Finally, nutritional pathology may arise from the presence of specific adventitious toxic factors or contaminants within certain foodstuffs, including:
a) Intentional additives- binders and stabilizers (carboxymethyl cellulose, alginates, gums)
- therapeutic drugs (antibiotics, sulphonamides, nitrofurans, arsenilic acid)
- growth promotants (as above, plus anabolic steroids, synthetic androgens)b) Toxic factors arising from processing
- solvent residues present in solvent extracted oilseeds (methylene chloride, ethylene dichloride, trichloroethylene, acetone, iso-propyl alcohol)- lipids spoiled by oxidation and/or heat (rancidity, oxidation products).
c) Contaminants of biological origin
- protozoan toxins from spoiled fish
- algal toxins from shellfish/fish
- fungal toxins in stored foods (i.e. aflatoxins)
- bacterial toxins from contaminated foodstuffs (i.e. botulinum toxin)
- pathogens (viable bacteria, viruses and fungi)d) Synthetic contaminants
- pesticide residues (chlorinated hydrocarbons)
- organochlorine compounds (polychlorinated biphenyls)
- petroleum hydrocarbons
- heavy metals
As with plant anti-nutritional factors, dietary toxicological studies have not been performed with the majority of the above mentioned contaminants. For review see NRC (1983); Lovell (1984).
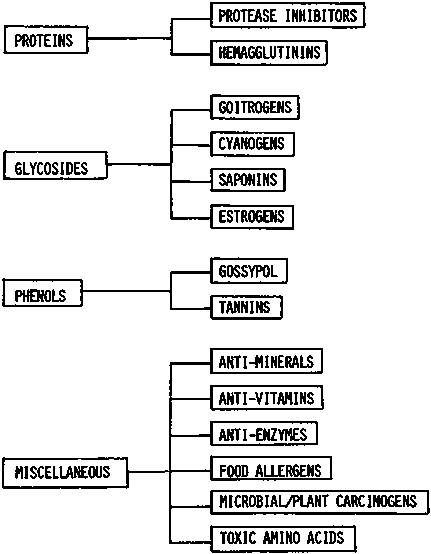
Figure 1. Classification of endogenous toxic factors occurring in plant foodstuffs of agricultural importance according to chemical properties (adapted after Liener, 1975)