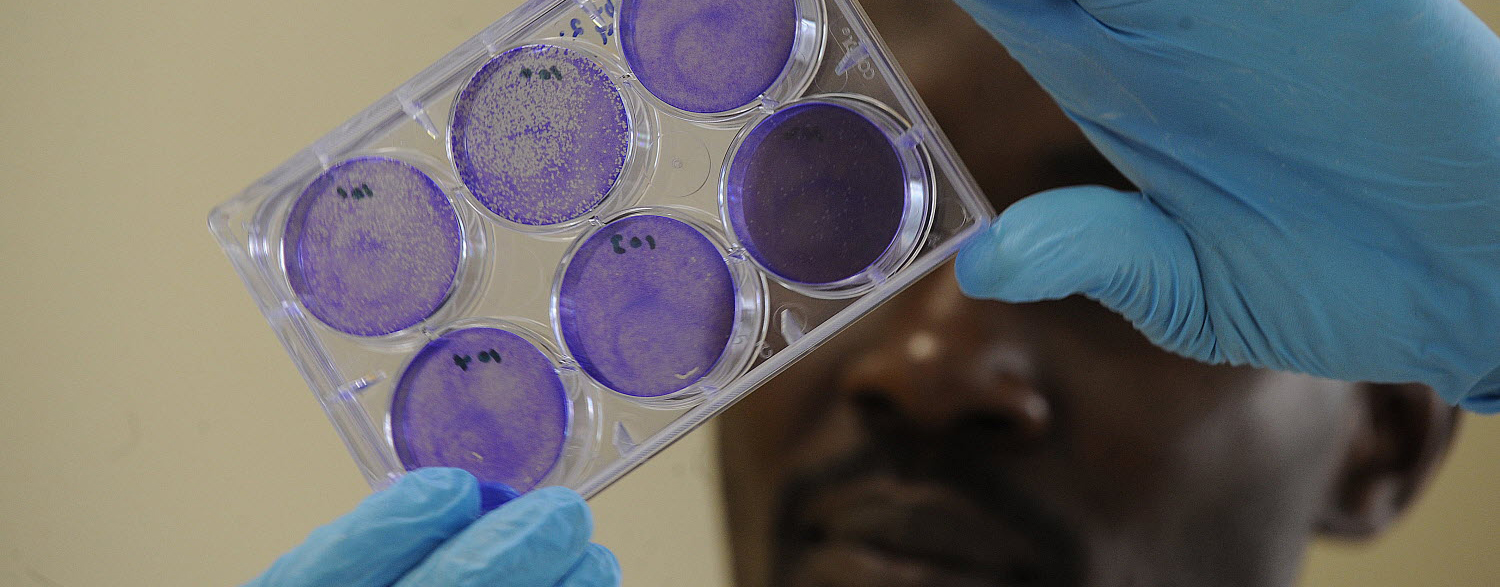
人畜共患病
人畜共患病是动物(包括牲畜、野生动物和宠物)和人之间可相互传染的疾病。人畜共患病可对动物和人类健康均构成严重风险,并可能对经济和生计产生深远影响。人畜共患病通常在人类-动物-环境界面传播,人与动物在共同的环境中相互接触。人畜共患病可以是食源性、水源性或通过病媒传播,或者通过与动物直接接触传播,或通过污染物或环境污染间接传播。
“同一个健康”方针单靠一个部门无法有效解决人类-动物-环境界面的健康问题。需要负责健康工作的所有部门和学科携手合作,以解决人畜共患病和人类-动物-环境界面上的其他共同健康威胁。这一协作方式被称为“同一个健康”。
60%的人类传染病是动物源性的,大约75%是跨物种的。
集锦

Highlights
One Health timeline
14/02/2025
This timeline explores the evolution of One Health and chronicles key milestones, initiatives, and achievements that have shaped One Health.

Video
Building a primary healthcare business for unemployed animal health technicians in South Africa
09/12/2024
This video showcases FAO's initiative on sustainable animal health service provision in South Africa, focusing on training veterinary paraprofessionals.
.tmb-th600x400.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=f438e864_1)
Highlights
From the ground up: Why soil health is key to One Health solutions
05/12/2024
Soil, a critical yet often overlooked element, is at the heart of the One Health approach, connecting human, animal, and environmental health to address...
