Small-ScaleDairy Farming Manual |
Volume 3 |
|
|
|
SILAGE MAKING |
 |
|
|
What should you know about silage making?
 |
What is silage and why is silage important?(5-12)
1 You should know:
|
 |
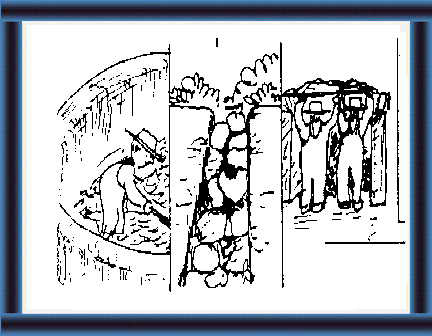
How can you make a "silo"?(13-56)
2 You should know:
|
 |
How do you prepare the crop and handle silage?(57-82)
3 You should know how to:
|
 |
How do you feed silage?(83-87)
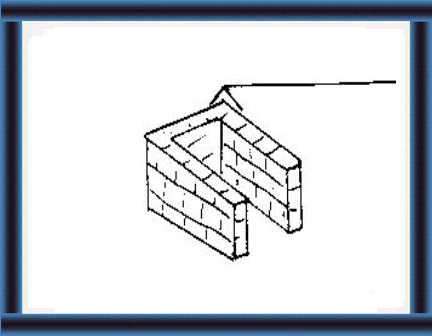
4 You should know how to:
|
What is silage?
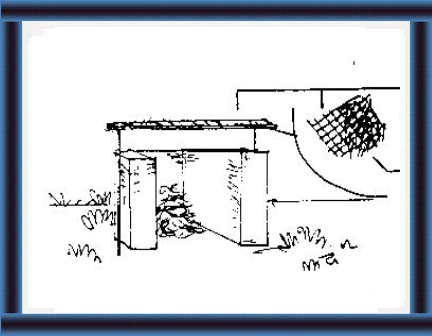
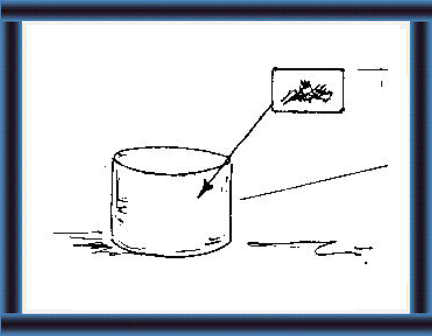 |
5 Silage is cut plant material
sealed
in a silo without air and water.
Rainy Season Dry season |
 |
6 You can store the silage for many
months and still have good animal feed
- up to 85% of the energy and protein value of the original crop. |
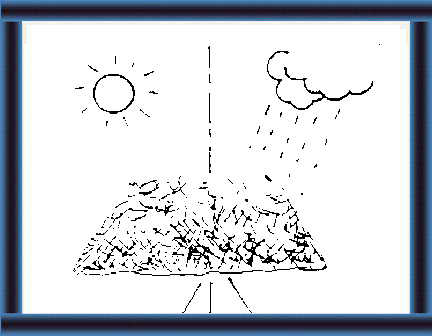 |
7 If you store the cut plant material with air and water |
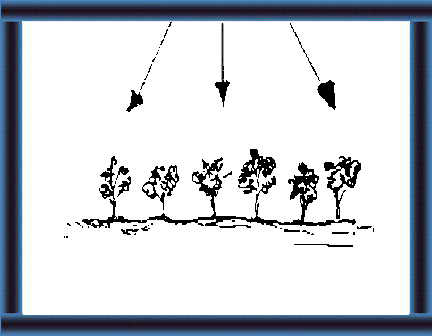 |
8 it becomes rotten material/ compost.
|
Why make silage?
 |
9 You can store extra feed as silage |
 |
10 and use it as animal feed when plants are not growing. |
 |
11 You can harvest your crops when they have highest feed value and store them for use throughout the year. |
| 12 What are the steps in
making silage?
|
Making a silo.
Where is a good place for the silo?
 |
What is important in making a silo?
Right size 14 Big silos cost more. Very small silos have a lot of waste. |
 |
15 The smallest silos should have
4-5 m3 of silage. You need to cut the plant, carry it and fill the silo in one day. |
 |
16 You need enough silage to feed your animals
throughout the dry season. Make more
small silos not one big silo.
