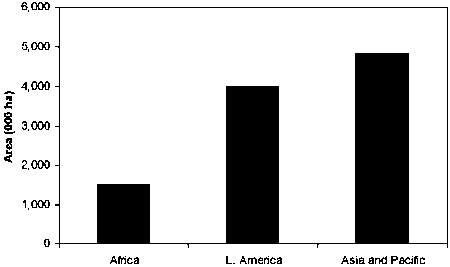
The largest planted genus, Eucalyptus, had major areas in India (30%) and Brazil (26%) followed by China (7%), South Africa (5%), Viet Nam (5%), Uruguay (3%), Peru (3%), Argentina (2%) and others. Eucalypt plantations in African countries like Morocco, Madagascar, Ethiopia, Rwanda, Sudan each had significant area (> 50,000 ha) grown mainly for fuelwood and other non-industrial purpose. Most of the eucalypt plantations of Peru and Uruguay were also for non-industrial purpose whereas Brazil and Argentina were for industrial purposes. Eucalypt plantations in India, Vietnam and Pakistan met both industrial and non-industrial needs (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Distribution of Eucalypts plantations in the geographic regions.
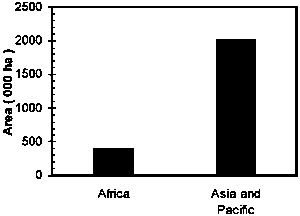
The species group “Other Acacias” (Acacia nilotica, A. senegal, A. holosericea, A. albida, A. seyal, A. radiana) were mainly planted in tropical Asia and tropical Africa (Figure 4). Of the total plantation of 2.4 million ha 78% were located in India, most of which were A. nilotica. Significant plantations were also found in Pakistan (mostly A. nilotica) and Myanmar. Plantations of “Other Acacias” in tropical Asia basically met non-industrial functions. In tropical Africa Sudan had the largest area of 222,750 ha, 60% of which were A. senegal for the extraction of gum arabic and rest were A. nilotica for the production of industrial wood. Other African countries having significant plantation of Other Acacias were Tunisia, Rwanda, Niger and Senegal.
Figure 4. Distribution of “Other acacias” plantations in the geographic regions.
Acacia auriculiformis was planted both for industrial and non-industrial purposes. Of the total net planted area of about 818,000 ha, 98% was located in tropical Asia, 75% in India alone. Other countries that had significant plantation areas were Vietnam, Thailand and Myanmar.
Large scale plantations of Acacia mangium were of recent origin; the estimated net area was about 453,000 ha of which 99% were in tropical Asia, established for industrial purposes. Countries with major areas were Indonesia (67%), Malaysia (14%), Vietnam (13%), Bangladesh (3%) and Philippines (2%).
Plantations of Acacia mearnsii were used for tanbark and the total estimated net area was about 325,000 ha. Most of the plantations were in Africa (South Africa, Kenya, Morocco, Zimbabwe) and Brazil.
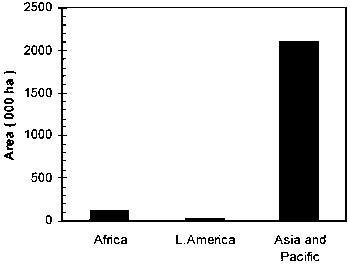
Teak (Tectona grandis) was the most widely planted for high quality timber. The global net area of teak plantations was about 2.3 million ha. Major areas of plantations were in India (44%) and Indonesia (31%). Thailand, Myanmar, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka had also significant area under teak plantations. In tropical Africa significant area of teak plantations were found in Nigeria, Cote d’Ivoire, Sudan, Ghana, Togo and Benin. In tropical America the total area under teak plantations was about 33,062 ha, 42.5% of which was in Costa Rica and 22.7% in Trinidad and Tobago (Figure 5).
Figure 5. Distribution of teak plantations in the geographic regions.
Casuarina spp. occupied about 1.1 million ha net area in plantations, 65.3% of which were located in tropical Asia, mostly in India, Viet Nam and Thailand[1]. Significant plantation areas of this species also existed in Cuba, Senegal, Mozambique and Madagascar. Most of the plantations of Casuarina spp. were for non-industrial purposes - shelterbelt, coastal dune fixation and fuelwood.
