
Animal health

13 June 2024, 08:30 hours; Rome
Overview
Hazard: African swine fever (ASF) is a viral disease affecting pigs and wild boar with up to 100% case fatality rate.
ASF reported countries since August 2018: China, Mongolia, Viet Nam, Cambodia, Democratic People’s Republic of Korea, Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Myanmar, The Philippines, Republic of Korea, Timor-Leste, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, India, Malaysia, Bhutan, Thailand, Nepal, Singapore, and Bangladesh.
Map 1. ASF situation in Asia (for the past 10 weeks)
Source: Republic of Korea, Viet Nam: WAHIS & media information, the Philippines: WAHIS & government websites, Indonesia: official database ‘isikhnas’, Other: WAHIS.
Situation update
Mongolia: Since its first report on 15 January 2019, 14 outbreaks in 6 provinces and in Ulaanbaatar were reported [reference1,
reference2]. An ASF outbreak was recently detected in Saykhan District in Selegen Province with the onset on 25 February
2024 [reference3].
Democratic People’s Republic of Korea: The Ministry of
Agriculture confirmed the occurrence of the first ASF outbreak in Chagang-do on 23 May 2019 [reference].
Republic of Korea:
Since the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) confirmed the first ASF outbreak on 17 September 2019, ASF were detected in 41 domestic pig farms: Gyeonggi-do (18), Incheon
City (5), and Gangwon-do (17), and Gyeongsangbuk-do (1). On 21 May, ASF outbreak was detected on a farm in Cheorwon County, Gangwon-do [reference1, reference2]. As of 13 June 2024, a total of 4 073 ASF virus infected wild boars were confirmed in: Gyeonggi-do: Yeoncheon (418), Paju (100), Pocheon (94), Gapyeong (62); Gangwon-do: Cheorwon (37), Hwacheon (431), Yanggu (81), Goseong (12), Inje (158), Chuncheon (222), Yeongwol (260), Yangyang (36), Gangneung (111), Hongcheon (63), Pyeongchang (46), Sockho (1), Jeongseon (181), Hoengseong (63), Samcheok (106), Wonju (83), Donghae (8), Uljin (68), Taebaek (19); Chungcheongbuk-do: Danyang (198), Jecheon (95), Boeun (73), Chungju (115), Goesan (12); Gyeongsangbuk-do: Sangju (128), Mungyeong (78), Yeongju (20), Bonghwa (90), Yecheon (19), Yeongdeok (124), Eumseong (1), Andong (70), Yeongyang (106), Cheongsong (102), Pohang (84), Yeongcheon (46), Uiseong (27); Busan (25) [ reference3],
according to media.
China: Since the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs (MARA) confirmed the first outbreak in Liaoning Province on 3 August 2018, ASF was detected in 32 provinces/autonomous regions/municipalities/special
administrative region. The latest outbreak was reported from Hong Kong SAR in November 2023 – January 2024 in Lau Fau Shan, San Tin in Yuen Long and in Sheung Shui in North District [reference].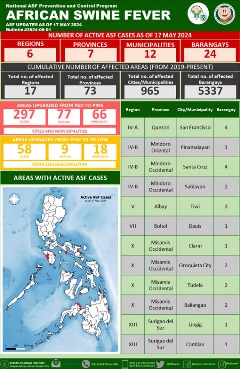 The Philippines: The Department of Agriculture (DA) confirmed the first outbreak in July 2019 [reference1]. Since the first detection, ASF outbreaks have occurred in 73 of its 82 provinces; as of 7 June 2024, there are 32 barangays in 16 municipalities of 10 provinces having active ASF cases [reference2]. On Luzon, the threat of ASF persists as 12 cases are being monitored in the Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR), including seven in Abra Province, two in Apayao, and three in Benguet [reference3]. In Eastern Visayas, blood samples from a backyard piggery in Calingonan village, Calbiga Municipality, Samar Province (Region VIII) tested positive for ASF [reference4]; ASF cases were reported also in San Sebastian municipality, Samar Province recently [reference5]. In Bicol (Region V), a pig from Barangay Santa Cruz tested positive for ASF at a slaughter house in Legazpi City [reference6]; on Mindanao, eight blood samples collected after mysterious deaths of pigs were reported in Ipil, Zamboanga Sibugay Province, Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM, Regions XIX), all tested positive for ASF [reference7], in addition to ASF confirmation in Basilan Province, BARMM [reference8, reference9] according to media. The latest update on ASF zoning status (as of 30 April 2024) is available [reference10].
The Philippines: The Department of Agriculture (DA) confirmed the first outbreak in July 2019 [reference1]. Since the first detection, ASF outbreaks have occurred in 73 of its 82 provinces; as of 7 June 2024, there are 32 barangays in 16 municipalities of 10 provinces having active ASF cases [reference2]. On Luzon, the threat of ASF persists as 12 cases are being monitored in the Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR), including seven in Abra Province, two in Apayao, and three in Benguet [reference3]. In Eastern Visayas, blood samples from a backyard piggery in Calingonan village, Calbiga Municipality, Samar Province (Region VIII) tested positive for ASF [reference4]; ASF cases were reported also in San Sebastian municipality, Samar Province recently [reference5]. In Bicol (Region V), a pig from Barangay Santa Cruz tested positive for ASF at a slaughter house in Legazpi City [reference6]; on Mindanao, eight blood samples collected after mysterious deaths of pigs were reported in Ipil, Zamboanga Sibugay Province, Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM, Regions XIX), all tested positive for ASF [reference7], in addition to ASF confirmation in Basilan Province, BARMM [reference8, reference9] according to media. The latest update on ASF zoning status (as of 30 April 2024) is available [reference10].
Malaysia: The first ASF outbreaks were confirmed in February 2021 in Sabah State on Borneo [reference1] and on the Malay Peninsula in December 2021. ASF was detected in Perak State in wild boars in July 2023 followed by ASF outbreaks in pig farms in Perak and Kedah states in late October [
reference2].
Singapore: The first cases of ASF was confirmed in February 2023 in
wild boar carcasses found in forested areas and nature parks [reference1,
reference2]. In April, ASF was detected at a slaughterhouse in carcasses of live pigs imported from Bulan
Island, Indonesia [reference3,
reference4].
Indonesia: Since the Ministry of Agriculture (MoA) reported an ASF outbreak
in North Sumatra Province in 2019 [reference1,
reference2], ASF has been officially reported in 23 out of 34 provinces on Sumatera, Bangka Belitung, Java, Kalimantan, Bali, East Nusa Tenggara,
Sulawesi and Riau Islands [reference3, reference4]. Since the beginning of 2024, a total of 1 456 ASF cases have been confirmed in five provinces: East Nusa Tenggara (NTT) (1 035 cases),
Central Sulawesi (30), South Sulawesi (324), West Kalimantan (30), and Central Java (37) [reference5]. In NTT, ASF cases were detected in Boru, Wulanggitang District, East Flores Regency [reference6, reference7]; a number of pigs died suddenly in Biboki Anleu, Biboki Moenleu, Kota Kefamenanu, and Insana Utara districts in North Central Timor Regency, ASF is suspected to be the cause of the deaths [reference8, reference9]; hundreds of pigs recently have died suddenly in Maurole District, Ende Regency [reference10]; also in Nubatukan District of Lembata Regency, 239 pigs have died since May 2024, and two samples tested positive for ASF [refrence11]; as of 10 June, ASF cases reported in NTT since the beginning of this year reached 2 500, of which 1 420 were recorded in Central Sumba Regency, followed by Ngada (492), Nagekeo (410), Sikka (43), East Flores (29), West Sumba (28), East Sumba (22), Southwest Sumba (13), East Manggarai (13), Belu (8), Ende (8), South Central Timor (7), Manggarai (5), West Manggarai (5), and North Central Timor (1) [reference12], according to media.
Timor-Leste: After the Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries announced the confirmation of ASF outbreak on 27 September
2019 [reference1], ASF spread to almost all villages within one year. At least 129 000 pigs, 28 percent of the total pig population, have died
for ASF or CSF [reference2], affected >70 percent of households [reference3]. From December 2021 and from March 2023, there were small outbreaks of mortality 100-pigs level and were controlled through quick diagnosis and response [reference4].
Papua New Guinea: The National Agriculture Quarantine and Inspection Authority (NAQIA) confirmed ASF outbreaks in Southern Highlands Province in March
2020 [reference1,
reference2]. As of 12 April 2024, the current status of ASF in Papua New Guinea was as follows:
i) infected zone – Hela, Southern Highlands, Enga and Jiwaka provinces; ii) buffer zone – Eastern Highlands and Simbu provinces; iii) non-infected zone – the rest of the country.
