To enhance the performance of the Thai AGRIS management, both in knowledge repositories and service provision, the centre has collaborated with the Specialty Research Unit of Natural Language Processing and Intelligent System Development (NAiST), within the computer engineering department at Kasetsart University. Some of the cooperative work has been mentioned in the previous chapters but the following specifically looks at the efforts to enhance the performance of the Thai AGRIS system by applying natural language processing (NLP) techniques.
The Thai AGRIS system currently includes two important functions: storage and retrieval. In the storage subsystem, Kasetsart researchers have developed an annotation tool for attaching metadata to a document. Additionally, a converter tool is being used to generate text representation from major electronic file formats. An automatic indexing tool is used to extract important keywords from the document. An image-enhancement tool is used to remove noise from the document image. In the retrieval subsystem, the researchers have developed an intranet search engine that provides a standard Boolean-query mechanism. Furthermore, it provides query expansion using ontology knowledge for improving the retrieval process efficiency.
Background and motivation
There are three main problems in Thai AGRIS management that affect the performance of both the information retrieval system and the machine translation system:
Document preparation is done through manual typing and indexing, translating from Thai to English and English to Thai. Furthermore, 90 percent of Thai agricultural documents are hard copies that need to be scanned.
Information access via Thai WebAGRIS is often difficult. Reasonable levels of precision and recall are only achieved when the search is done using keywords coming from controlled vocabularies. In addition, search engines can only retrieve data on a purely syntactic basis. It is not possible to embed common-sense, context or domain-specific knowledge into the search engines’ queries.
Thai-English AGROVOC needs constant maintenance in relation to translation, terms coverage (especially proper names and technical terms) and domain-specific restrictions (common words for scientific names, etc.). It is therefore necessary to extend the thesaurus database by recycling existing sources.
To enhance the Thai AGRIS management performance and address these three primary problems, the Thai AGRIS Centre has collaborated with Kasetsart’s NAiST laboratory in a project called Development of Agricultural Information System for Knowledge Acquisition and Dissemination. It is a five-year project, which began in 2001, to integrate Thai language processing techniques to Thai agricultural information processing. It consists of:
Developing annotation tools for supporting document preparation, such as automatic indexing and metadata translating;
Developing semantic search engine for providing smart service with query expansion by utilizing Thai AGROVOC and ontologies extracted from AGROVOC;
Developing tools for maintaining the Thai-English AGROVOC by extracting new terms from the corpus and technical dictionaries; and
Developing machine-aided translation from Thai to English and vice versa.
From STREDEO to Thai AGRIS management
STREDEO3 multimedia, multilingual document storage, retrieval and delivery system for e-organization is a prototype document management system being developed by the NAiST laboratory (research started in 2001). Because the Thai AGRIS Centre was using the same concept model, the STREDEO was applied to the Thai AGRIS system management, consisting of automatic document indexing for both image and text, automatic document classification and dissemination, and intelligent search engine with query expansion:
3 Funded by KURDI (Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute).
Based on automatic document indexing for both image and text, the document could be retrieved with full-text meaning instead of controlled vocabulary. This model could enhance both precision and recall of retrieved information.
Based on automatic document classifying, the document will be classified according its domain concept. This model could support the process of meta-data annotation.
Based on capturing the user’s intention, the document will be disseminated according to his/her interest.
Based on Thai AGROVOC ontology and NLP-based techniques, such as soundex and transcription, the search engine could work more efficiently both in precision and recall.
Previous problems in document management systems of the Thai AGRIS Centre
In general, document management systems still have a few shortcomings that need to be resolved:
Storage
Electronic documents usually store in a variety formats. Some of them are not open formats and the mechanisms for converting their content are not available.
Document representation is generally not enough for effective retrieval. A good designed tool must be developed to ease the task of annotation, such as including automatic indexing with the metadata annotating tool.
Maintenance of document images. Scanned documents may contain noise, which should be removed before further processes such as OCR.
