

1. Overview
1.1. Jamaica's characteristics
Independent country since 1962
Surface area: 1 096 416 hectares (include bays and cays)
Latitude: 170 30" to 180 45" North
Elevation to 2 256 metres
Mean annual rainfall: 75 to 500 centimetres
Population (1997): 2 557 000
Originally described as the "land of wood and water", still derives important benefits from the forests and the production and trade in wood and wood-products. With over 31% of Jamaica classified as forests and 30% as forests and cultivation (see Figure 1), the management of the forests for production, consumption and trade of wood-products plays an important role at different levels of the society.
At the local level, wood-products:
Support food production through the use of yam-stick, fence posts and fish pots;
Provide shelter and material for construction and household use;
Provide wood fuel requirements for large number of people in both rural and urban areas;
Provide income-generating activities in wood harvesting and transport, and small-scale wood processing activities.
At the national level, wood-products:
Increase the development potential of rural areas and decrease the need for rural-urban migration;
Provide opportunities for development of a range of wood-base industries;
Provide a source of renewable energy;
Provide for the creation of employment opportunities in the various phases of the production and marketing chain and for earning export revenue to improve the balance of payment.
Forest-products from which benefits have derived include roundwoods (logs), sawnwoods, wood charcoal and wood fuel.
Roundwood is used mainly as fence posts, yam sticks, wood fuel and wood charcoal.
Local hardwoods are utilised mainly by the furniture industry while softwoods are used mainly in the construction industry. Production of local sawnwood is seen in Table 1.
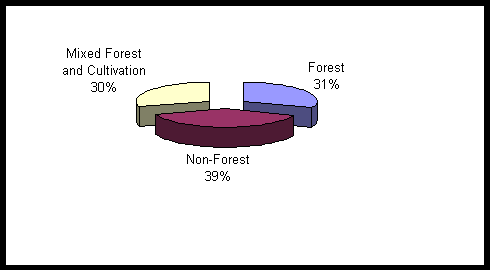 Figure 1: Proportion of Jamaica Covered by Forests
Figure 1: Proportion of Jamaica Covered by Forests
Source: Forestry Department, December 1999
Table 1: Estimated Lumber Production for Years 1995-1999
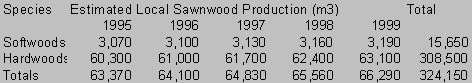
Source: Developed from Statistical Institute of Jamaica and Campbell (1993)
Figures are derived by incrementing the 1993 domestic production estimates of softwoods-3 000 cubic metres and hardwoods- 59 000 cubic metres by annual population growth rate.
Imported wood-products are also important in the local economy as they generate employment for many in the wood-products industries. These products have shown fluctuations during the past 5-year with roundwood, wood charcoal, wood residues, chips and particles, some wood-based panels, and paper and paperboards showing increases. Others as sawnwood, wood pulp, and other wood-based panels have shown decreases. See Table 2.
Table 2: Imports of Wood-based Products 1995-1999
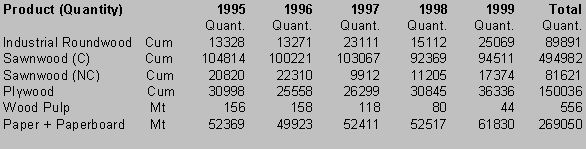
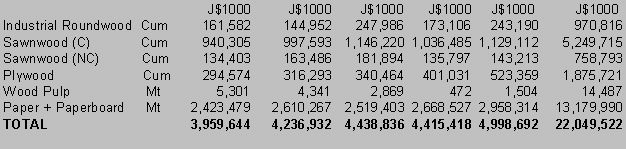 Source: Developed from data in External Trade (var. issues), Statistical Institute of Jamaica.
Source: Developed from data in External Trade (var. issues), Statistical Institute of Jamaica.
Note: Sawnwood include quantity and value for v-jointed, beaded etc.
Since early 1993 when fire destroyed the West Indies Pulp and Paper mill, the company has since imported stocks in bulk and then cut to desired sizes. This has resulted in a steady increase in imported paper products and a decline in wood pulp over the ensuing years.