IMPORTANT: How many animals do you have? How much feed does each animal need? How much spare crop do you have for silage?
|
 |
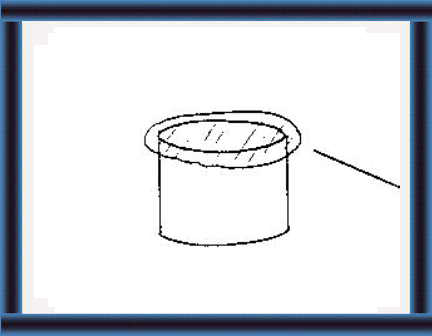
Strength
17 You must compact the silage to remove air. The silo must be strong enough for this. |
 |
No air
18 Air in silage causes problems:
|
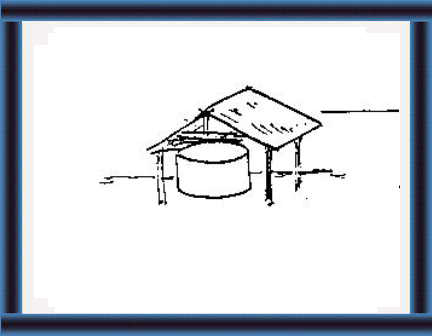 |
No water/sun 19 Make a roof to protect silage from rain and
sun.
|
 |
Drainage
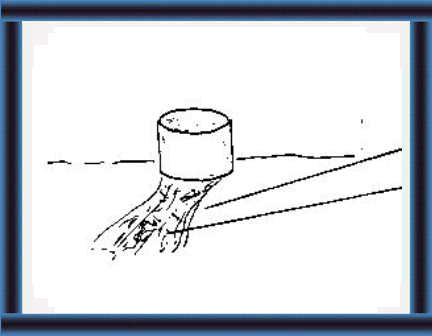
20 Silage produces a lot of effluent. Make drains on each side of the silo floor to remove waste. Fill the drains with stones and rocks. Make sure the drains do not go near drinking water. |
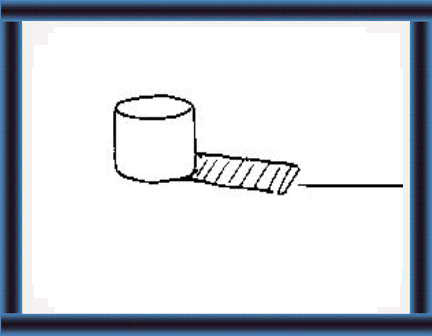 |
Base
21 If your silo is large, make a base for unloading equipment. |
Types of silo
How can you make a stack silo?
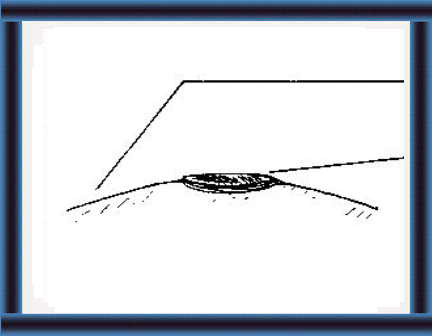 |
22 Choose a site with good drainage
and firm soil base.
If possible, lay a concrete floor. |
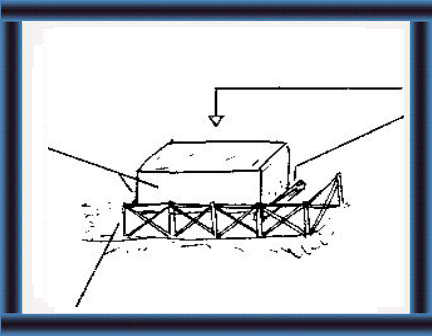 |
23 Stack the cut crop carefully.
Make it high at the sides and the ends. Compact the stack.
|
| Advantages
Disadvantages
1 Low cost.
1 Lot of waste at sides and ends.
|
Material Labour Manhours1 Earth bricks 1 Brick laying 90
2 Cement (12 bags) 2 Make walls 32
& concrete
3 Sand (3 m3) 3 Dig drains & fill 8
trenches with stones
4 Wire-mesh (34 m)
& staples (.8 kg)5 Broken stones for drainage (1.6 m3)
Total man/hrs: 130
How can you make a walled clamp silo?
 |
24 Make earth into bricks and
bake them hard in the sun.
Cover the wire-mesh with a layer of concrete.
|
 |
25 Build the walls of the silo from the bricks. |
 |
26 Put wire-mesh on the inside of the walls. |
 |
27 Make a roof out of wire-mesh and cover with
a thin layer of straw.
|
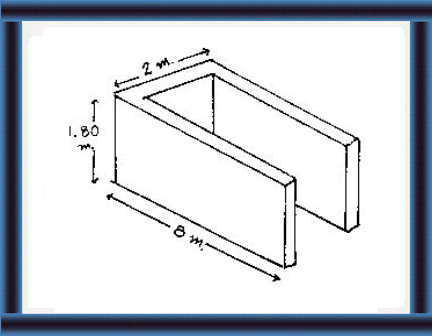 |
28 The silo has a capacity of about 35 m3
(11,000 kg).
