The triggerfish (Balistes capriscus) seems to be divided into two separate stocks off West Africa, with no apparent interchange. The western stock, with its center of distribution off Guinea and Guinea Bissau, was fully surveyed twice in the Dr. Fridtjof Nansen programme, in May-81 and Feb-82. In Sept-81 the stock was only partly covered. The eastern stock with its center off Ghana has only been covered once (Jun-81).
Figure 46 based on the integrator readouts classified as triggerfish shows the distribution of the Guinea stock at three levels of density during the three coverages. Figure 47 on the other hand shows the distribution of the same species during the same coverages, but solely on basis of the trawl catches. This figure includes spurious occurrences in the fringes of the distribution area but no density levels. The Guinean stock of triggerfish was distributed north to Cape Timiris and south to Sherbro Island. The main distribution is south of Cape Verde and substantial quantities are from Bissagos Islands and southwards. There seems to be a tendency of increasing length with increasing latitude in the younger part of the population, i.e. for the small and middle sized individuals . Figure 48 shows this for the three coverages. In May-June this pattern is not apparent, but the minimum values show that all fish of 16 cm or less are located south of 11°30'N. The results from the two other coverages show a clear tendency to increasing mean and minimum lengths by latitude. The size distribution could be due to a gradual northward migration within the younger part of the population. A possibility of a location-dependent growth, corresponding with a general decreasing productivity southwards, should also be considered. The maximum values in the samples do not show a similar trend. The figures also indicate that there is little or no recruitment of young fish into the population during the period of the surveys, as the minimum values increase with each survey along the coast.
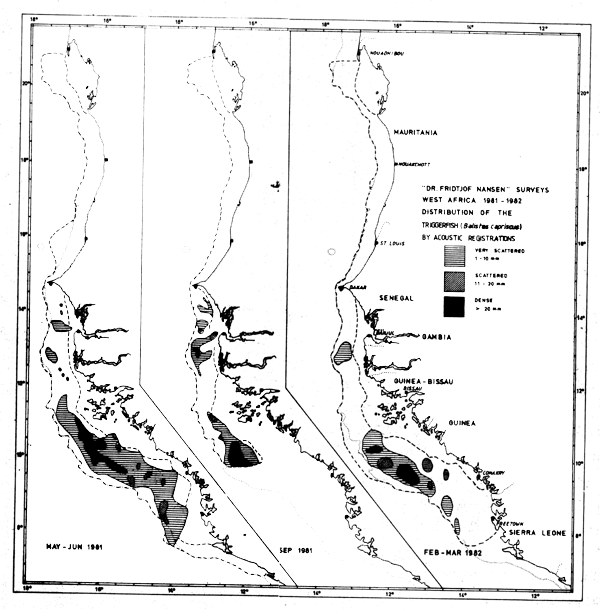
Fig. 46 Distribution of triggerfish (Balistes capriscus) from Cape Verde to Sherbro Island, 1981–1982.
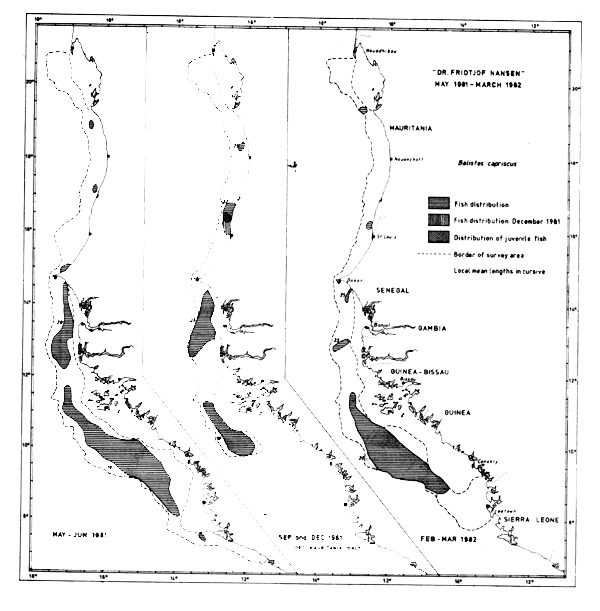
Fig. 47 Distribution of Balistes capriscus from occurrence in trawl catches, Cape Blanc to Sherbro Island, 1981–1982.
