According to proposition 4.3 the WOMA of a flat population constitutes a lower limit for all convex populations and an upper limit for all concave populations with size N. In this section it will be shown that this limit has value:
|
|
(5.1) |
Let us assume a flat(=equidistant) population with elements
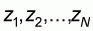 , size N and mean
, size N and mean
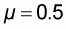 . It is clear that each of
its elements can be written as:
. It is clear that each of
its elements can be written as:
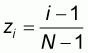 with
i=1,2,...,N
with
i=1,2,...,N
Since the population is symmetrical the worst accuracy curve
will be formulated by working either from left to right or from right to left.
We choose to work from left to right with sample sizes 1,2,...,N. In this
manner and by using the property
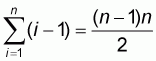 , the sample mean at each
size n will be:
, the sample mean at each
size n will be:
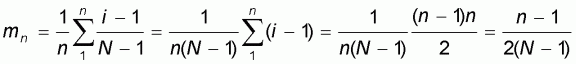
and, recalling that
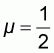 , the resulting accuracy
will be:
, the resulting accuracy
will be:
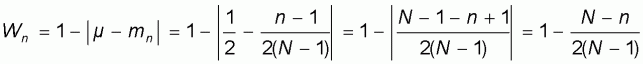
By using the notation
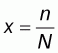 , then n=Nx and the
above expression can be written as:
, then n=Nx and the
above expression can be written as:
|
|
(5.2) |
Expression (5.2) represents a "Global Line" G(x) of the general form:
|
|
(5.3) |
where the intercept a is given by the formula:
|
|
(5.4) |
From (5.2) it follows that when x starts from its
minimum 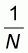 the line
G(x) takes the value:
the line
G(x) takes the value:
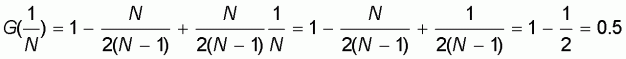
while for the maximum x=1 it becomes 1. Therefore the
area formed by the line G(x) and the interval
[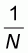 , 1] on the x-axis
(also representing the WOMA
, 1] on the x-axis
(also representing the WOMA 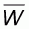 of the flat population), will be given by:
of the flat population), will be given by:
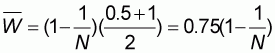
which explains the value of
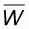 given in (5.1).
given in (5.1).
Fig. 5.1. Feasible domain of A-curves for non concave populations (N=200)
Figure 5.1 illustrates an example of a global boundary G(x) for all A-curves of convex and flat populations with size N=200. In this particular example the target population is flat and its distribution is shown in the small graph inside the plot.
It is easy to verify that the expression (5.4) for the intercept a is equivalent to:
|
|
(5.5) |
with 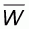 given as in (5.1).
given as in (5.1).
In fact by substituting in (5.5) the value
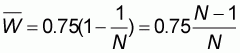 we obtain:
we obtain:
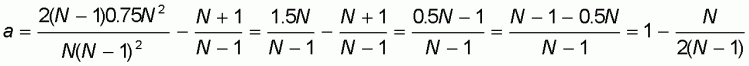
thus resulting in the same expression for a as in (5.4).
As it will be seen in Section 5.4 this observation will be useful in summarizing the formulae for the global boundaries G(x) and using a single formula for a.
In the previous Section it was shown that there exists a lowest WOMA for all flat and convex population of the same size, and this lower limit has the value given in expression (5.1). The question now arises as to whether there exist fixed feasible domains for all A-curves in populations of the same size, that is including all three population categories: convex, flat and concave.
In response to this question it will be demonstrated that for all populations of a given size N, the feasible domain of all A-curves has a lower boundary corresponding to a WOMA with value:
|
|
(5.6) |
Proposition 4.3 stated that by making a population more concave, its new WOMA becomes lower than the original one. The concluding paragraph of 4.3 also stated that by using the same transformation process for concave populations there will be a point at which all population elements will become extreme values 0 and 1. The question then arises as to which proportions of zero and non-zero elements will result in the lowest possible WOMA.
It will be presently shown that this proportion, denoted by r, will be given by:
|
|
(5.7) |
If M is the unknown number of zero elements then the
ratio r will be 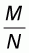 . The
number of elements with value 1 will be (N-M) and the population mean
will thus be:
. The
number of elements with value 1 will be (N-M) and the population mean
will thus be:
|
|
(5.8) |
We can now assume that
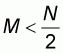 which is equivalent to
r<0.5 and implies that the population mean 1-r is found to the
right of 0.5 (the opposite assumption for M would lead to the same
results by means of a symmetrical approach).
which is equivalent to
r<0.5 and implies that the population mean 1-r is found to the
right of 0.5 (the opposite assumption for M would lead to the same
results by means of a symmetrical approach).
