Carbon neutral commodities
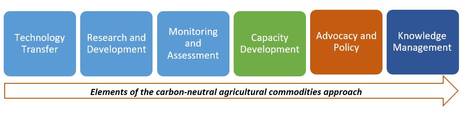
A carbon neutral agricultural commodities approach (CNAC) identifies options that can make the agricultural sectors an integral part of the global carbon-neutral future. It is an innovative approach for climate change mitigation and adaptation.
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Special Report on Climate Change and Land, agri-food systems currently contribute to more than 30% of global greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for agricultural production, land-use changes and energy consumption derived from processing.
At the same time, agriculture has unexplored potential to substantially reduce its emissions through measures that are mostly adaptation measures. The CNAC approach focuses on mitigating climate change throughout food and agriculture value chains.
The Carbon neutral agricultural commodities approach also aims to achieve other strategic objectives, such as biodiversity conservation, poverty reduction, food security and adaptation to climate change.
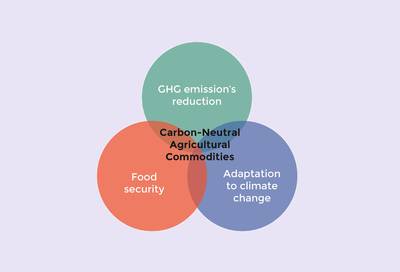
- Potential synergies derived from carbon neutral agricultural commodities
More
Applying the approach can therefore simultaneously contribute to sustainable development and help countries in fulfilling their climate change commitments.
Examples of low carbon agricultural commodity practices leading to carbon neutrality include:
- Using varieties adapted to climate change/variability;
- Optimizing/reducing the application of fertilizers and pesticides;
- Enhancing carbon sequestration by increasing soil organic carbon and through agroforestry systems;
- Using and developing new cultivars – drought and disease resistant; and
- Using renewable energy and improving energy efficiency throughout food chains.
FAO supports countries in implementing CNAC measures by:
Engaging with both public and private sector actors
Developing carbon-neutral pilot projects, to be scaled-up nationally and regionally
Making policy recommendations and developing national carbon-neutral agriculture
Developing national capacity on greenhouse gas accounting and MRV strategies
Developing a supportive environment for complementary standards and certification schemes on carbon-neutral agriculture
Implementing suitable digital technologies and other innovative practices
Supporting South–South knowledge and technology transfers between countries demonstrating carbon-neutral agricultural best practices