Viet Nam: Since the Ministry
of Agriculture and Rural Development (MARD) confirmed its first ASF outbreak on 19 February 2019, all provinces/municipalities experienced outbreaks. The number of outbreaks in Viet Nam has decreased from > 6 000 outbreaks (2019) to 1 256
(2022) [reference1,
reference2], and 714 in 2023 [reference3]. For 2024, as of 9 June, ASF was detected in 142 districts/towns/cities in 39 provinces/municipalities, 13 655 pigs have been destroyed [reference4]. In Northern Viet Nam, ASF has flared up again in Bac Ka, Quang Ninh, Hoa Binh, Bac Giang, Lang Son, Dien Bien, Yen Bai, Thai Nguyen, Lao Cai, and Hai Phong provinces [reference5, reference6, reference7, reference8, reference9, reference10, reference11, reference12, reference13, reference14]. In Bac Kan Province, from January to 4 June 2024, ASF was detected in 1 414 backyard farms in 87 communes of 8 districts/towns, a total of 5 970 pigs have died or been culled , the loss due to ASF is estimated to be VND 15 billion (USD 590 000) [reference15]. In Quang Ninh Province, in addition to Quang Yen, ASF was detected in Hai Ha (4 communes) districts in May [reference16, reference17]. Hoa Binh Province confirmed ASF outbreaks in 5 districts namely Da Bac, Kim Boi, Yen Thuy, Mai Chau, and Lac Son and Hoa Binh City since the beginning of this year [reference18]. In Lang Son Province, 55 ASF outbreaks have occurred in 10 out of 11 districts/cities (53 communes) since January 2024; as of 7 June, 2 374 pigs have been culled (over 13.7 percent of the total number of pigs destroyed in Viet Nam due to ASF for the same period) [reference19]. In Lao Cai Province, ASF occurred in 2 districts (Van Ban and Bao Yen) at the end of May [reference20]. In Dien Bien Province, ASF recurred in Dien Bien District and has been spreading for more than a month; 35 outbreaks in 17 villages in 4 communes have been confirmed by 28 May [reference21]. In Yen Bai province, between 9 and 27 May, ASF was detected in Luc Yen district (Lam Thuong commune) [reference22]. In Thai Nguyen Province, between 13 May and 3 June, 28 ASF outbreaks were confirmed in Vo Nhai District (Trang Xa and Dan Tien) [reference23]. Hai Phong Province announced one outbreak in Kien Thuy District (Ngu Doan) occurred in the end of May [reference24]. And according to media, Cao Bang Province is currently monitoring five outbreaks in 3 districts namely Bao Lac (Son Lo and Hong Tri), Ha Quang (Can Yen), Trung Khanh (Chi Vien and Kham Thanh). Nearly 100 pigs have died/been culled during May alone; since the beginning of the year, 45 outbreaks have been recorded in 5 districts (Bao Lac, Bao Lam, Ha Quang, Hoa An, and Trung Khanh) [reference25]. In Central Viet Nam, ASF outbreak was recently detected in Ca Dy commune, Nam Giang District, Quang Nam Province; as of 5 June, together with Zuoih and Dac Toi communes, 31 households in the district have been affected [reference26]. In Southern Viet Nam, Ca Mau Province recorded 17 ASF outbreaks occurred in 6 districts (15 communes and 2 towns) since the beginning of 2024 till the end of May [reference27].
Lao People’s Democratic Republic: Since the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry confirmed the first outbreak in Salavan Province on 20 June 2019, ASF outbreaks were reported in all 18 provinces [
reference]. The last reported outbreak was in November 2022 in Kham District, Xiangkhouang Province.
Cambodia: Since the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF) confirmed the first outbreak in Ratanakiri Province in April 2019, ASF outbreaks were
detected in five provinces [reference1]. The last reported outbreak was in July 2019 [reference2].
Thailand: Department of Livestock Development (DLD) announced in January 2022 the confirmation of ASF in pet pigs in Bangkok [reference1]. So far, a total of 114 outbreaks have been reported in 35 out of 77 provinces/special administrative area [reference2]. The latest ASF case was reported in September 2023, Chiang Rai Province detected its first ASF cases in Ban Doi Sa Ngo Village, Chiang Saen District [reference3, reference4,
reference5].
Myanmar: Since the Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Irrigation confirmed the first ASF outbreak in August 2019,
a total of 12 outbreaks were reported in Shan (8), Kachin (1), Kayah (1) states, and Sagaing Region (2) [
reference1,
reference2, reference3, reference4, reference5, reference6, reference7, reference8].
Bangladesh: The first ASF outbreak in Bangladesh was reported on 21 December 2023 on a government development pig farm located in Rangamati Sadar in Rangamati District, Chittagong Division [reference].
Bhutan: Since the first ASF outbreak occurred in May 2021 [reference1], ASF outbreaks have been reported in seven districts [reference2,
reference3,
reference4, reference5,
reference6]. In February 2024, outbreaks were reported in Pemagatshel District [reference7], and Chhukha District [reference8]. On 7 May, ASF was confirmed
for the first time in wild boars, which were found dead in a forest in Chhumig, Bumthang District. This was also the first time that ASF was detected in the central part of the country; earlier outbreaks occurred within 30 km from the southern border
[reference9, reference10].
Nepal: Since the first ASF outbreaks occurred in Kathmandu Valley in March 2022, as of 4 February 2024, 43 ASF outbreaks were detected in pig farms in Bagmati, Province No.1, Lumbini, Gandaki, Karnali, Sudurpashchim, and Madhesh
provinces [reference1]. In January 2024, Gandaki Province detected the first ASF outbreaks in Lamjung and
Tanahu districts [reference2]. According to media, ASF cases have been confirmed in five districts during
surveillance, including Kathmandu (Kirtipur Municipality), Lalitpur (Godavari Municipality) districts in Bagmati Province, and Tanahun, Lamjung, and Kaski districts in Gandaki Province [
reference3].
India: Since the first ASF outbreaks
occurred in Assam State in January 2020 [reference1], ASF outbreaks have been officially reported in Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland
[
reference2], Sikkim [reference3],
Bihar [reference4], Kerala [
reference5], Punjab [reference6, reference7], Haryana [reference8], Tripura [reference9], Andhra Pradesh, Goa, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Karnataka,
Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand states and Delhi National Capital Territory [reference10]. Media wrote that ASF was also confirmed in Gujarat State [reference11]. In Assam State, ASF was detected in Naginijan tea estate in Jorhat district [reference12]. In Nagaland State, ASF was recently detected in Kidima Village in Kohima District [reference13].
Mizoram State recently confirmed ASF in Aizawl, Champhai (Leithum, Vanzau), Saitual, Lawngtlai, Khawzawl (Tualte Village), and Serchhip (Khumtung and Chhingchhip villages) districts [reference14, reference15, reference16, reference17, reference18, reference19,
reference20, reference21, reference22]. Media wrote by quoting Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Department that in Mizoram State, ASF killed over 47 000 pigs between 2021 and 2023, while at least 25 000 pigs were culled during the period [reference23]; this year, 1 863 pigs in the state have already died due to the ASF outbreak, while 3 415 pigs have been culled to prevent the spread of the disease [reference24]. In
Assam State, ASF was recently detected in Dima Hasao District after no new cases for a few months [reference25]; also
in Nagaland State, ASF cases were also reported in Phek Vilalge in Phek District [reference26], according
to media.
Disputed territory (Arunachal Pradesh): In April 2020, ASF outbreak occurred in eight districts [reference1,
reference2], deaths of wild boars were also reported [reference3,
reference4]. ASF was also confirmed in pigs died in Nirjuli area between December 2021 and February 2022 [reference5] according to media.
Actions taken
Actions taken by Mongolia: Control measures have been implemented [reference1, reference2].
Actions taken by the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea: The Democratic People’s Republic of Korea developed the National Strategy for ASF prevention and control during 2020-2025 (issued in May 2021).
Actions taken by the Republic of Korea: The ASF Task Force has implemented “Measures to block the spread of ASF in the Gyeongsangbuk-do region” through enhanced wild boars capturing by professional capture teams and use of advanced drones; installation of 'automatic door closing devices, and strengthened management of gates frequently used by agricultural vehicles. Information on ASF detection in wild boars has been shared through the Animal Quarantine Management System (KAHIS) as well as distribution of wild boars across the country [reference1].
