Small-ScaleDairy Farming Manual |
Volume 3 |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
What should you know about minerals and mineral block making?
 |
Why do your animals need minerals?(5-9)
1 For good
|
 |
How can you feed minerals to your animals?
(10-16)
2 By consulting your extension worker and using mineral blocks. |
 |
How can you make mineral blocks?(17-27)
3 By:
|
 |
How can you store mineral blocks? (28-29)
4 By:
|
|
Husbandry Unit 5.7: Technical Notes Note: Numbers in brackets refer to illustrations in the Extension Materials. Minerals are an essential component in the diet of all animals. In dairy cattle and buffalo, minerals are required for the maintenance of general health and for proper growth and reproductive functions as well as to meet the quantities of minerals that are secreted in the milk. (5-6) The quantities of minerals required vary with the type of mineral, type of animal and stage in the life cycle. Some animals may be able to obtain all the requirements of the minerals that they need from their normal diet. On the other hand, most animals may not show any obvious signs of a deficiency even if they do not receive adequate quantities of minerals. However, they will yet be susceptible to diseases, will not become pregnant in time and will have a slower growth and lower production than can be obtained, had they received an adequate supply of the required minerals. (7-9) |
 |
Why do your animals need minerals?
5 Dairy cattle and buffalo need
minerals
for:
|
 |
6
- reproduction - milk production. |
 |
7 The amounts
of minerals
required depend upon:
- type of mineral - type of animal - age and use of animal. |
 |
8 If your animals do not have
enough
minerals, they may look normal but they will:
- get disease more easily - grow more slowly |
| As the normal feeds offered to dairy cattle and buffalo may not contain the required amounts of minerals, additional quantities are usually supplied in the form of mineral supplements. The mineral supplements available in the market are produced to a standard formula and it may not be economical to feed such supplements under some conditions of feeding. In addition, there are considerable losses due to wastage when minerals are given to animals in the form of powders. (10-11) |
 |
9
- get pregnant late - have low production.
|
 |
How can you feed minerals to your animals?
10 Normal feeds may not
contain enough minerals:
|
 |
11 But:
- commercial supplements are expensive - powder supplements have a lot of waste. |
 |
12 It is better to use mineral blocks. |
| To avoid these difficulties, minerals
can be offered in the form of blocks. The advantages of offering
minerals in the form of blocks (over powders) are:
- farmers can themselves make blocks economically using components purchased from the market; (13) - the composition of the blocks can be changed according to needs e.g. type of feeds available and quantities of minerals that animals can obtain from them; (14) - the blocks can be left in the barn for the animals to obtain their requirements by licking; - there is less wastage, even when the blocks are left in the barn. (15) |
 |
13 Advantages
of
mineral
blocks (over powders) are:
- you can make the blocks yourself with materials from the market |
 |
14
- you can choose the composition of the block for your feeds and your animals |
 |
15
- you can leave the blocks in the barn for your animals to lick - even in the barn, there is less wastage. |
 |
16 Using mineral blocks:
|
| The procedure for making mineral
blocks may be explained in several stages as follows:
Stage I: Composition of the mixture to be used for making the block Some components in the mixture can be increased or decreased depending on the availability of minerals from the feeds consumed by the animals. Extension officers should give necessary advice on this aspect. (17) An example of a mixture that would be suitable to make five blocks, each weighing 1 kg is given opposite. However, if the animals receive a feed containing adequate quantities of good quality rice bran, which is rich in phosphorous, the amount of dicalcium phosphate in the mixture can be reduced. (18) |
How can you make mineral blocks?
 |
Choosing a mixture
17 Consult your extension worker about the correct mixture for your feeds and your animals. |
 |
18 This example mixture can
make 5 blocks of l kg each.
If your feed has enough rice bran, rich in phosphorus, you can reduce the dicalcium phosphate in the mixture. |
| Component
Cement Quicklime Common Salt Dicalcium Phosphate Cobalt Chloride Copper Sulphate Potassium Iodide Zinc Oxide Sodium Selenate |
Quantity
in grams
1000.0 125.0 1750.0 2000.0 1.0 25.0 3.0 95.0 1.0 |
| Stage 2:
The block
A wooden block can be made as shown to make blocks weighing about 1 kg each. (19) Stage 3: Mixing the components Cement, quicklime, dicalcium phosphate, common salt and zinc oxide. Crush any crystals and large particles of these components and sieve to obtain a fine powder. Mix them well in a bucket or other suitable container. (20) Cobalt chloride, copper sulphate, potassium iodide and sodium selenate. (21) Dissolve each component separately in about 100 ml (1/2 a cupful) of clean water. Add the cobalt chloride solution to the mixture made above and mix thoroughly. (22) |
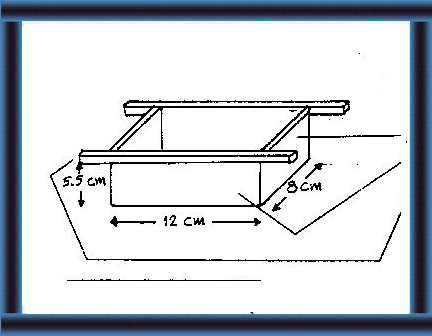 |
Making the frame 19 Make a frame for 1 kg blocks using the following materials: 2 planks 1.5 x 5.5 x 8 cm 2 planks 1.5 x 5.5 x 12 cm 2 pieces of wood 2 x 2 x 25 cm |
 |
Preparing the mixture
20 Take the cement, quicklime, dicalcium phosphate, common salt and zinc oxide: - crush crystals and large pieces - put through a fine sieve - mix together in a bucket. |
 |
21 Take the cobalt chloride, copper sulphate,
potassium chloride and sodium selenate:
- dissolve each one in 100 ml (1/2 cup) of clean water. |
 |
22 Add each solution from 21 (begin with cobalt
chloride) one-by-one to the mixture in 20.