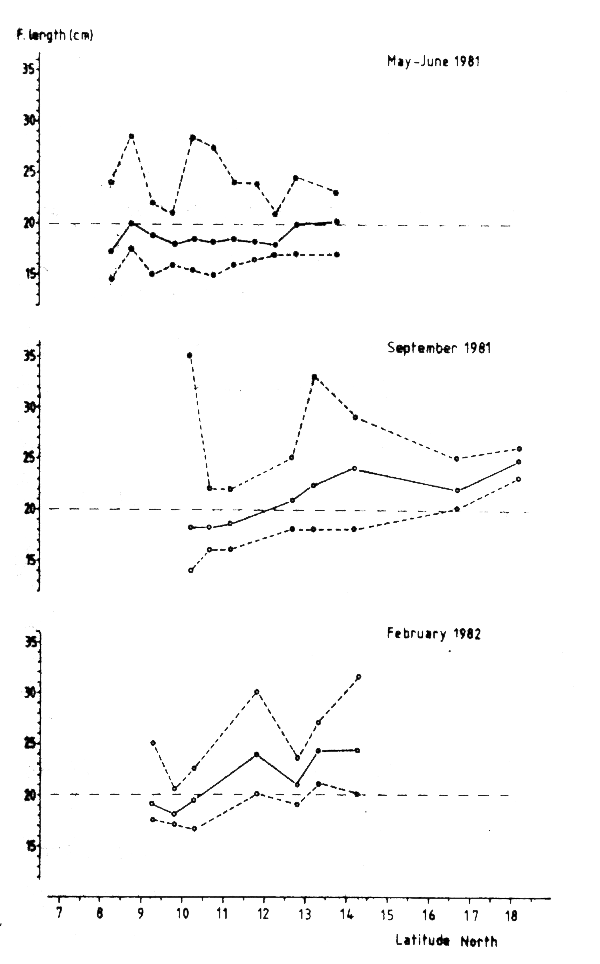
Fig. 48 Recorded maximum, mean and minimum length by latitude and survey in pooled samples of triggerfish (Balishtes capriscus).
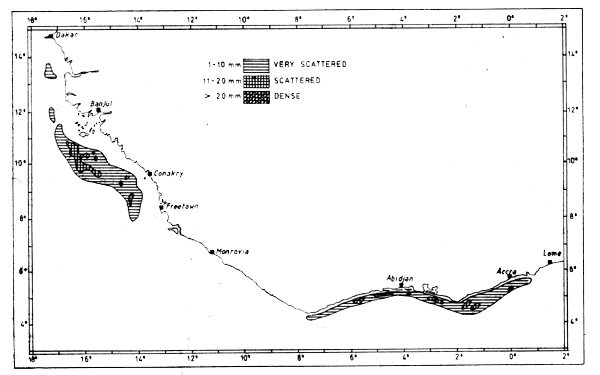
Fig. 49 Distribution of triggerfish (Balistes capriscus) from Cape Verde to Togo, June 1981.
The distribution of the Ghana stock in Jun-81 is shown in Figure 49. The triggerfish is distributed from the border between Liberia and the Ivory Coast and eastward almost to Togo. The length distributions show the same pattern as for the Guinea stock; the mean and minimum lengths observed tend to increase westwards (see Annex III st. 171–200). From Figure 49 it is also seen that the triggerfish is virtually absent from Liberia. From this we assume that the two populations do not mix.
The biomass estimates were as follows (thousand tonnes):
| May-Jun-81 | Sept-81 | Feb-82 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guinea stock | 1050 | 490* | 1350 |
| Ghana stock | 500 | n.s. | n.s. |
| By EEZ's: | |||
| Senegambia | 70 | 140 | 40 |
| Guinea Bissau | 380 | 350 | 590 |
| Guinea | 510 | n.s. | 720 |
| Sierra Leone | 80 | n.s. | 10 |
| Liberia | 2 | n.s. | n.s. |
| Ivory Coast | 190 | n.s. | n.s. |
| Ghana | 310 | n.s. | n.s. |
The triggerfish seem to react very little to the research vessel, and the species is generally very even in its distribution. We therefore consider the estimates for this species to be the most reliable obtained during the programme.