Actions taken by China: In April 2021, MARA issued the “Work Plan for Regional Prevention and Control of African Swine Fever and Other Major Animal Diseases (Trial)”. The whole country was divided into five regions, and pig movement has been restricted only within the region. ASF-free zones are created in each region, only pigs from the free zones, breeding pigs and piglets are allowed to move beyond respective regions [reference1].
Actions taken by the Philippines: The reduced tariff rates of imported pork has been extended until 31 December 2024 [reference1, reference2]. The local authorities are mandated to strictly follow the National Zoning implementation and movement plan depending on the level of ASF risks [reference3]. The President announced that the government is in the process of procuring ASF vaccines and aims to administer the immunization shots within June or July [reference4]. On 22 May, DA informed that a vaccine for ASF was in the last stage of trials [reference5]. On Luzon, DA has allocated PHP 300 million (USD 5 million) for the National Swine Production Initiatives for Recovery and Expansion (INSPIRE) program to improve pig industry in the CAR Region [reference6]. In Central Visayas, the city government of Cebu will soon classify the entire locality under the pink zone category of ASF, given that no ASF cases have been reported in the city since last November [reference7]. Dauis Municipality has been declared under a state of calamity because of ASF since 23 April 2024 [reference8, reference9, reference10]. BAI, in collaboration with FAO, organized the National ASF Communications workshop under a project funded by MAFRA [reference11].
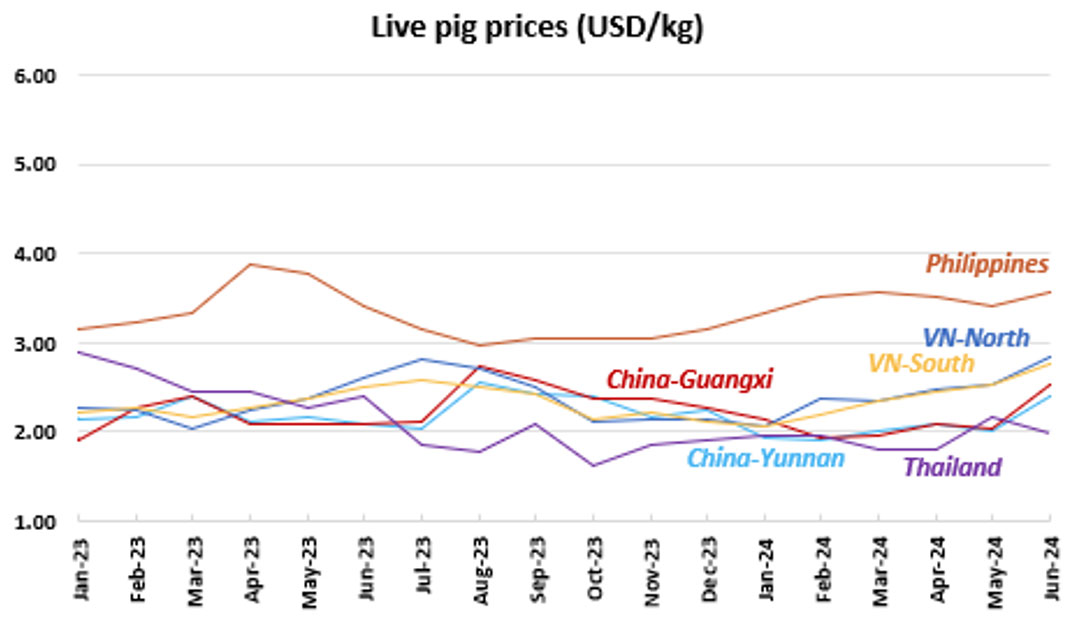
Figure 1. Live pig prices in China, Viet Nam, Cambodia, the Philippines and Thailand (USD/kg)
Actions taken by Malaysia: After the first confirmed outbreak in Sabah State in 2021, surveillance has been intensified in the whole country [reference].
Actions taken by Singapore: After confirming the first case of ASF in wild boar, the government is monitoring the health of wild boars in nature reserves, parks, and green spaces [reference1, reference2].
Actions taken by Indonesia: In December 2019, Ministry of Agriculture recommended the public the application of biosecurity and good management of pig farms as the main strategic steps to prevent ASF, as well as strict and intensive monitoring of high-risk areas [reference1]; the Livestock and Animal Health Services (DG PKH) formed Emergency Posts with Rapid Response Teams at all levels [reference2]. According to media, in response to the suspected ASF outbreak in Banyumas, Central Java, the transport of live pigs, carcasses, and other pork products to and from the affected area have been banned [reference3]; in NTT, Nagekeo Regency and Lewoleba City have prohibited the transport of pigs, pork products, and by-products from areas infected with ASF and temporarily stopped the sale of pigs in markets to stop the spread of the disease [reference4, reference5]; in Central Papua Province, authorities banned the movement of processed pork from infected areas in Mimika District [reference6, reference7]; concerning the increasing death rate in pigs since February 2024 in Jayapura Regency, the Governor of Papua declared the State of Emergency for the ASF outbreaks in pigs on 6 June [reference8, reference9].
Actions taken by Timor-Leste: The Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries (MAF) reactivated their public awareness campaign in collaboration with the Market Development Facility Australia to provide more accurate information for farmers and promote better practices [reference1]. To move a pig, pig transportation license for the driver, and pre-movement testing of pigs are required; and everybody are encouraged to follow biosecurity measures [reference2]; a Biosecurity Development Program has been implemented since April 2023 [reference3, reference4], according to media. MAF has introduced EpiCollect 5.0 for data collection since 2021, and progressively improved diagnostic capacity by LAMP test, portable lab, and PCR [reference5].
Actions taken by Papua New Guinea: NAQIA stepped up its ASF national risk communications and awareness campaign; strengthened responses for affected provinces and preparedness for non-infected provinces along the highway; urged farmers to practice biosecurity measures. “Quarantine Areas” and checkpoints at strategic locations have been set to control the movements of pigs and pork products. A restricted pig movement permit system has been implemented [reference1, reference2]. NAQIA is encouraging all provinces to develop their own ASF preparedness and response plans. NAQIA is now in the Recovery Phase of the ASF Response Plan with the aim to re-establish pig farming in the infected zone. The ASF impact survey Conducted in Upper Highlands illustrated strong need for value-chain and behaviour change communication (VC/BCC) [reference3]. NAQIA launched the ASF repository website. On 12 April 2024, NAQIA announced the official stand-down of the emergency response phase and transition to normalcy including consolidation of value chain resilience and sectoral recovery (long-term management).
Actions taken by Viet Nam: The “National Plan for the Prevention and Control of African Swine Fever for the period of 2020 – 2025” endorsed on 7 July 2020 (972/QD-TTg) set goals for ASF control, pig farm biosecurity application and laboratory capacity development to be achieved; defined restocking conditions, sampling requirements, surveillance, conditions for culling and moving-to-slaughter. The Department of Animal Health announced the licensing of NAVET-ASFVAC (manufactured by NAVETCO Company) in June 2022, and another vaccine AVAC ASF LIVE (manufactured by AVAC) in February 2023 [reference1]. On 24 July, the official letter No. 4870/BNN_TY was sent to notify all 63 provinces/municipalities that MARD approved the nationwide use of the two ASF vaccines [reference2, reference3, reference4]. On 9 April 2024, MARD issued an official letter urging all provincial People's Committees to direct all relevant departments, sectors and localities to implement preventive/control measures against ASF [reference5]. DAH sent a document to the Departments of Agriculture and Rural Development of Lang Son and Bac Kan provinces on strengthening the prevention and control of ASF, requesting the two provinces to focus resources and urgently direct local veterinary agencies/units to correct disease prevention and control in accordance with the regulations [reference6]. In the document No. 1276/TY-DT sent to Lang Son, DAH pointed out very high risk of ASF spread in the province due to insufficient and incorrect awareness in some districts/communes, urged them to announce outbreaks, implement prevention and control measures in accordance with the Animal Health Law, and timely reporting through VAHIS system, etc [reference7].
Actions taken by Lao People’s Democratic Republic: When an ASF outbreak confirmed, the Ministry designates Red Area around an outbreak to control the movement of pig and pork products and prohibits pork consumption; and yellow Area (3 km radius from the red areas) as designated surveillance zones. The Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry temporarily banned the importation of live pigs, pork, and pork related products from Thailand and Viet Nam [reference].