Retrieval
Use of controlled vocabularies in natural language processing on search queries causes low precision.
In light of these problems, the STREDEO model has been applied to Thai AGRIS management as follows:
Annotation tool for intelligent management of knowledge repositories
Figure 8 shows the overview of a developed system, consisting of an annotation tool, an image enhancement tool and a search engine module.
Figure 8: Electronic document management system architecture
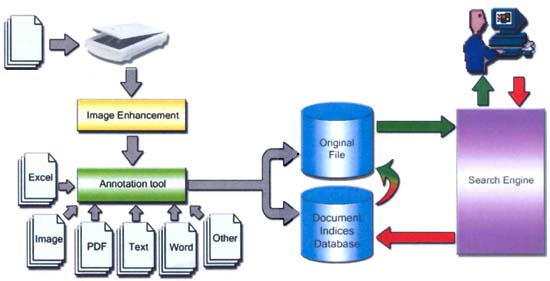
The annotation tool is responsible for generating document representation. It consists of three main components: converter (converts the electronic document to standard text file format), automatic indexing (used to generate keywords of document automatically) and annotation interface (allows user to attach metadata to the document).
To remove the noise from the document image, NAiST researchers have developed an image enhancement tool that is essentially a pipeline of three image enhancement processes consisting of deskew, auto crop and auto align.
Smart search for smart service
The search engine module is derived from the Kasetsart University search engine, which uses a Thai text retrieval system for intranet document searching. It has two functions: basic search and advanced search. The basic search, like several search engines, provides a standard Boolean-query search mechanism.
The advanced search is used to increase the efficiency of a search engine. To improve the effectiveness of information retrieval, the query expansion has been developed. It uses knowledge from metadata information and an ontology in order to uncover indirect connections between query terms and document content. Both of them can improve searching performance.
Automatic Thai ontology construction tool
Ontology plays an important role in many applications, such as information integration and document classification in taxonomies, including the information retrieval system. To enhance a search engine performance, ontology is used to boost the correctness and coverage of the system. However, there remains a problem of building large and adequate ontology within a short time frame and at low cost. The following present both a recycling approach to engineering ontology and general maintenance architecture for discovering new instances from text.
An overview of the ontology construction and maintenance system
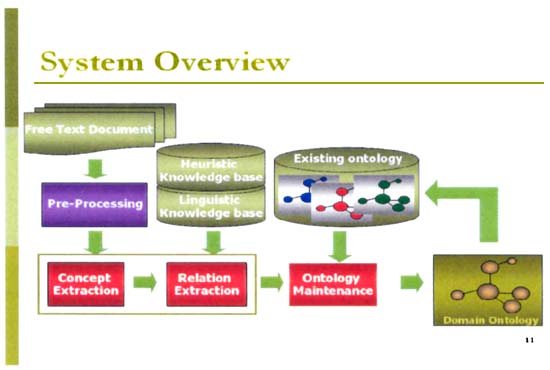
Figure 9 illustrates on overview of the ontology system, which contains four steps: lexical pre-processing (for identifying word strings), ontology term acquisition and relation extraction (to extract all single nouns and compound nouns from the tagged corpus and their relations), and term/relation organization (to organize the terms according to the relations).
Figure 9: Thai ontology construction and maintenance system architecture
From Thai AGROVOC to ontology relationship
The AGROVOC database was converted into the text file to recycle the original relation to ontology relationship (e.g. from BT/NT to IS-A). However, all BT/NT relations in AGROVOC could not be defined to the IS-A relation. Their semantic relations could be defined as “ingredient of” and “property of”.
Heuristic method has been used to resolve this problem. A compound noun in NT will be processed to find a head noun; if head noun is consistent to BT, their relation will be defined to IS-A relation. If they are not compatible, the system will alert an expert to confirm this relation. This method will create many sub-trees where the root is a top term in AGROVOC. In the future those top terms will be extended by using the corpus-based ontology extraction algorithm for maintaining and constructing large ontology.