The first and last surveys fully encompassed the population of the Guinea stock, and the two estimates seem to be in fair agreement, allowing for some growth in the intermediate period. As seen, the western stock is approximately twice the size of the eastern stock.
Earlier estimates (FAO/CECAF, 1981b) of the Ghana stock are 68 thousand tonnes for Ghana (1976) and 8 thousand tonnes for the benthic part on Ivory Coast (1977). The estimate from the “Dr. Fridtjof Nansen” survey thus far exceeds the earlier assessments of the Ghana stock.
Earlier estimates of the Guinea stock are (FAO/CECAF, 1981a and b) (1 000 tonnes):
| USSR survey 1975 | 80 |
| Capricorne Nov 1978 | 440 |
| Capricorne Mar 1979 | 440 |
| Cornide de | |
| Saavedra 1980 | 760 |
The results from the “Dr. Fridtjof Nansen” surveys also indicate a considerable recent growth in the Guinea stock.
The distribution of the catches of triggerfish is shown in Table 12. Except for two cases, both off Cape Roxo, all hauls in the western stock exceeding 1 tonne/hour were obtained from the Bissagos Islands and south to the Guinea - Sierra Leone border. In the Ghana stock four hauls were above the same level, within 60 miles from Cape Three Points. The fish was generally very easy to catch and the best catch (12 tonnes/hour at stn 87) is in no way outside the range of the expected catches.
| NUMBER OF HAULS IN CATCH GROUPS (kg/hr) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <1 | 1–10 | 10–50 | 50–200 | 200–1000 | >1000 | |
| Guinea stock, May-June 1981 | 1 | 8 | 12 | 7 | 11 | 12 |
| Ghana stock, June 1981 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 7 | 6 | 4 |
| Guinea stock, September 1981 | 0 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 11 | 2 |
| Guinea stock, February 1982 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 4 |
The size-dependent distribution along the coast of West Africa has already been touched in the foregoing chapter. The same pattern is shown when the samples are pooled by countries. Figure 50 shows the pooled length distributions from Ghana, Ivory Coast and Guinea Bissau waters from the May-June survey. The distributions from the three areas have clearly distinct modes: Ghana 14.5 cm, Ivory Coast 16 cm and Guinea Bissau 19 cm.
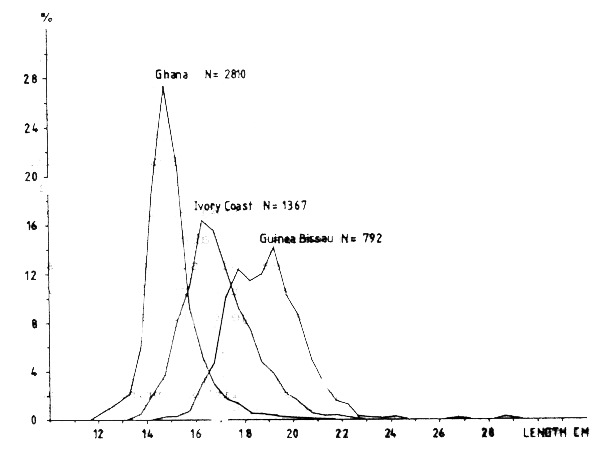
Fig. 50 Length frequency distributions of triggerfish (Balistes capriscus) off Ghana, Ivory Coast and Guinea-Bissau, June 1981.
Weight measurements were carried out on length grouped material, and the weight data were later pooled in 1/2 cm length groups. The relationship between the fork length and weight is given in Figure 51. An exponential regression analysis on all data with more than 5 specimens in the length interval gave the equation
W(g) = 0.035209.L(cm) 2.1817r2 = 0.972
for the relationship. This agrees well with earlier results (Gerlotto, Stéquert and Barbieri, 1980).