Actions taken by Cambodia: Cambodia temporarily suspended imports of pigs from neighbouring countries [reference1, reference2], in-country pig movement control has also been strengthened [reference3, reference4, reference5] according to media.
Actions taken by Thailand: DLD implements ASF contingency plan with clinical practice guidelines [reference1] while the provinces monitor and follow-up the situation in accordance with the guidelines [reference2]. DLD is promoting the improvement of disease prevention systems and biosafety on farms according to media [reference3], and also raising awareness and strengthening border control to stop illegal import of pork products from affected countries [reference4].
Actions taken by Myanmar: Various control measures including movement control, surveillance, official carcass disposal have been implemented and raised awareness on good animal husbandry practices [reference].
Actions taken by Bangladesh: Various control measures including inspection, disinfection, control of vectors, movement control, disinfestation, official disposal of carcasses, by-products and waste, surveillance, quarantine, screening have been implemented [reference].
Actions taken by Bhutan: The authority implemented 3D (Depopulation, Disposal and Disinfection) operation, surveillance, quarantine, movement control, awareness raising, import ban, and encouraged farmers to adopt good pig farming practices [reference1]. Media wrote that ASF was confirmed in imported pork in March this year through random testing. Approximately 67 tonnes of contaminated pork have been stored in cold storages in Phuentsholing, 18 tonnes have already been distributed, of which 8 tonnes were recalled, the rest have already been consumed [reference2]. The Government is advising farmers not to feed pigs with kitchen/hotel/restaurant waste containing pork and pork products, other kitchen waste should be cooked before feeding pigs, prevent contact between domestic and wild pigs, and stop visitors entering farms [reference3]. FAO is implementing multi-donor project FVC/GLO/184/MUL in 11 countries including Bhutan to build resilience against threats such as ASF by promoting sustainable farming practices to improve food security, livelihoods, environment and income of rural population through the adoption and promotion of innovative approaches for the better value chain of Special Agricultural Products [reference4].
Actions taken by Nepal: In response to the ASF outbreaks in Myagdi District in Gandaki Province, authorities requested pig raisers to isolate any ASF suspected pigs and report without delay, and dispose dead pigs by burial [reference1], according to media. The Directorate of Livestock and Fisheries Development of Bagmati Province has sent a letter to the local level and requested them to carry out awareness programs; while authorities in Lalitpur District under the province started alerting farmers about the disease [reference2], according to media.
Actions taken by India: The Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying (DAHD) released the Disease Control Strategy Plan in June 2020 as guidance for State / UT Governments for ASF prevention, control and containment [reference1]. Individual ASF detected area implements control measures with reference to the guidance. India has released the statistics on the number of pigs lost due to ASF by state during 2022 -2023 [reference2]. In Nagaland State, Kohima District has declared the infected and the surveillance zones in Kidima Village; bans on the slaughter of pigs, import and export of pigs and piglets, and transportation of pigs and pork have been imposed [reference3]. Mizoram State declared various villages and localities in Champhai, Aizawl, Saitual, Lawngtlai, Khawzawl and Serchhip districts as infected areas and imposed the prohibition of pig export and import from/to infected areas, besides the sale or slaughter of both healthy and sick pigs within infected areas [reference4, reference5, reference6, reference7, reference8, reference9, reference10, reference11, reference12, referece13]. According to media, the Mizoram state government has so far compensated about 2 500 pig raisers for pig losses due to ASF and has requested additional compensation from the central government to additional families [reference14].
FAO's recommendation
ASF virus can be transmitted through pork and pork products (raw/frozen/dried/under-cooked) in which the virus can survive for a long time. Intensive border/customs control of passengers’ luggage, parcels at international post offices is recommended. The test results of border control in China showed the new reassortant ASF virus may be transported by travellers. Warning signs should be placed clearly at the border/customs entry including airports and seaports, stating the consequences of bringing pork and pork products from ASF-infected countries/regions, and instructing passengers to discard pork products in designated disposal places or to hand over to the customs personnel.
Countries of the region
- Animal disease containment in its broadest sense should be prioritized within the highest levels of governments.
- Preparedness (e.g. contingency planning, standard operating procedures, secured financial support) based on the principles of early warning, detection and notification, early reaction, and coordination. It needs to be reviewed periodically in relation to changing disease situation.
- Application of strict biosecurity measures specific to the different swine producing sectors including frequent cleaning and disinfection of farms, transport vehicles, and improved husbandry practices and production systems.
- Strengthening surveillance and monitoring of transport of live pigs as well as pork products.
- Good communication and coordination with swine producing commercial sector and swine famers are essential to strengthen cooperation in ASF prevention, detection, and control. Awareness and training of all stakeholders, from veterinarians to farmers, intermediaries and other value chain actors is needed.
- Communication to public is to be in place to avoid the rumours leading to food safety perceptions and consumption disruption.
- Prohibition of swill feeding where feasible. When it is unavoidable than swill feed should not contain the remains of pigs. Swill should be boiled and allowed to cool before feeding.
- Farm registries, animal identification and censuses are essential to enable to locate animals in the event of outbreaks and animal health interventions.
- Strengthening proper disposal of food waste (food services, airports, seaports), which may contain uncooked pork products.
- Extra vigilance is recommended regarding the proliferation of fake ASF vaccines.
- Sustainable outbreak control strategies must be in place. The strategies need to be developed in consultation with the private sector (pig production and allied industries, such as transport, feed operators) who should be actively involved in disease management options.
National Considerations, Inter-Regional Collaboration and Solidarity
- Strengthening intraregional networks on disease management and diagnostic protocols.
- Understanding pig and pork value chains within the country and with neighbouring countries is essential for improved risk management.
FAO's actions
- In the Philippines, BAI with the support of FAO and MAFRA, conducted the Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices (KAP) Survey on ASF in Nueva Ecija Province to assess and improve the National ASF communications Strategy [link].
- In Cotabato City in the Philippines, the ASF Preparedness Tabletop Exercise (APTTX) for the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region of Muslim Mindanao (BARMM) was conducted on 13-17 May 2024 With the support from FAO and the government of Australia [link].
- The FAO with the support from the USAID co-organized the annual meeting of the Provincial, Cities, and Municipalities League of Veterinarians on 21-23 May 2023 in Zamboanga City, the Philippines to discuss global, regional, and local initiatives as well as provide updates on ASF and other TADs [link].
- FAO regional technical consultation for African swine fever control in Asia and Pacific region held on 7-9 May in Seoul, the Republic of Korea.
- FAO with technical support from the Trust in Animals and Food Safety (TAFS) Forum, will organize the launch meeting for the ASF information exchange platform from 12-13 June 2024 in Bangkok, Thailand. [link]
- FAO Subregional Office for the Pacific Islands (SAP) has provided critical laboratory consumables, personal protective equipment (PPE) and high-quality farm equipment to the Cook Islands, Fiji, Samoa and Vanuatu to aid in ASF surveillance activities since January 2024. [link]
- In Indonesia, FAO and the Ministry of Agriculture launched the Community ASF Biosecurity Intervention (CABI) programme for small scale pig producers in Pontianak City and Landak Regency in West Kalimantan with support from MAFRA, Republic of Korea. [ link1, link2].
- FAO headquarters with support of FAO Emergency Center for Transboundary Animal Disease Control (ECTAD) Philippines organized a national hybrid workshop "Utilizing Geographic Information System (GIS) for Enhanced Surveillance and Control of ASF in the Philippines: An Introductory Review and Presentation of the Concept" on 30 April in Manila. The event was organized for participants from the Bureau of Animal Industry (BAI), particularly Animal Health and Welfare Division (AHWD), the ASF Prevention and Control Program, Animal Disease Diagnostic and Reference Laboratory (ADDRL), Philippine Animal Health Information System (PhilAHIS), and the National Veterinary Quarantine Services Division (NVQSD). In addition, participants from the National Meat Inspection Service (NMIS), the National Livestock Program (NLP), expert from Central Luzon State University also attended.
- FAO RAP organized the regional meeting on African swine fever in wild pigs from 24-25 January 2024. [link]
- FAO RAP released a poster and a leaflet with nine essential activities on biosecurity, encouraging stakeholders to adopt them daily. The cute piglet drawing will help raising awareness about ASF and promote biosecurity. [poster, leaflet]
2023
- The Global Consultation on ASF Control was organized from 12 to 14 December 2023 at FAO, Rome. [link]
- FAO RAP in collaboration with Philvet Health Services developed and launched a new course on ASF management in smallholder settings. [link]
- FAO SAP released the Risk assessment for the introduction of African swine fever into Vanuatu. [link], Kiribati [ link], Solomon Islands [link], Cook Islands [link], Federated States of Micronesia [link], Tuvalu [link], and the Pacific Islands countries [link].