We then proceed to the formulation of the worst PSA as described in Section 3.4 by considering four different sampling patterns depending on the sample size n.
Sampling pattern 1
In this first pattern the sample size n varies between 1 and M. All left-to-right sample means will be zero and all right-to-left sample means will be 1.
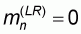
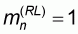
Evidently, the worst accuracy
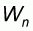 will correspond to
will correspond to
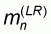 since, according to (5.8)
and the assumption that r<0.5, these sample means will be more distant
from m = 1-r than
since, according to (5.8)
and the assumption that r<0.5, these sample means will be more distant
from m = 1-r than
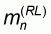 . The corresponding worst
accuracy will thus be:
. The corresponding worst
accuracy will thus be:
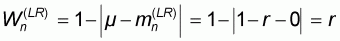
and it will be constant when n varies between 1 and M.
A second observation is that by referring to the accuracy plot
with the independent variable x taking values from
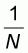 to
to
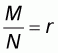 , the area of the rectangle
formed by the horizontal line W=r and the interval
[
, the area of the rectangle
formed by the horizontal line W=r and the interval
[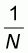 , r] on the
x-axis will be:
, r] on the
x-axis will be:
|
|
(5.9) |
Sampling pattern 2
In this second sampling pattern the sample size n
varies between M and
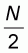 . The left-to-right sample
means and worst accuracy are computed as:
. The left-to-right sample
means and worst accuracy are computed as:
|
|
|
|
|
(5.10) |
The right-to-left sample means and worst accuracy are computed as:
|
|
(since
|
|
|
(5.11) |
It is easy to verify that
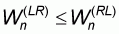 . In fact, the relationship
. In fact, the relationship
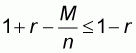 is equivalent to
is equivalent to
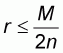 which is true because
which is true because
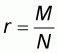 and in the current sampling
pattern it was assumed that
and in the current sampling
pattern it was assumed that
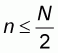 .
.
It has thus been shown that in the second sampling pattern the worst accuracy W will still be computed by using left-to-right samples and according to expression (5.10).
By referring again to the accuracy plot with the independent
variable x taking values from
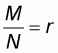 to
to
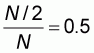 , the area formed by the
curve W and the interval [r, 0.5] on the x-axis will
be:
, the area formed by the
curve W and the interval [r, 0.5] on the x-axis will
be:
|
|
(5.12) |
Sampling pattern 3
Here the sample size n varies between
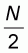 and N-M. The
left-to-right and right-to-left sample means are computed as in sampling pattern
2 and the resulting worst accuracy values are given by expressions (5.10) and
(5.11). However, in this pattern we have
and N-M. The
left-to-right and right-to-left sample means are computed as in sampling pattern
2 and the resulting worst accuracy values are given by expressions (5.10) and
(5.11). However, in this pattern we have
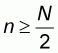 which is equivalent to
which is equivalent to
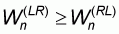 and implies that in the
third sampling pattern the worst accuracy W will be constant and equal to
1-r.
and implies that in the
third sampling pattern the worst accuracy W will be constant and equal to
1-r.
By referring to the accuracy plot with the independent
variable x taking values from
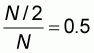 to
to
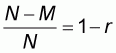 , the area of the rectangle
formed by the horizontal line W=1-r and the interval [0.5, 1-r] on
the x-axis will be:
, the area of the rectangle
formed by the horizontal line W=1-r and the interval [0.5, 1-r] on
the x-axis will be:
|
|
(5.13) |
Sampling pattern 4
Finally, in the fourth sampling pattern the sample size n varies between N-M and N. The left-to-right sample means and worst accuracy are computed as:
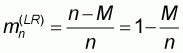
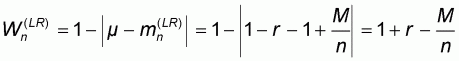
The right-to-left sample means and worst accuracy are computed as:
|
|
|
|
|
(5.14) |
Next step is to test that
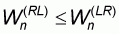 . This is equivalent
to:
. This is equivalent
to:
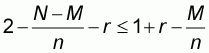 ,
or
,
or
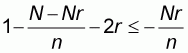 ,
or
,
or
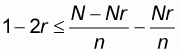 ,
or
,
or
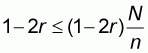
The last relation is true because 1-2r>0 and
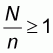 . This observation implies
that in the fourth sampling pattern the worst accuracy W should be
formulated by using right-to-left samples and according to expression
(5.14).
. This observation implies
that in the fourth sampling pattern the worst accuracy W should be
formulated by using right-to-left samples and according to expression
(5.14).
