
IDENTITY
Biological features
Porphyra spp. appears on rocky shorelines throughout the world, including a few species in the tropics or at the poles. The greatest diversity is found in cold-temperate and boreal regions. Most species appear as winter or summer annuals. Porphyra can bear desiccation, so can live in the highest, driest reaches of the intertidal zone. Porphyra thalli appear in nature as free-living organisms, and their microscopic filaments bore into calcium carbonate substrates such as oyster shells. Porphyra blades may be from circular to linear in outline, and from a few centimetres to over a metre in length. Their colour is also variable, from rose-pink in species that live entirely submerged, to variously mottled reds, yellows, browns and greens in intertidal species. The life history of Porphyra is complex. Its microscopic stage is diploid and called the conchocelis, which consists of filamentous branches. Under specific conditions the filaments form swollen branches called conchosporangia that extrude their contents as individual cells without walls - conchospores. Meiosis takes place in each conchospore, which will develop into Porphyra thalli. In some species, monospores produced at thallus margins reproduce the blades asexually. Spermatia and carpogonia are formed in packets at the blade margins. Spermatia attach and effect fertilization. The zygote then divides to form a packet of diploid cells, carposporangium. Diploid carpospores are released from the carposporangium and form diploid conchocelis filaments again for over-summering.
Images gallery
 |
 |
Porphyra thallus and its holdfast (copy from MBARA in internet) |
Conchocelis filaments breeding facilities |
 |
 |
Manually harvesting |
Harvesting with special machine |
 |
 |
Porphyra processing |
Sushi in different cuisine |
PROFILE
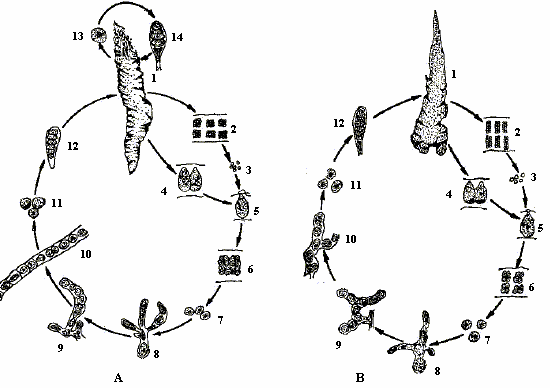
The conchocelis phase is diploid. Under specific conditions of light intensity and quality, day-length and temperature stimulate the production of gametes. These filaments form swollen branches ("conchosporangia") in which the cells develop the plastid features of blade-phase cells (stellate plastids with conspicuous pyrenoid). These branches protrude from the substrate and eventually release their contents as individual cells ("conchospores").
Male gametes (see diagram, 3: "spermatia") are produced in packets (2) at the blade margins and are released by dissolution of the margin. Female gametes (4: "carpogonia") are formed some way back from the margin. A receptive surface ("trichogyne") protrudes from each carpogonium and through the surrounding matrix, to which spermatia attach and effect fertilization (5). The zygote then divides to form a packet of diploid cells (6: the "carposporangium"). Diploid "carpospores" (7) are released from the carposporangium by dissolution of the blade margin. Germination of the carpospores, to form diploid conchocelis filaments (8), is not dependent on the presence of solid calcium carbonate; however, apparently, in natural conditions only those carpospores that manage to germinate on, and subsequently penetrate, this substrate (normally mollusc shells) avoid getting eaten by snails and other small marine grazers.
Under certain conditions, conchocelis filaments (9-10) develop and form conchospores (11). In autumn, these conchospores are released from the developed sporangia in swollen conchocelis filaments into the water and settle (12) on the substratum and begin their new life cycle (1).
In addition to this process, P. yezoensis (see diagram A above) also reproduces asexually, by producing monospores at the margins of the thalli. This does not occur in P. haitanensis (see diagram B above) .
The optimum conditions, such as temperature, salinity, and light intensity for the growth of Porphyra thalli vary. Generally, young thalli can bear higher temperature than their adults; lower temperatures will influence the normal growth of P. yezoensis and P. haitanensis (less than 3 °C and 8 °C respectively). High light intensity (5000-8000 lux) is good for the growth of both species. Porphyra thalli are tolerant to desiccation; for example, P. haitanensis can survive for one week even though losing 70 percent of its moisture. Porphyra is an autophyte; nutrients such as nitrate-nitrogen or ammonium-nitrogen are essential. Experiments indicate that 100-200 mg nitrogen/m3 is needed for normal growth; growth will be inhibited if the nitrogen level is lower than 50 mg nitrogen/m3.