- FAO ECTAD Indonesia and the Ministry of Agriculture organized an Advocacy meeting on Community ASF Biosecurity Intervention (CABI) programme in North Sulawesi on 13 September 2023 with the funding support from the Ministry of Agriculture and Food and Rural Affairs of the Republic of Korea.
- FAO ECTAD Cambodia, in collaboration with the General Directorate of Animal Health and Animal Production/Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF), organized ASF community forums in Battambong, Oddor Meanchey, Kampong Speu, Banteay Meanchey, and Siem Reap provinces.
- FAO ECTAD Cambodia, in collaboration with General Directorate of Animal Health and Animal Production/MAFF, organized ASF SOP outbreak response management training in Kampot Province on 19-20 October 2023 with 52 participants from Kep, Kampot, Koh Kong, Kampong Speu and Prey Veng provinces
- FAO in collaboration with the Philippines’ Ministry of Agriculture, MAFRA organized a three-day campaign on the ASF Threat to Domestic and Wild Pigs in Cagayan De Oro City, Northern Mindanao Region on 18-20 October 2023. [link]
- FAO SAP assisted the Solomon Islands Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock (MAL) in conducting ASF awareness training and simulation exercise from 23-27 October 2023. [link]
- FAO SAP organized a Simulation Exercise on ASF Outbreak Investigation with the Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries (MAF), Samoa from 5-7 December 2023. [link].
- FAO RAP organized the Regional Simulation Exercise on ASF outbreak investigation from 15 to 17 August 2023. [link]
- FAO ECTAD Indonesia in collaboration with MoA and the Ministry of Environment and Forestry organized ASF risk assessment workshop in North Sulawesi from 13 to 16 August 2023. [link]
- FAO Philippines supported BAI conveying the National ASF Prevention and Control Task Force in August 2023 through a project funded by the Republic of Korea.
- FAO and USDA had a meeting to share knowledge and experiences, explore research opportunities and develop joint strategies to strengthen the response against ASF. [link]
- FAO EMC-AH mission was conducted in Bhutan on 22-26 May to support response and discuss best approaches.
- FAO participated in ASEAN ASF Workshop held on 2 - 4 May 2023 in Manila, the Philippines. [link]
- FAO Lao handed over the guidelines for ASF prevention and control in smallholder pig farming to the DLF, the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry. [link]
- FAO released a global alert message on increased risk of ASF spread during holidays season in December 2022. [link]
- FAO ECTAD RAP organized a one-hour webinar on 15 November 2022 on practical guidelines for ASF prevention and control in smallholder settings. [link]
- FAO ECTAD RAP released a series of info-cards targeting farmers, animal health workers, traders, general public and travellers etc. to raise awareness on ASF. Links available at the Useful Links below.
- FAO and Department of Livestock and Fisheries (DLF) in Lao PDR conducted trainings to strengthen capacity to prevent and control ASF for livestock officers and veterinarians in Champasack, Saravan, Savannakhet, Khammouane, Bolikhamxay, Houaphanh, Xiengkhuang, Xayaboury provinces, and Vientiane Capital (2022), and in Phongsaly, Oudomxay, Bokeo, Sekong, Attapue, and Xaysomboun provinces (March to June 2023).
- FAO ECTAD in Indonesia and the Ministry of Agriculture prepared technical guidelines for basic services for zoonoses outbreaks and animal health events with a high socioeconomic impact (e.g. FMD, LSD, ASF) and held and advocacy meeting on the Minimum Service Standards (SPM) which will assist subnational governments in dealing with future zoonoses outbreaks and emergencies. The SPM will be piloted in Lampung Province.
- FAO released the new Global Animal Disease Information System - EMPRES-i+. [link]
- FAO and NAQIA conducted the ASF Stock inspectors field practical training in August 2022 in Port Moresby. [link]
- FAO participated in a workshop to design a comprehensive ASF management plan in response to the negative impacts of the disease on the livelihoods of farmers in the northeast of India, held on 8 July in Assam. [link]
- FAO presented OutCosT at the Global African Swine Fever Research Alliance (GARA) 2022 Scientific Meeting was held on 24-27 May 2022 in Punta Cana, Dominican Republic.
- FAO Webinars on the use of the OUTbreak COSting Tool (OutCosT) were held on 25, 27 and 29 April. [link]
- FAO ECTAD RAP collaborated with colleagues from City University of Hong Kong to introduce the newly produced FAO guidelines for ASF prevention and control smallholder pig farming in Asia. [link1, link2, link3, link4, link5]
- FAO ECTAD RAP piloted online trainings on the application of FAO ASF practical guidelines for smallholders in Papua New Guinea and Cambodia; course materials are being adapted for the Virtual Learning Center for wider use in the region.
- FAO and the Directorate of Animal Health (DGLAHS) Indonesia conducted a technical training on ASF response for veterinarians in Kalimantan, and ASF response training for extension workers in 13 districts in West Kalimantan Province.
- FAO ECTAD Cambodia and GDAHP organized ASF community forum from 22 November to 17 December 2021 in Tboung Khmum, Rattanakiri, Takeo, Svay Rieng and Kandal provinces.
- FAO and OIE co-organised the Standing Group of Experts for African Swine Fever (SGE-ASF) for Asia and the Pacific, held online on 15 December 2021.
- FAO RAP completed the 4-week ASF virtual training for the Pacific Island Countries launched on 12 October 2021 through the Virtual Learning Centre.
- FAO ECTAD Cambodia and GDAHP organized series of trainings at provincial level on investigation and emergency response in Kandal (22-23 September), Tboung Khum (29-30 September), and Ratanakiri (12-13 October). [link]
- FAO co-organised the Standing Group of Experts for African Swine Fever (SGE-ASF) for Asia and the Pacific, together with the OIE, held online on 7 September 2021.
- FAORAP organized a virtual workshop on development of ASF tabletop simulation exercises for Asia.
- FAO Regional Office for Latin America and the Caribbean (RLC) launched the ASF website [link]
- FAO co-organised the Standing Group of Experts for African Swine Fever (SGE-ASF) for Asia and the Pacific, together with the OIE, held online on 7 September 2021.
- FAO, IUCN and OIE issued a joint communique encouraging members to increase efforts to address ASF [link]. A joint article was published in a Newsletter of the IUCN SSC Wild, Peccary and Hippo Specialist Group.
- Third Regional GF-TADs Coordination Meeting on ASF on 25 August. [link]
- FAO organised a Virtual Regional Training on Value Chain Analysis for Animal Disease Risk Management, focus on ASF as case study on 17-31 August 2021. [link]
- FAO supported the Pig Value Chain Workshop organized by NAQIA, Papua New Guinea on 12-13 August 2021 in collaboration with PHAMA Plus, DFAT, and NFAT. [link]
- OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2021–2030 (includes projection of Meat) released.
- GF-TADs virtual meeting: Stop ASF: Public and private partnering for success (Jun 2021). [link]
- FAORAP organised the third regional training of trainers on ASF detection and emergency response engaging animal health officials from Lao PDR, the Philippines and Thailand on 15-26 March 2021 [reference].
- FAORAP organised a 2-day virtual regional consultation workshop on ASF preparedness and response for Asia & Pacific (9-10 March 2021) [meeting report].
- Alert letter on unlicensed ASF vaccine use in the region was sent out to Chief Veterinary Officers (CVOs) on 29 March 2021 by regional secretariat for FAO/OIE GF-TADs for Asia and the Pacific.
- FAO co-organised the Standing Group of Experts for African Swine Fever (SGE-ASF) for Asia and the Pacific, together with the OIE, held online on 5 February 2021 [reference].
- GF-TADs virtual meeting: Stop ASF: Public and private partnering for success - Live technical session on 21, 28 June [register, agenda, recording, networking]
- FAO ECTAD Myanmar conducted a sub-national level virtual interactive training on ASF detection and emergency response in Myanmar, together with the Livestock Breeding and Veterinary Department (LBVD), in collaboration with FAO ECTAD RAP. The course comprises seven modules with excercise, 85 participants from public and private veterinary sectors, academia, and associations.
- FAO ECTAD Cambodia held a series of training courses on ASF in Svay Rieng, Takeo and Kampong provinces [link].
- FAO ECTAD RAP organized a 2-day virtual training on ASF risk communication for Asia & Pacific (December 2020).