This is enough to feed 5 milking cows for 90 days. |
| Note:
1 Other materials for walls: metal or wood e.g. railway sleepers. 2 Silage produces acids. Treat materials with asphalt to protect them. |
How can you make a trench silo?
29 Choose a site with sloping land and firm soil.
Side view
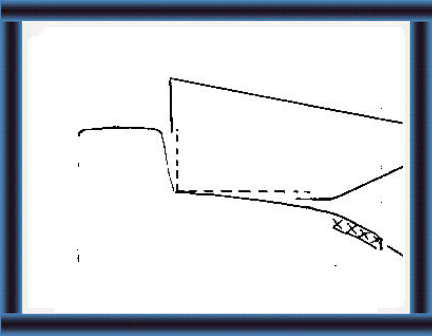 |
30 Dig a trench:
- with a 10% slope on the back wall and bottom. This will carry the waste towards the drains. |
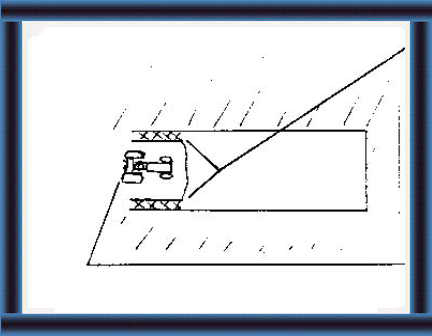 |
31
- wide enough for a tractor or cart to enter. |
 |
32 Dig drains and fill with rocks or stones.
|
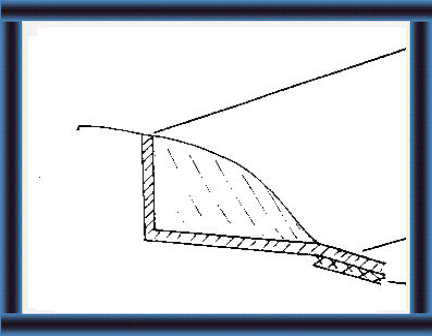 |
33 Your trench silo will be better if you line
the sides, bottom and walls with a 10 cm layer of concrete.
Extend the concrete for 3-4 m on the slope. Drains |
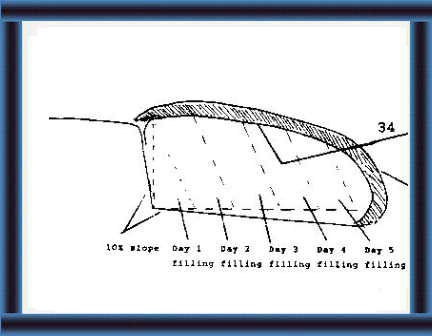 |
34 Cover the silage with a polythene sheet.
This will keep the air and water out.
Make the slope of the back wall and bottom 10
%.
|
 |
35 Make a roof.
This is bamboo with a "cadjan" covering. |
| Materials
Labour
1 Broken
stones (drainage)
1 Dig trench
|
Size
Capacity
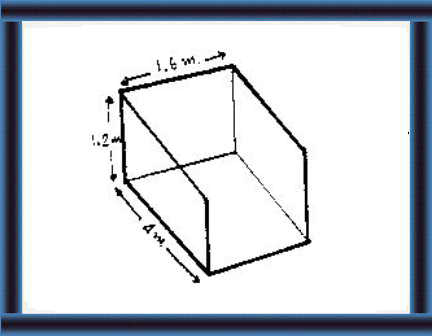 |
36 This silo has a capacity of about 10 m3
(3,500 kg).
This is enough to feed 2 cows and 2 calves for 60 days. It is suitable for small - medium scale silage
operations.
|
| Note:
1 Replace roof mats every year. 2 Replace roof structure every 3 years. 3 Replace trench after 5 years. |
| Advantages
Disadvantages
1 Low cost,
about US$ 5-10 per m3 1
Needs a good, sloping site
|
How can you make a circular wattle silo?
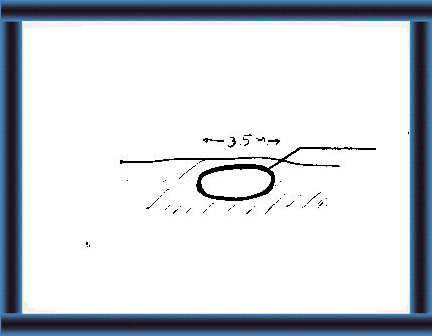 |
37 Choose a well-drained site
with firm soil.