Historical background
Cultivation of Porphyra began in the 17th century, in Japan, Korea and China, and has since become one of the most important industries using shallow water areas in all of these countries. Originally, laver farming had to depend on natural seed (conchospores) due to poor knowledge about its life cycle and where its seeds came from. However, in 1949, Kathleen Drew Baker discovered that the alga Conchocelis rosea was actually a stage in the life history of Porphyra. This was a great discovery for the farming industry, which solved the bottleneck that prevented the artificial production of seeds. Since then, Chinese and Japanese experts have developed the techniques of breeding conchocelis and collecting conchospores. Now, no laver farm collects seeds from the wild any more. Laver farming has become a prosperous sector of aquaculture in China, RO Korea, and Japan. Besides these traditional producers, laver farming activities are gradually expanding to other continents, including Africa, North America and Europe.
Main producer countries
The following map shows the distribution of Porphrya tenera, which is similar to that of P. yezoensis.
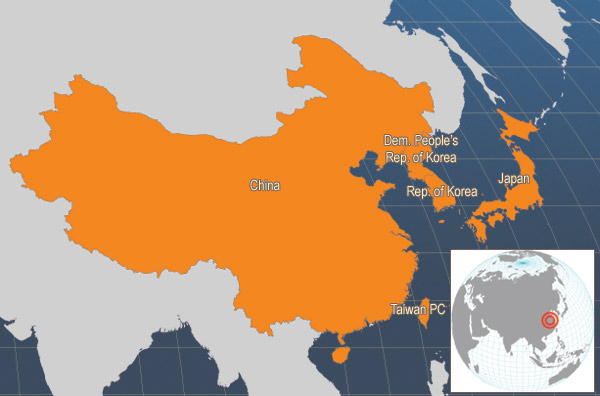

Main producer countries of Porphrya tenera (FAO Fishery statistics, 2006)
Habitat and biology
In China, Porphyra haitanensis is found in southern areas, whereas P. yezoensis is found in the north. The life stage that is commonly called nori or laver, comprises the thalli of the species (see n.1 in figure shown below), which emerge in autumn or earlier winter along rocky coasts. Its seeds are called conchospores and are released from the filamentous conchocelis stage (see n. 8 in same figure), which are found settled on mollusc shells in the summer and autumn. Before 1949, the filamentous phase was thought to be a separate species, Conchocelis rosea.

Life cycle diagram of Porphyra spp. - A = Porphyra yezoensis; B = Porphyra haitanensis. 1 thallus; 2 spermagonium; 3 sperm; 4 carpogone; 5 fertilized egg; 6 carposporangium; 7 carpospore; 8 filamental conchocelis; 9 sporangium branch of conchocelis; 10 releasing conchospores; 11 conchospore; 12 young thallus; 13 monospore and young thallus |
The conchocelis phase is diploid. Under specific conditions of light intensity and quality, day-length and temperature stimulate the production of gametes. These filaments form swollen branches ("conchosporangia") in which the cells develop the plastid features of blade-phase cells (stellate plastids with conspicuous pyrenoid). These branches protrude from the substrate and eventually release their contents as individual cells ("conchospores").
Male gametes (see diagram, 3: "spermatia") are produced in packets (2) at the blade margins and are released by dissolution of the margin. Female gametes (4: "carpogonia") are formed some way back from the margin. A receptive surface ("trichogyne") protrudes from each carpogonium and through the surrounding matrix, to which spermatia attach and effect fertilization (5). The zygote then divides to form a packet of diploid cells (6: the "carposporangium"). Diploid "carpospores" (7) are released from the carposporangium by dissolution of the blade margin. Germination of the carpospores, to form diploid conchocelis filaments (8), is not dependent on the presence of solid calcium carbonate; however, apparently, in natural conditions only those carpospores that manage to germinate on, and subsequently penetrate, this substrate (normally mollusc shells) avoid getting eaten by snails and other small marine grazers.
Under certain conditions, conchocelis filaments (9-10) develop and form conchospores (11). In autumn, these conchospores are released from the developed sporangia in swollen conchocelis filaments into the water and settle (12) on the substratum and begin their new life cycle (1).
In addition to this process, P. yezoensis (see diagram A above) also reproduces asexually, by producing monospores at the margins of the thalli. This does not occur in P. haitanensis (see diagram B above) .