- FAO ECTAD Indonesia, in collaboration with DGLAHS, organized an online capacity building course on ASF prevention & control for eight high risk provinces. The course included: biosecurity, biosafety, market / value chain management, etc against ASF introduction; and online ASF ToT course is being planned.
- FAO ECTAD RAP launched an animation video for farmers on basic farm biosecurity “Be a Champion Farmer! – Biosecurity is key to stop African Swine Fever” available in different languages used in Asia & Pacific [reference].
- GF-TADs Webinar - African swine fever: An unprecedented global threat - A challenge to livelihoods, food security and biodiversity - Call for action, was successfully held in October 2020 [reference].
- FAO ECTAD Viet Nam and DAH held workshops on risk communication of animal diseases in October 2020 [reference]
- FAO ECTAD RAP published “Addressing African Swine Fever: Laboratory protocols and algorithms” in collaboration with the Australian Centre for Disease Preparedness (ACDP, formerly AAHL) [reference].
- Alert message on high risk for African swine fever emergence and spread to Pacific Islands sent out on 16 March 2020.
- The 4th Standing Group of Experts (SGE) on ASF for Asia meeting to discuss ‘Outbreak management’ was postponed due to the COVID-19 pandemic situation.
- FAO conducted an ASF risk assessment mission in Samoa to provide support for ASF preparedness to prevent the disease entering the country (February 2020) [reference].
- The Global Meeting to address the “ASF unprecedented global threat: a challenge to food security, wildlife management and conservation” in Rome, Italy, initially planned in April 2020, was substituted by series of webinars took place in October 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic situation [reference].
- FAO and OIE launched a new joint initiative for the Global Control of African swine fever - A GF-TADs initiative 2020-2025 [press release].
- Virtual regional Training of Trainers on ASF detection and emergency response was organized in June-July 2020 engaging animal health officials from Cambodia, Myanmar, Viet Nam and Regional FETPV.
- Online meeting with CVO Papua New Guinea (PNG) and FAO (HQs, RAP and FAO-PNG) and development partners was held in June 2020 to discuss situation and support to ASF response in PNG.
- Online course on ASF preparedness for Asia was successfully finished with 490 participants from 27 countries in Asia and Pacific Region with a dozen tutors (May-June 2020).
- Under the Global Framework for the Progressive Control of Transboundary Animal Diseases (GF-TADs) umbrella, OIE, Secretariat of the Pacific Community (SPC) and FAO organized a video call focusing on ASF by engaging several exerts on epidemiology, laboratory, biosecurity and prevention as well as socioeconomic aspects. Each participating country provided update on ASF preparedness in the individual countries (March 2020).
- The production of the Korean version of the manual African swine fever in wild boar: ecology and biosecurity manual in collaboration with the Korean National Institute is completed.
- Dr B. Tijani, Assistant Director General, FAO participated in the High-Level International Conference - The future of global pork production under the threat of African swine fever, organized by the European Commission in Berlin (January 2020) [reference].
- The first cohort of trainees have completed the FAO tutored e-learning course on ASF (December 2019) and plans to offer this in 2020 to multiple regions developed.
- FAO EMC-AH mission to Timor-Leste to assess ASF situation and response strategy (December 2019).
- The 2019 Annual Coordination meeting of the Project Steering Committee for the FAO-China South-South Cooperation project was held in Kunming City, China, including discussion on ‘ASF prevention and control’ (December 2019).
- ECTAD/FAO co-organized the 3rd Meeting of the GF-TADs standing group of experts on African swine fever (SGE-ASF) for Asia and4th regional workshop on swine disease control in Asia (November 2019) [reference].
- The Regional Laboratory Coordinator undertook a mission to the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea to provide laboratory equipment, reagents and training on ASF diagnostic methodologies (November 2019)
- FAO EMC-AH mission to Papua New Guinea to assess ASF preparedness and response strategy (October 2019) [reference]
- ECTAD Viet Nam uploaded a video clip to YouTube on technical advice (September 2019) [reference].
- Inception Workshop for the Regional Technical Cooperation Programme on African Swine Fever Emergency Preparedness and Response in East and Southeast Asia was held in Bangkok (August 2019) [reference].
- ECTAD/FAO Regional office for Asia and the Pacific attended the 2nd standing group of experts on African swine fever (SGE-ASF) meeting for Asia held in Tokyo, Japan (July 2019) [reference].
- FAO EMC-AH mission to Lao PDR to assess the ASF situation and preparedness and response strategy (June 2019)
- FAO and World Bank - joint presentation on ASF at the G7 CVO meeting (May 2019).
- OIE and FAO - joint presentation on ASF at the 87th OIE General Session, OIE, Paris (May 2019).
- FAO deployed an EMC-AH mission to Cambodia to assess the ASF situation and response strategy (May 2019).
- In Cambodia, the private sector organized an awareness-training program entitled "Breeding pigs under ASF threat", at which FAO ECTAD Cambodia presented the regional ASF situation (May 2019).
- FAO project on ASF Emergency Preparedness and Response in East and Southeast Asia” started (April 2019).
- Beijing International Symposium on ASF was jointly organized by MARA, FAO and OIE in Beijing (April 2019).
- The GF-TADS Standing Group of Experts on ASF for Asia was held in Beijing, hosted by MARA (April 2019).
- FAO in collaboration with the General Directorate of Animal Health and Production (GDAHP), Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Cambodia, organized a National Consultative Workshop on the Development of ASF Preparedness and Response Plan (ASF-CPRP) in Cambodia (April 2019).
- FAO Technical Cooperation Programme project “African Swine Fever Emergency Preparedness and Response in East and Southeast Asia” (TCP/RAS/3704) started on 23 April 2019.
- FAO organized a workshop on ASF Preparedness & Response Plan and portable PCR in Cambodia (April 2019).
- FAO deployed an EMC-AH mission to Viet Nam from in March 2019 to assess ASF situation and response strategy.
- FAO Myanmar is advising Veterinary Service on appropriate active surveillance and on laboratory diagnosis. FAO completed an EMC-AH mission to Myanmar to assess ASF preparedness, including laboratory capacity (March 2019).
- FAO deployed an EMC-AH Emergency Response Mission to Mongolia to assess ASF situation (February 2019).
- FAO deployed an EMC-AH mission to Democratic People’s Republic of Korea to assess ASF preparedness [reference].
- FAO and MARA, China jointly organized the Multilateral Cross-Border Meeting in Greater Mekong Subregion to Strengthen Collaboration of Transboundary Animal Disease Control in Beijing, China, in November 2018 which included “African Swine Fever Emergency Preparedness training” for Lao PDR, Myanmar, Viet Nam and China [reference].
- FAO-China, Chief/AGAH and CVO met with MARA Vice Minister and senior staff of Veterinary Bureau and China Animal Disease Control Center in November. A call for solidarity to address the expanding global threat of ASF to the G20 was suggested by Chinese officials [reference].
- In October 2018 and again in February 2019, FAO Chief Veterinary Officer sent a message to CVOs in the region and throughout the world encouraging preparedness and vigilance [reference].
- FAO and MARA jointly held a Technical Consultation on ‘Application of Technology to Strengthen ASF Control through Rapid Detection and Response’ in October 2018 in Beijing, China [reference].
- FAO organized an Emergency Regional Consultation on African Swine Fever in Bangkok, September 2018 [reference].
- FAO released a publication on ASF spread in Asia (March 2018) and urged regional collaboration and preparedness [reference].
- FAO and World Bank delivered a joint presentation at the G7 CVO meeting (May 2019).
- OIE and FAO delivered a joint presentation on ASF at the 87th OIE General Session, OIE, Paris (May 2019).
- FAO project on ASF Emergency Preparedness and Response in East and Southeast Asia” started from April 2019.
- FAO deployed an EMC-AH mission to Cambodia from 27 May to assess the ASF situation and response strategy.
- In Cambodia, the private sector organized an awareness-training program entitled "Breeding pigs under ASF threat" on 9 May, at which FAO ECTAD Cambodia presented the regional ASF situation.
- Beijing International Symposium on ASF was jointly organized by MARA, FAO and OIE on 8-9 April in Beijing [reference].
- The 1st meeting of GF-TADS Standing Group of Experts (SGE) on ASF for Asia was held in Beijing, hosted by MARA.
- FAO in collaboration with the General Directorate of Animal Health and Production (GDAHP), Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Cambodia, organized a National Consultative Workshop on the Development of ASF Preparedness and Response Plan (ASF-CPRP) in Cambodia on 8-9 April 2019.
