Method of compost application at the time of fruit tree seedling plantation
Three "watch" for fertilizer application for raising seedling
Straw blanket - a successful way to increase rainfed crop yields
A good traditional way to spray fertilizer and pesticide
Wheat or corn straw bedding for soil fertility improvement in orchards
13 Compiled by Lu Weixin, Department of Water Resources, Linxian People's County Government, China.
This method is common in Hunan Province. A pit of 1 X 1 X 1 m3 dimensions is dug. Then loosen soil and get rid of gravel, grasses and roots in the pit bottom. Apply compost (70 kg) in each pit and mix it with the loosened soil at the pit bottom. The height of thus mixed compost and loosened soil should be about 80 cm from of pit bottom. Finally, dig a hole in the mixture and plant fruit tree seedling. Cover it with soil and water the seedling. The seedling is planted 20 cm deep.
While applying fertilizer to seedling three "Watch" are observed for stronger and better seedling growth.
First "Watch" is to watch the weather. During spring, the temperature is a little bit low, sufficient organic fertilizer such as compost, green manure, pond silt should be applied but the rapid effect fertilizer can not be applied too early and too much, because the baby seedling absorbs fertilizer very slowly and in small amounts. During the summer, the temperature is high, the fertilizer should be applied many times and much less, and the land after applying should be kept damp so that the roots can absorb and utilize the fertilizer. Application of the fertilizer is better in the evening when the weather is clear. The chemical fertilizer should not touch the leaves and stem of seedling as they can be scorched.
Second "Watch" is to watch the soil quality. If the base fertilizer is sufficient, then less amount should be applied, otherwise apply the fertilizer many times but each time the amount should be less. For heavy clay soil, the fertilizer should be applied on the shallow layer to favor decomposition of fertilizer and assimilation for seedling.
Third "Watch" is to watch the seedling. According to the changes in morphology of the seedling, the problem of lack of fertilizer can be diagnosed. The seedling with short stem, thin or small leaf, less leaves, yellow-green color, dead side sprout, is short of nitrogen fertilizer. The seedling with short branches, purple or copper leaves, and leaves dropping off easily on the lower part of stem is short of phosphate fertilizer. If the stem and leaves become emaciated with the top of the leaves withering first and then the sides, the seedling is considered to be short of potassium.
An 5-10 cm thick straw blanket covers the ground between row crops in this method. Thus about 3, 000- 4, 500 kg/ha of straw is needed. This leads to a decrease in evaporation while it helps accumulate and infiltrate rainfall. Organic matter content of the soil is increased and the weeds are controlled with in 5 days of covering the ground. Thus there is no need of plowing for weed control. By this method in rainfed areas, the irrigation frequency is reduced by 1 -2 times as compared to the fields without ground cover. The method also has been seen to increase yields by about 8% in field crops.
A 60 ml liquid fertilizer or pesticide bottle is hung 20 cm above ground level on the
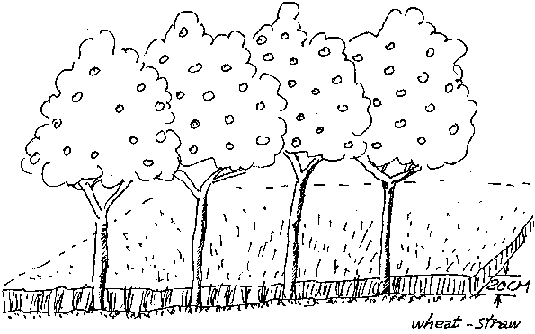
20 cm thick bedding of wheat or corn straw on the ground of an orchard at a
rate of 22, 500 kg/ha for two continuous years, increases the organic matter
content of the soil by 0.7%. This is as good as applying 2.500 kg of compost.
It can increase fruit production by about 450 kg. It can also reduce pests,
diseases
and saves water (see figure below).