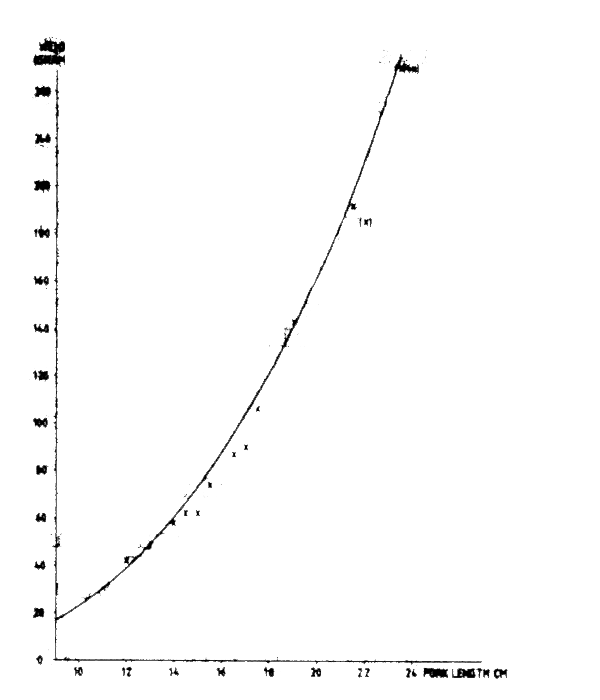
Fig. 51 Relationship between fish lenght and weight of troggerfish (Balistes capriscus) off Ghana and Guinea, June 1981.
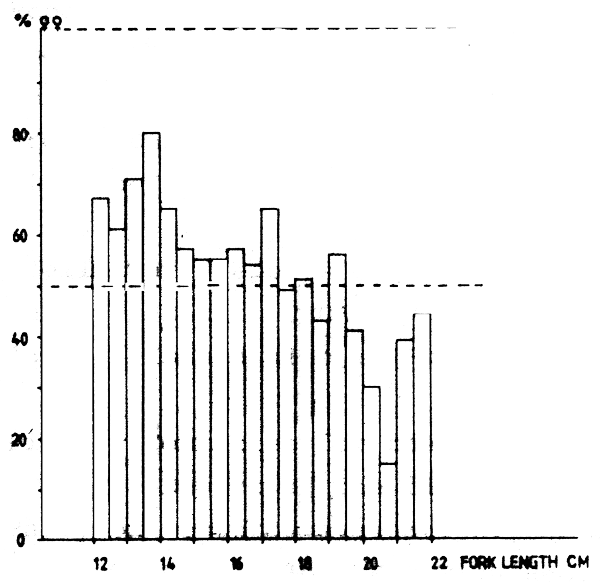
Fig. 52 Percentage of identified females by .5 cm length intervals of triggerfish (Balistes capriscus) off Guinea - Ghana in June 1981. Fig. 46 Distribution of triggerfish (Balistes capriscus) from Cape Verde to Sherbro Island, 1981–1982.
2 500 specimens were also sex analysed. The difficulties involved in identification of males of Balistes capriscus have earlier been reported (Gerlotto, Stéquert and Barbieri, 1980). Figure 52 shows the percentage of identified females within each 1/2 cm length interval.
REFERENCES
Aglen, A. et al. 1982 Surveys of mesopelagic fish resources in the Gulf of Oman and the Gulf of Aden July - Aug. 1979 and Jan. - Feb. 1981. In Reports on the surveys with the R/V Dr. Fridtjof Nansen. Norway, Institute of Marine Research, 70 p.
Blache, J., J. Cadenat and A. Stauch. 1970 Clés de détermination des poissons de mer signalés dans l'Atlantique oriental (entre le 20e parallèle N et le 15e parallèle S). Faune Trop.ORSTOM, Paris, (18):479 p.