The optimum conditions, such as temperature, salinity, and light intensity for the growth of Porphyra thalli vary. Generally, young thalli can bear higher temperature than their adults; lower temperatures will influence the normal growth of P. yezoensis and P. haitanensis (less than 3 °C and 8 °C respectively). High light intensity (5000-8000 lux) is good for the growth of both species. Porphyra thalli are tolerant to desiccation; for example, P. haitanensis can survive for one week even though losing 70 percent of its moisture. Porphyra is an autophyte; nutrients such as nitrate-nitrogen or ammonium-nitrogen are essential. Experiments indicate that 100-200 mg nitrogen/m3 is needed for normal growth; growth will be inhibited if the nitrogen level is lower than 50 mg nitrogen/m3.
PRODUCTION
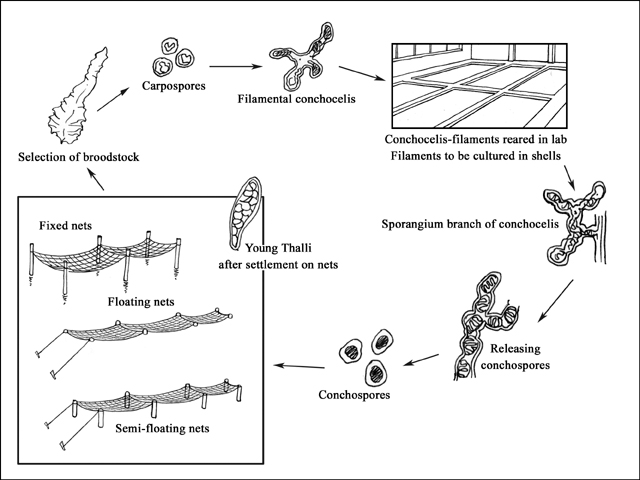
Production cycle

Production cycle of Porphyra spp.
Production systems
Due to its complex life cycle, the farming system for Porphyra can be divided into 5 distinct phases: conchocelis culture; collection of conchospores; ongrowing in open sea; harvesting; and processing.
Rearing conchocelis
As described earlier in this fact sheet, the farming of nori occurs in two stages. The first occurs indoors, from May to October, where the conchocelis stage is cultivated and conchospores produced. The second stage occurs from October until April or May; in this phase farmers focus on the cultivation of the thalli in the field.
In early and mid-May, Asiatic hard clam (Meretrix meretrix) are seeded by desiccating the conchocelis to release the conchospores; a suspension of them is then sprayed onto the substrate, or the substrate is submerged in the suspension. Cultivation occurs in large elongated shallow tanks filled with 20-30 cm of seawater that has been subjected to sedimentation and to which nitrogenous and phosphate nutrients have been added. At this stage, the temperature is not controlled and is allowed to fluctuate with ambient air temperature. However, optimal growth occurs between 20-25 °C. The carpospores develop into the conchocelis phase.
In mid-May to early June, the water temperature is raised to 22-23 °C, to encourage vegetative growth of the conchocelis phase. In July, the light intensity is reduced to encourage the formation of conchosporangia, which will eventually release the conchospores. From early July to late August, the water temperature is gradually raised to reach 27-28 °C by mid-August. After this, the water temperature is gradually decreased again.
By late August to late September, the water temperature has been lowered to 23 °C; during this period of the conchosporangia form. The light intensity is held at the same level to encourage the formation of the conchospores in the conchosporangia but the day length is reduced to 8-10 hours. Conchospores are present by late September but mass discharge occurs in early and mid-October.
Once the conchospores are released, they are seeded onto special cultivation nets which are placed in the tanks. When 50 000 spores are being released per day, the light intensity is increased slightly to encourage thallus germination. The water in the tanks is also agitated to distribute the spores evenly and ensure their contact with the cultivation nets. This procedure of collecting conchospores is called "collecting seeds". About 50 percent of laver farms rear the seeds by themselves, while the rest buy culture nets from seed suppliers.
There are three main farming methods: (a) on floating, (b) semi-floating; and (c) fixed nets. A fourth technique is known as "freezing nets" (see below).
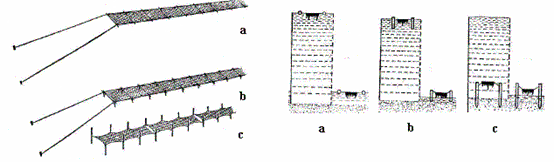
Three methods farming Porphyra spp.
Floating system
This method has been used in Japan and has recently been widely adopted by Chinese farmers. The nets are attached to buoys floating on the surface of the sea, so the nori thalli would be constantly soaked in water. With this method it is possible to cultivate the thalli even in areas outside shallow bays, in depths of 10-20 m.
