust
fine particles created when sawing wood
NOTE Most of the material has a typical particle length of 1 to 5 mm
slabs
parts of woody biomass created when cuts are made into the edges of logs and whereby one side shows the original rounded surface of the tree, either completely or partially, with or without bark
stacked volume
volume of stacked wood including the space between the wood pieces
used wood
wood substances or objects which have performed their intended purpose
NOTE 1 See also recovered construction wood and demolition wood
NOTE 2 Proposal within the Draft CEN Report Solid Recovered Fuels [11]
chipped woody biomass in the form of pieces with a defined particle size produced by mechanical treatment with sharp tools such as knives. Wood chips have a sub-rectangular shape with a typical length 5 to 50 mm and a low thickness compared with other dimensions
NOTE See also cutter chips, forest chips, green chips, stemwood chips, and whole-tree chips.
wood energy, forest energy
energy derived from woodfuels corresponding to the net calorific value of the fuel
wood energy systems
All the (steps and/or) unit processes and operations involved for the production, preparation, transportation, marketing, trade and conversion of woodfuels into energy
woodfuels, wood based fuels, wood-derived biofuels
all types of biofuels originating directly or indirectly from woody biomass
NOTE See also fuelwood, forest fuels, and black liquor.
wood processing industry by-products, wood processing industry residues
woody biomass by-products originating from the wood processing as well as the pulp and paper industry
NOTE See also bark, cork by-products, cross-cut ends, edgings, fibre board by-products, grinding dust, particle board by-products, plywood by-products, sawdust, slabs and wood shavings
wood shavings; cutter shavings
shavings from woody biomass created when planning wood
woody biomass
biomass from trees, bushes and shrubs
NOTE See also forest wood, wood processing industry by-products, fibre board by-products, particle board by-products, plywood by-products and used wood