- FAO organized a training workshop on operationalizing the ASF Preparedness and Response Plan and how to use portable PCR for ASF in Cambodia on 10-11 April 2019.
- FAO participated at International Symposium on ASF and Standing Group of Exerts (SGE)–ASF meeting (Beijing, April 2019).
- FAO deployed an EMC-AH mission to Viet Nam from 11 to 16 March to assess ASF situation and response strategy.
- FAO Myanmar is advising Veterinary Service on appropriate active surveillance and on laboratory diagnosis. FAO completed an EMC-AH mission to Myanmar to assess ASF preparedness, including laboratory capacity by expert from an OIE/FAO reference laboratory (March 2019).
- FAO deployed an EMC-AH Emergency Response Mission to Mongolia to assess ASF situation (February 2019).
- FAO deployed an EMC-AH mission to Democratic People’s Republic of Korea to assess ASF preparedness [reference].
- FAO and MARA jointly organized the Multilateral Cross-Border Meeting in Greater Mekong Subregion to Strengthen Collaboration of Transboundary Animal Disease Control in Beijing, China in November 2018 which included “African Swine Fever Emergency Preparedness training” for Lao PDR, Myanmar, Viet Nam and China [reference].
- On 16 November, FAO-China, Chief/AGAH and CVO met with MARA Vice Minister and senior staff of Veterinary Bureau and China Animal Disease Control Center. A call for solidarity to address the expanding global threat of ASF to the G20 was suggested by Chinese officials [reference].
- In October 2018 and again in February 2019, FAO Chief Veterinary Officer sent a message to CVOs in the region and throughout the world encouraging preparedness and vigilance [reference].
- FAO and MARA jointly held a Technical Consultation on ‘Application of Technology to Strengthen ASF Control through Rapid Detection and Response’ in October 2018 in Beijing, China, with participants from Veterinary Bureau/MARA, China Animal Disease Control Center (CADC), China Animal Health and Epidemiology Center (CAHEC) [reference].
- FAO organized an “Emergency Regional Consultation on African swine fever: Risk reduction and preparedness” in Bangkok, 5-7 September, 2018, with the overall objective to:
- review the ASF situation and risks to the rest of China and the region;
- develop a regional approach for ASF risk reduction, preparedness and response;
- identify priority actions required for countries in a short, medium and longer term; and
- facilitate the development of a stakeholder network for ASF.
- FAO's Emergency Centre for Transboundary Animal Diseases (ECTAD) is communicating closely with authorities in China’s Veterinary Bureau to monitor the situation and to respond effectively to the outbreak inside the country.
- FAO ECTAD is likewise in contact with authorities in neighbouring countries, to raise the importance of preparedness to respond to the threat of further spread.
- The FAO Manual on ASF Detection and Diagnosis was recently translated into Chinese in collaboration with Veterinary authorities and ASF national reference laboratory in China, and distributed in the regions.
- FAO undertook a mission in Mongolia (16-23 April) to explore the feasibility of wild boar surveillance along the border with Russia. Following this mission an awareness pamphlet was produced and delivered to herders/hunters and some rangers in the provinces that border with Russian Federation.
- FAO warned of the risk of African swine fever threatens to spread from China to other Asian countries, and urges regional collaboration including stronger monitoring and preparedness measures [reference].
- FAO released a rapid risk assessment of ASF introduction in March 2018: “African Swine Fever Threatens People’s Republic of China” [reference].
- FAO and authorities in China jointly developed a Field Epidemiology Training Programme for Veterinarians (FETPV) in China to strengthen epidemiological investigation, disease situation tracking, risk assessment and emergency preparedness. ‘Graduates’ of the programme have been mobilized for epidemiological investigations, sampling and response activities.
- An event for ASF policy in East and Southeast Asia was organized Under FAO-led international H2020 research consortium for the coordination of animal health research between China and EU (LinkTADs).
- FAO provided TCP/CPR/3501 “Developing Prevention and Control Strategies for African Swine Fever (ASF) in China” (Jul 2014 - Dec 2015; USD 380,000) to improve the capacity in ASF prevention, ASF preparedness, risk assessment, diagnostic techniques, epidemiology, raising awareness, strengthening national ASF laboratory coordination mechanism, and set up an ASF contingency plan.
Important links
- FAO RAP ECTAD’s ASF resource portal: ASF awareness materials, ASF online courses, ASF publications
- African swine fever prevention, detection and control in resource-limited settings [link]
- FAO Virtual Learning Center - African Swine Fever Introductory Course [link]
- Good practices for biosecurity in the pig sector [link]
- Carcass management guidelines [link]
- African swine fever detection and diagnosis. A manual for veterinarians [English, Русский, 中文, Español]
- Addressing African Swine Fever: Laboratory protocols and algorithms” in collab. with ACDP (formerly AAHL) [link]
- Guidelines for African swine fever (ASF) prevention and control in smallholder pig farming in Asia series:
- Farm biosecurity, slaughtering, and restocking [English, Tiếng Việt, Khmer]
- Clean chain approach for African swine fever in smallholder settings [English, Tiếng Việt, Khmer]
- Culling and disposal of pigs in an African swine fever outbreak [English, Tiếng Việt, Khmer]
- Monitoring and surveillance of ASF [English, Tiếng Việt, Khmer]
- African swine fever in wild boar - Ecology and biosecurity. 2nd edition [link]
- African swine fever field manual [link]
- Global Animal Disease Information System - EMPRES-i+ [link]
- FAO FOOD OUTLOOK June 2023 [link]
- OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2023-2032 [link]
- Standing Group of Experts on African swine fever in Europe [link]
- Risk communication in animal disease outbreaks and emergencies [link]
- Joint ASF communication campaign [link]
- African swine fever: WOAH warns Veterinary Authorities and pig industry of risk from use of sub-standard vaccines [link]
- OIE ASF Reference Laboratory Network’s overview of African swine fever diagnostic tests for field application [link]
- OIE guidelines on compartmentalisation for ASF [link]
- Global ASF Control: a GF-TADs Initiative 2020-2025 [English, Française, 中文, Русский, Español]
- VIDEO: FAO RAP. Biosecurity to fight ASF [link]
- VIDEO: FAORAP. Be a Champion Farmer! [English, 中文, Khmer, Lao, Vietnamese, Indonesia (Bahasa, Bali, Batak, Kupang), Nepali, Burmese, Malaysia (Malay, Iban Sarawak), Philippines (Tagalog, Cebuano, Ilocano), Portuguese]
- FAO ECTAD RAP info-cards – Biosecurity for farmers: How to avoid, Biosecurity, Protect your livelihoods, Protect your farm, Swill feeding spreads, What is swill feeding, Stop swill feeding, Isolate new pigs, Report unusual event; For veterinarians: Biosecurity is key, Differentiate ASF from other diseases; For border checkpoints: Border control, Stop at animal checkpoints; Do your part: Clean and disinfect vehicles, Hunt responsively, Travel responsively, Sell only certified pork, Buy safe pork, When buying online…
- POSTER: FAO ECTAD, on biosecurity - Don’t let your pigs die from African Swine Fever [English1, English2, French1, French2, Chinese1, Chinese2, Bahasa Indonesia1, Bahasa Indonesia2, Burmese, Khmer, Korean1, Korean2, Lao, Nepali1, Nepali2, Portuguese1, Portuguese2, Thai1, Thai2,Vietnamese1, Vietnamese2, Arabic1, Arabic2, Hindi1, Hindi2, Tagalog, Ilocano, Cebuano]
- POSTER: FAO/OIE, for vets [English, Française, 中文, Русский, Español], for farmers [English, Française, 中文, Русский, Español]
FAO publications
- Global ASF Control: a GF-TADs Initiative 2020-2025 - Annual Report 2021 [link]
- Carcass management guidelines - Effective disposal of animal carcasses and contaminated materials on small to medium-sized farms (2020)
- Global control of African swine fever: A GF-TADs initiative (2020)
Also available in: Chinese - Spanish - French - Russian - Biosecurity practices and border control to stop the spread of
African swine fever (2020) - African Swine Fever in wild boar: Ecology and biosecurity (2019)