Draw a circle on the earth, 3.5 m in diameter. |
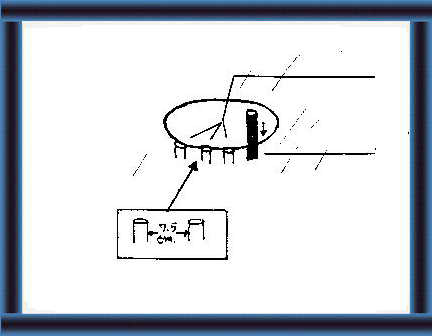 |
38 Make holes around the circle,
7.5 cm apart. Errect the poles. |
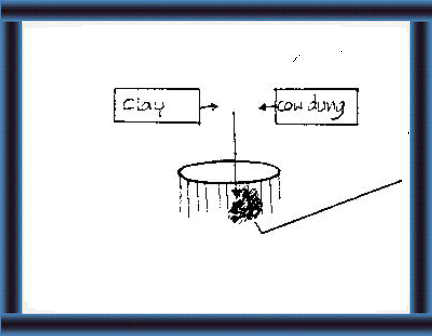 |
39 Mix clay and cow dung.
Plaster over the poles. |
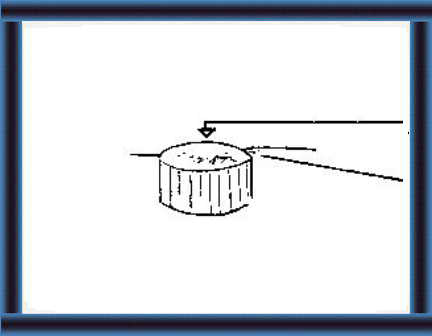 |
40 Add and compact the crop.
Seal the top with a mixture of soil and straw or with a plaster jacket.
|
41 Build a roof for the silo.
42 A "wattle and daub" silo.
Materials Labour1 140 wooden poles (2.20 m long, 1 Dig holes for poles
0/ 0.06 m diameter)2 Poles 2 Erect & connect poles
3 Soil, cattle manure, 3 Prepare mud
straw chaff (to produce mortar
for wall coating)4 Plastic jacket 4 Plaster walls
43 This silo has a capacity of about 18 m3 (6,000 kg).
This is enough to feed 3 cows and 3 calves for 60 days (daily ration: 25 kg/cow, 6 kg/calf).
Note:
1 Replace plastic jacket after 1 year.
2 Replace basic structure after 2 years.
How can you make a bamboo silo?
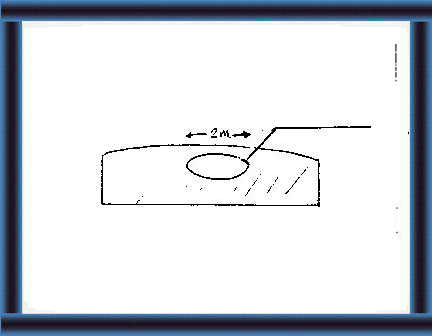 |
44 Choose a well-drained site
with firm soil.
Draw a circle on the earth 2 m in diameter. |
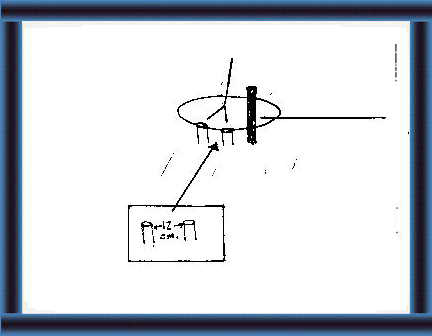 |
45 Make holes around the circle
12 cm apart. Erect the poles. |
 |
46 Attach wire-mesh to the walls.
This supports the cement lining. |
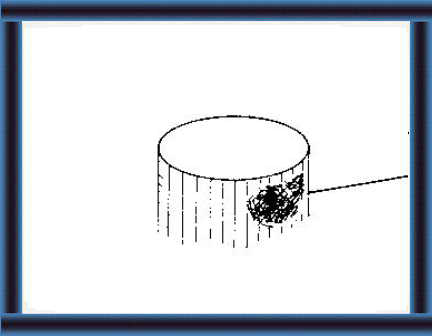 |
47 Mix 1 part cement with 2 parts sand and water. Plaster over the wire-mesh. |
| Materials
Labour
1 20 bamboo
poles
1 Dig holes for poles
|
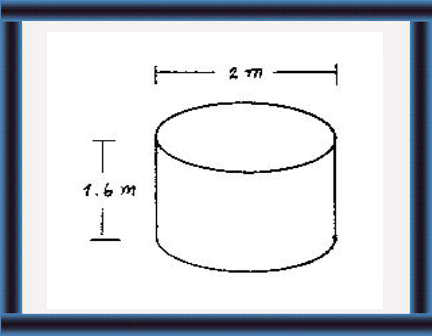 |
SIZE
48 Capacity
Note:
|