Mix thoroughly before adding the next solution. |
| Stage 4:
Adding water
Add clean water to the mixture while mixing it thoroughly until it attains the consistency of a dough. (23) Stage 5: Making the blocks Spread a piece of polythene on level ground to cover the area of the block and place the wooden block on the polythene sheet. (24) Add a sufficient quantity of the mixture to fill the block and compact it well. (25) While adding the mixture, place two or three sticks (with a diameter of the size of a pencil) in position as shown to form two or three holes in the blocks. These holes will facilitate drying and can also be used to hang the block). (26-27) |
 |
Adding water |
 |
Making the blocks
24 Place a piece of polythene on level ground and put the wooden frame on top. |
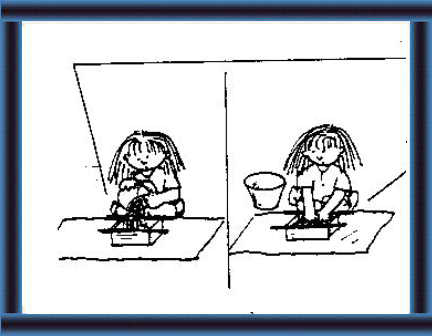 |
25 Add enough mixture to fill the frame.
Compact the mixture well. |
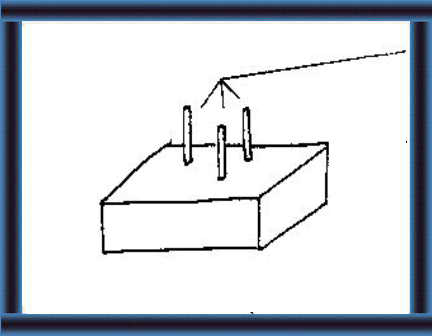 |
26 Add 2 or 3 sticks (the size of a pencil) to
make holes in the block.
|
| Stage 6:
Storage
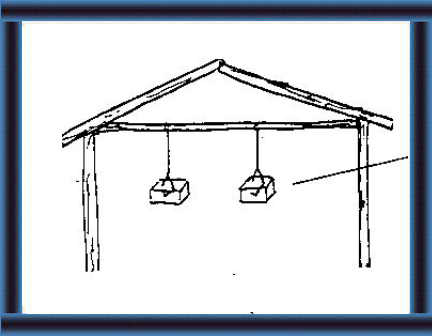
The blocks can be left in the barn (in a suitable place to prevent them getting wet) for animals to lick. The blocks that are not required immediately and are to be kept for future use should be wrapped up in polythene and stored without exposure to air and water. |
 |
27 You need holes in the blocks to:
- help the blocks dry - make it easy to hang the blocks. |
 |
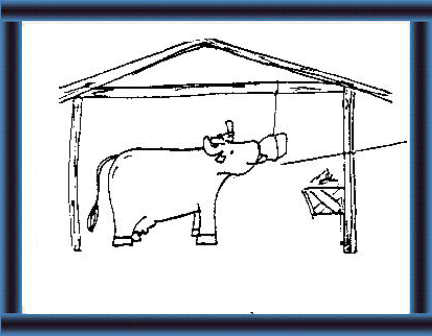
How can you store mineral blocks?
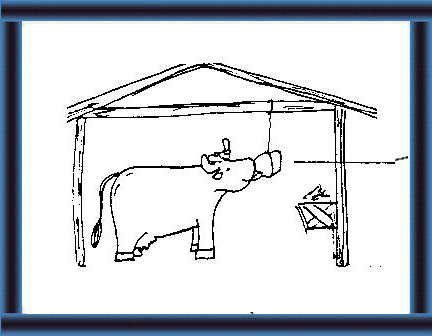
28 When dry, hang a block - where it does not get wet - where your animals can lick it. |
 |
29. Wrap the other bricks up in polythene and store in a dry place for later use. |
|