Boely, T. and P. Fréon. 1980 Coastal pelagic resources. FAO Fish. Tech.Pap., (186.1):13–76. Issued also in French
FAO/CECAF. 1979 Report of the ad hoc working group on West African coastal pelagic fish from Mauritania to Liberia (26°N to 5°N), CECAF/ECAF Ser., (78/10):161 p. Issued also in French
FAO/CECAF. 1981 Report of the evaluation meeting of the 1980 cooperative acoustic survey and the planning meeting for the 1981 Dr. Fridtjof Nansen survey in the CECAF area. Dakar, CECAF, CECAF/TECH/81/29:42 p. Issued also in French
FAO/CECAF. 1981a Preliminary reports of the cooperative acoustic survey. Dakar, CECAF, CECAF/TECH/81/30: 166 p. Issued also in French
FAO/CECAF. 1981b Fishery Committee for the Eastern Central Atlantic (CECAF), Report of the fifth session of the Working Party on resource evaluation. Dakar, Senegal, 15–17 October 1980. FAO Fish.Rep., (244):127 p. Issued also in French
Fischer, W., G. Bianchi and W.B. Scott (eds.). 1981 FAO Species identification sheets for fishery purposes. Eastern Central Atlantic; fishing areas 34, 47 (in part). Canada Funds-in-Trust. Ottawa, Department of Fisheries and Oceans Canada, by arrangement with the FAO of the UN, vols. 1–7: pag. var.
Garcia, S. 1982 Distribution, migration and spawning of the main fish resources in the northern CECAF area. CECAF/ECAF Ser., (82/25): 9 p.
Gerlotto, F., B. Stéquert and M.A. Barbieri. 1980 Premiers résultats d'observations sur la biologie de Balistes capriscus (Gmel) dans la partie occidentale du Golfe de Guinée. CECAF/ECAF Sér., (80/21): 29–48
Marchal, E. and T. Boely. 1977 Evaluation acoustique des ressources en poissons du plateau continental ouest-africain des îles Bissagos (11°N) à la pointe Stafford (28°N), Cah.ORSTROM (Sér.Océanogr.), 15(2):139–61
Marchal, E. F. Gerlotto and E. Josse. 1981 Acoustic survey of the pelagic resources in Senegal, Gambia and Mauritania waters in 1980: main results from cruises ECHOSAR 1 and ECHOSAR 2 of R/V Capricorne. Dakar, ORSTOM, January 1981 (MS)
Marchal, E. and E. Josse. 1981 Résultats préliminaires de la campagne ECHOSAR 2 du N/O Capricorne: prospection des stocks pélagiques le long des côtes du sénégal, de Gambie et de Mauritanie. Dakar, ORSTOM, January 1981 (MS)
Marchal, E. and E. Josse. 1982 Résultats de la campagne ECHOSAR 3 du N/O Capricorne (mai 1981): répartition et abondance des poissons pélagiques du Cap Blanc au Cap Roxo (côte occidentale de l'Afrique). Brest, COB, ORSTOM,Juin 1982, unpag. (mimeo)
Mittelstaedt, E. 1982 Large-scale circulation along the coast of Northwest Africa. Rapp.P.-V.Réun.CIEM, (180):50–7
StrÆmme, T., G. Saetersdal and H. GjÆsaeter (eds.). 1981 Preliminary report on surveys with the R/V Dr. Fridtjof Nansen in West African waters 1981. Bergen, Institute of Marine Research. Also presented at the CECAF Working Party on Resource Evaluation Sixth Session, Dakar, 2–6 February 1982. pag.var.
StrÆmme, T., G. Saetersdal and A. Raknes. 1982 Comparison of fish biomass assessment by experimental trawling and acoustic survey. Paper presented to the ICES/FAO Symposium on Fisheries Acoustics. Bergen, Norway, 12–27 June 1982. Doc. (45):16 p. (mimeo)
StrÆmme, T., L. FÆyn and G. Saetersdal. 1983 Survey of the offshore sub-surface community from Togo to Cameroon and of the shelf from equatorial Guinea to the Congo. In Reports on surveys with the R/V Dr. Fridtjof Nansen. Bergen, Norway, Institute of Marine Research, 29 p.
Saetersdal, G. et al. 1983 Some observations on frequency dependent back scattering strength. FAO Fish.Rep., (300):150–6
Troadec, J.-P., and S. Garcia (eds.). 1980 The fish resources of the eastern central Atlantic. Part 1: The resources of the Gulf of Guinea from Angola to Mauritania. FAO Fish.Tech.Pap., (186–1):166 p. Issued also in French