Also available in : Korean - Lithuanian - Spanish - Prudent and efficient use of antimicrobials in pigs and poultry (2019)
Also available in : Russian - African Swine Fever threatens People's Republic of China - A rapid risk assessment of ASF introduction (2019)
- Carcass management for small- and medium-scale livestock farms. Practical considerations (2018)
Also available in: French - Romanian - Russian - Serbian - Spanish - Ukrainian - African swine fever, a transboundary threat that requires regional and international cooperation (2018)
- African swine fever (ASF) detection and diagnosis. A manual for veterinarians (2017)
Also available in: Albanian - Chinese - Lithuaninan - Macedonian - Serbian - Spanish - Russian - The Global Platform for African swine fever and other important diseases of swine (2014)
- African swine fever training activities in Eastern Europe and Central Asia (2014)
- Regional strategy for the control of ASF in Africa (2017)
- The Global Platform for African swine fever and other important diseases of swine (2014)
- African swine fever in the Russian Federation: risk factors for Europe and beyond (May 2013)
- African Swine Fever (ASF) recent developments - timely updates Worrisome dynamics: Steady spread towards unaffected areas could have disastrous impact (2012)
- Good practices for biosecurity in the pig sector – Issues and options in developing and transition countries (2010)
Also available in: Chinese - French - FAO takes a close look at the threat of African swine fever introduction into Eastern Europe (2010)
- Preparation of African swine fever contingency plans (2009)
Also available in: Armenian - Georgian - French - Russian - Spanish - African swine fever spread in the Russian Federation and the risk for the region (2009)
- African swine fever in the Caucasus (2008)
- Manual on the preparation of African swine fever contingency plans (2001)
Scientific publications
- Descriptive and multivariate analysis of the pig sector in Georgia and its implications for disease transmission
PLoS ONE 13(8): e0202800 - Wild boar mapping using population-density statistics: from polygons to high resolution raster maps
PloS ONE 13(5): e0193295 - The African swine fever epidemic in West Africa, 1996 – 2002
Transbound Emerg Dis. 2018;65:64–76 - Modeling the live-pig trade network in Georgia: Implications for disease prevention and control
PLoS ONE 12(6): e0178904
Videos/Audios
- VIDEO: GF-TADs. African swine fever (ASF) kills pigs [full video, short video]
- Biosecurity is key to stop African Swine Fever - Be a Champion Farmer! (2020)
- Raising awareness about African swine fever in Ukraine (2016)
- African Swine Fever spreads to the Philippines
FAO Target Zero Hunger podcast - Response to rumours on African Swine Fever (ASF) treatment in Viet Nam
Interview to Pawin Padungtod, FAO ECTAD Senior Technical Coordinator - EFSA
- NAQIA, Papua New Guinea [link1, link2]
- MDF, Timor-Leste
- BAI/DA, the Philippines
ASF reported administrative areas since August 2018
China: Anhui, Heilongjiang, Henan, Jilin, Liaoning, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Shanxi, Yunnan, Hunan, Guizhou, Hubei, Jiangxi, Fujian, Sichuan, Shaanxi, Qinghai, Guangdong, Gansu, Shandong, Hainan and Hebei provinces,
Tianjin, Chongqing, Shanghai and Beijing municipalities, Inner Mongolia, Ningxia Hui, Guangxi Zhuang, Xinjiang Uygur, and Tibet (Xizang) autonomous regions and Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (SAR).
Mongolia:
Bulgan, Darkhan-Uul, Dundgovi, Orkhon, Selenge, Töv provinces and Ulaanbaatar
Viet Nam: All provinces and municipalities.
Cambodia: Ratanakiri,
Tboung Khmum, Svay Rieng, Takeo and Kandal provinces.
Democratic People’s Republic of Korea: Chagang-Do.
Lao People’s Democratic Republic:
All provinces and municipality.
Myanmar: Shan, Kachin, Kayah states and Sagaing Region.
The Philippines: Abra, Agusan del Norte, Agusan del Sur,
Aklan, Albay, Antique, Apayao, Aurora, Bataan, Batangas, Benguet, Bohol, Bulacan, Cagayan, Camarines Norte, Camarines Sur, Camiguin, Capiz, Catanduanes, Cavite, Cebu, Davao de Oro, Davao del Norte, Davao del Sur, Davao Occidental, Davao Oriental,
Dinagat Islands, Eastern Samar, Guimaras, Ifugao, Ilocos Norte, Ilocos Sur, Iloilo, Isabela, Kalinga, La Union, Laguna, Lanao del Norte, Leyte, Marinduque, Masbate, Maguindanao del Sur, Mindoro Oriental, Misamis Occidental, Misamis Oriental, Mountain,
Negros Oriental, Negros Occidental, North Cotabato, Northern Samar, Nueva Ecija, Nueva Vizcaya, Occidental Mindoro, Oriental Mindoro, Palawan, Pampanga, Pangasinan, Quezon, Quirino, Rizal, Romblon, Samar,Sarangani, Sorsogon, Southern Leyte, Sultan
Kudarat, Surigao del Norte, Surigao del Sur, Tarlac, Zambales, Zamboanga del Sur provinces and Metro Manila (Caloocan, Malabon and Quezon cities).
Republic of Korea: Gyeonggi-do, Gangwon-do, Incheon
City, Chungcheongbuk-do, and Gyeongsangbuk-do.
Timor-Leste: All districts.
Indonesia: North Sumatra, Riau, Riau Islands, West Sumatra, South
Sumatra, Lampung, Jambi, Bangka Belitung; West Java, Central Java, Yogyakarta, Banten, East Java; Bali; East Nusa Tenggara; West Kalimantan, Central Kalimantan, East Kalimantan and North Kalimantan; South Sulawesi, Central Sulawesi, West Sulawesi
and Southeast Sulawesi provinces.
Papua New Guinea: Southern Highlands, Enga, Hela, Western Highlands, Jiwaka, and Simbu provinces.
India: Assam,
Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Bihar, Kerala, Punjab, Haryana, Tripura, Andhra Pradesh, Goa, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand states, and Delhi National
Capital Territory.
Disputed territory: Arunachal Pradesh.
Malaysia: Sabah, Sarawak; Perak, Pahang, Malacca, Johor, Negeri Sembilan, Trengganu, Kelantan and Penang
(Pulau Pinang) states.
Bhutan: Chhukha, Samdrup Jongkhar, Sarpang, Trashigang, and Pemagatshel and Bumthang districts.
Thailand:
Buri Ram, Chachoengsao, Chaiyaphum, Chiang Mai, Chiang Rai, Chumphon, Kalasin, Kamphaeng Phet, Khon Kaen, Krabi, Mae Hong Son, Maha Sarakham, Mukdahan, Nakhon Phanom, Nakhon Phanom, Nakhon Sawan, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Nakhon Ratchasima, Nan, Nong Bua
Lam Phu, Nong Khai, Phangnga, Phatthalung, Phetchaburi, Phichit, Prachuap Khiri Khan, Ranong, Ratchaburi, Roi Et, Si Sa Ket, Songkhla, Suphan Buri, Trang, Ubon Ratchathani, Udon Thani provinces and Bangkok.
Nepal:
Bhaktapur, Kathmandu, Lalitpur, Kavrepalanchok, Sunsari, Jajarkot, Jhapa, Morang , Chitwan, Bardiva, Dang, Kaski, Surkhet, Sunsari, Kailali, Syangia, Bara, Jajarkot, Kanchanpur, Dadeldhura, Doit, Lamjung and Tanahu districts.
Singapore
Bangladesh: Chittagong Division.
New articles
- High mortality in free-ranging wild boars associated with African swine fever virus in India. [link]
- From pigs to wild boars, the rise of African swine fever in India. [link]
- Transcriptome profiles of organ tissues from pigs experimentally infected with African swine fever virus in early phase of infection. [link]
- The evolutionary and genetic patterns of African swine fever virus. [link]
- In vitro phenotypic characterisation of two genotype I African swine fever viruses with genomic deletion isolated from Sardinian wild boars. [link]
- Automated Detection and Counting of Wild Boar in Camera Trap Images. [link]
Disclaimer
Information provided herein is current as of the date of issue. Information added since the last ASF situation update in Asia & Pacific appears in orange. For cases with unknown onset date, reporting date was used instead. FAO compiles information drawn from multiple national (Ministries of Agriculture or Livestock and international sources (World Organisation for Animal Health [WOAH]), as well as peer-reviewed scientific articles. FAO makes every effort to ensure, but does not guarantee, accuracy, completeness, or authenticity of the information. The boundaries and names shown and the designations used on these map(s) do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of FAO concerning the legal status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers and boundaries. Dashed lines on maps represent approximate border lines for which there may not yet be full agreement.
Contact
If interested in a previous issue please send an email to EMPRES-Animal Health specifying the intended use of the document.