By referring to the accuracy plot with the independent
variable x taking values from
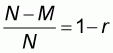 to
to
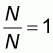 , the area formed by the
curve W and the interval: [1-r, 1] on the x-axis will
be:
, the area formed by the
curve W and the interval: [1-r, 1] on the x-axis will
be:
|
|
(5.15) |
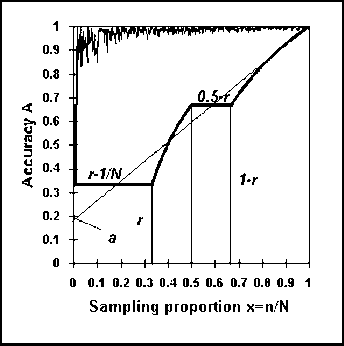
Fig. 5.2. The mixed curve W(x) representing the lowest WOMA for all populations with size N.
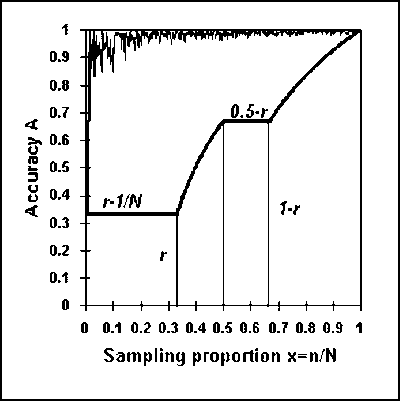
Figure 5.2 illustrates the process of formulating the mixed curve W(x) describing the lowest WOMA of all population categories with the same size N.
Computation of the lowest WOMA
The four sampling patterns defined above and illustrated in
Figure 5.2, have determined a worst accuracy curve W(x) consisting of two
line segments and two hyperbolic segments. The total area under this mixed curve
will be equal to the WOMA 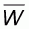 of the concave population with size N, elements 0 and 1 and the unknown
proportion of zero elements
of the concave population with size N, elements 0 and 1 and the unknown
proportion of zero elements
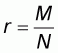 .
.
By adding up the areas given by expressions (5.9), (5.12), (5.13) and (5.15), we obtain:
|
|
(5.16) |
which is a function of the unknown proportion r. For
this area to have a minimum its first derivative
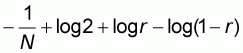 must be zero and this
occurs when:
must be zero and this
occurs when:
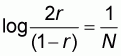 or:
or:
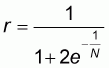
which explains the value of "worst proportion" r given in (5.7).
Expression (5.16) can be re-arranged to become:
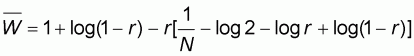 =
=
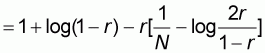
It is easy to verify that for
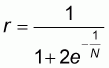 we have:
we have:
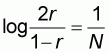 and the expression for
and the expression for
 becomes:
becomes:
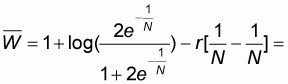
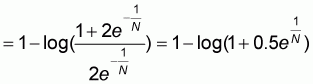
which explains the value of
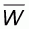 given in (5.6).
given in (5.6).
For purposes of convenience we will now transform the mixed curve described above to a line function G(x) forming the same area given by (5.6). This line should be of the general form:
|
|
(5.17) |
Its intercept a must be defined in such a manner that
the area formed by the line G(x) and the interval
[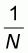 , 1] on the x-axis
must be equal to the area
, 1] on the x-axis
must be equal to the area 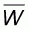 given in (5.6). This is equivalent to:
given in (5.6). This is equivalent to:
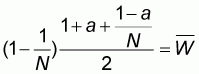
from which by solving for a we obtain:
|
|
(5.18) |
Figure 5.3 illustrates the formulation of the global line G(x) with an area equal to that formed by the mixed W(x) curve.
Fig. 5.3. The mixed W(x) curve and its equivalent global line G(x)
Based on the conclusions of the earlier sections and the formulae (5.1), (5.5), (5.6) and (5.18), it is evident that the construction of a global boundary line of the form:
|
|
(5.19) |
is a direct function of the WOMA value
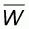 which, in turn, is based on
the assumption as to whether a target population of size N may or may not
be concave. Thus the value of the primary parameter
which, in turn, is based on
the assumption as to whether a target population of size N may or may not
be concave. Thus the value of the primary parameter
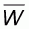 in the formulation of
G(x) is given by:
in the formulation of
G(x) is given by:
Population can be concave
|
|
(5.20) |
Population cannot be concave
|
|
(5.21) |
The parameter a representing the intercept of G(x) with the A-axis is given by the single formula:
|
|
(5.22) |
For large populations the intercept a takes the limit value of 0.189 (concave populations) or 0.5 (non-concave populations).