Semi-floating system
This method is a mixture of the floating and fixed net systems. At high tide the nets float on the surface, in the ebb tides, the system stands on the land. This combines the advantages of fixed net and floating systems, so it has been widely adopted in China.
Fixed nets
In this system, also known as the "pole system", the nori nets are hung between poles. During ebb tides, the nets are exposed to air and become dry. Intertidal pole cultivation is often preferred over floating or semi-floating cultivation in deep water, because it ensures periodic exposure of the proper duration, which helps to reduce the incidence of disease and the growth of competitive (weed) species, especially epiphytic diatoms. However, this type of cultivation is restricted to the inner portions of bays, with shallow, sandy bottoms
Freezing nets
This method has two advantages: preventing diseased nori, and improving the quality of the final product. The procedure for processing freezing nets is as follows:
Seed supply
Rearing conchocelis
As described earlier in this fact sheet, the farming of nori occurs in two stages. The first occurs indoors, from May to October, where the conchocelis stage is cultivated and conchospores produced. The second stage occurs from October until April or May; in this phase farmers focus on the cultivation of the thalli in the field.
In early and mid-May, Asiatic hard clam (Meretrix meretrix) are seeded by desiccating the conchocelis to release the conchospores; a suspension of them is then sprayed onto the substrate, or the substrate is submerged in the suspension. Cultivation occurs in large elongated shallow tanks filled with 20-30 cm of seawater that has been subjected to sedimentation and to which nitrogenous and phosphate nutrients have been added. At this stage, the temperature is not controlled and is allowed to fluctuate with ambient air temperature. However, optimal growth occurs between 20-25 °C. The carpospores develop into the conchocelis phase.
In mid-May to early June, the water temperature is raised to 22-23 °C, to encourage vegetative growth of the conchocelis phase. In July, the light intensity is reduced to encourage the formation of conchosporangia, which will eventually release the conchospores. From early July to late August, the water temperature is gradually raised to reach 27-28 °C by mid-August. After this, the water temperature is gradually decreased again.
By late August to late September, the water temperature has been lowered to 23 °C; during this period of the conchosporangia form. The light intensity is held at the same level to encourage the formation of the conchospores in the conchosporangia but the day length is reduced to 8-10 hours. Conchospores are present by late September but mass discharge occurs in early and mid-October.
Once the conchospores are released, they are seeded onto special cultivation nets which are placed in the tanks. When 50 000 spores are being released per day, the light intensity is increased slightly to encourage thallus germination. The water in the tanks is also agitated to distribute the spores evenly and ensure their contact with the cultivation nets. This procedure of collecting conchospores is called "collecting seeds". About 50 percent of laver farms rear the seeds by themselves, while the rest buy culture nets from seed suppliers.
Ongrowing techniques
There are three main farming methods: (a) on floating, (b) semi-floating; and (c) fixed nets. A fourth technique is known as "freezing nets" (see below).

Three methods farming Porphyra spp.
Floating system
This method has been used in Japan and has recently been widely adopted by Chinese farmers. The nets are attached to buoys floating on the surface of the sea, so the nori thalli would be constantly soaked in water. With this method it is possible to cultivate the thalli even in areas outside shallow bays, in depths of 10-20 m.
Semi-floating system
This method is a mixture of the floating and fixed net systems. At high tide the nets float on the surface, in the ebb tides, the system stands on the land. This combines the advantages of fixed net and floating systems, so it has been widely adopted in China.
Fixed nets
In this system, also known as the "pole system", the nori nets are hung between poles. During ebb tides, the nets are exposed to air and become dry. Intertidal pole cultivation is often preferred over floating or semi-floating cultivation in deep water, because it ensures periodic exposure of the proper duration, which helps to reduce the incidence of disease and the growth of competitive (weed) species, especially epiphytic diatoms. However, this type of cultivation is restricted to the inner portions of bays, with shallow, sandy bottoms
Freezing nets
This method has two advantages: preventing diseased nori, and improving the quality of the final product. The procedure for processing freezing nets is as follows:
- When the young thalli reach 1 to 3 cm long, they are brought back from the culture area, together with the nets.
- The nets are dried in the air until the moisture content of the thalli decreases by 20-40 percent, which usually requires 2 to 3 hours.
- Dried nets are put into vinyl bags.
- Dried nets are stored in a freezer at -20 ºC.
- When required, the nets are taken brought back to the nori fields for rearing.