Dalbergia sissoo plantations occupied about 626,000 ha net area, most of which were restricted to tropical Asia - India, Pakistan, Nepal and Bangladesh. Small plantations of this species were found in tropical Africa - Nigeria and Burkina Faso. The species is a high quality of timber and is used for industrial purposes.
Gmelina arborea plantations occupied about 425,000 ha net area, almost all for industrial use. The plantations were widely distributed in the three tropical regions with major areas in Indonesia (28%), Nigeria (17%), Brazil (10%), Cuba (9%) and Costa Rica (9%).
Terminalia spp. (Terminalia superba, T. ivorensis, T. myriocarpa, T. arjuna, T. tomentosa) were mainly planted for industrial use. The total net plantation area was about 304,000 ha, 84% of which was in tropical Asia (mostly in India) and 16% in tropical Africa. Species in tropical Africa were T. superba, T. ivorensis, where as in Asia are, T. myriocarpa, T. arjuna, T. tomentosa.
Plantations of Mahogany (Swietenia macrophylla, Khaya senegalensis) had a net area of about 151,000 ha. Major areas of plantations were in Indonesia (60%), Fiji (20%), Philippines (6%), Solomon Islands (3%) and Sri Lanka (3%). Relatively small plantations in African countries were of African Mahogany (Khaya senegalensis).
Other HW species (undifferentiated) occupied a relatively large area (40.8%) of hardwood plantations and comprised of those unspecified that were less extensively planted. About 90% of such plantations were in Asia, 43% in China alone (Figure 6). Many species of this group were of industrial value. Country-wise area with indication of main species of the selected countries is given in Table 3.
Figure 6. Distribution of other HW plantations in the geographic regions.
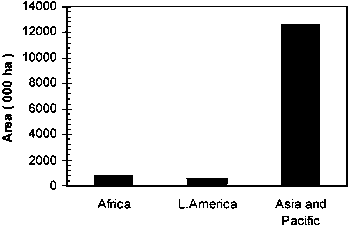
Table 3. Countries with more than 5,000 ha net plantation areas of Other HW species and indication of main species within this group.
|
Country |
Percentage |
Net area, ha |
Main species (% if any) |
|
Algeria |
16% |
155,500 |
Mainly Quercus spp. |
|
Argentina |
21% |
174,300 |
Salix alba (16%), Poplar spp.(3%) |
|
Bangladesh |
53% |
143,000 |
Mangroves (40%), P. falcataria (7%), Melia Azaderach, Shorea spp. and others |
|
Burkina Faso |
25% |
5,000 |
Prosopis spp. Azadirachta indica and others |
|
Burundi |
9% |
7,650 |
Grevelia robusta (3%) and natives spp. |
|
Cape Verde |
87% |
41,000 |
Prosopis juliflora (67%), Parkinsonia aculeata (19%) |
|
Chile |
5% |
33,600 |
Cassia siamea and native spp. |
|
China |
30% |
6,411,000 |
Populus spp.(14%), Robinia pseudoacacia, Magnolia spp. Quercus spp., Pawlonia spp. |
|
Colombia |
27% |
34,200 |
Bombacopsis quinata, Cordia alliodora,Cassia siamea and others |
|
Congo, PDR |
35% |
14,700 |
|
|
Costa Rica |
40% |
46,400 |
B. quinata (14.5%), C. alliodora (12%) Alnus acuminata and others |
|
Cote d'Ivoire |
21% |
17,000 |
Cedrela odorata (10%), Triplochiton scleroxylon (3%), Khaya spp.(2%) and natives |
|
Cuba |
21% |
83,000 |
Anacardium occidentale, Mangroves and others |
|
Former Ethiopia |
7% |
9,000 |
Native species |
|
Gabon |
85% |
17, 000 |
Mainly Aucoumea klaineana |
|
Guatemala |
10% |
5,700 |
C. odorata and others |
|
India |
29% |
3,582,000 |
Prosopis spp. (6%), Azadirachta indica (3%), Populus spp., Albizia spp. Shorea robusta, Bombax spp. and others |
|
Indonesia |
46% |
1,551,000 |
P. falcataria (20%), Shorea spp., Dipterocarpus spp. |
|
Kenya |
16% |
26,900 |
|
|
Madagascar |
18% |
42,000 |
|
|
Malawi |
5% |
6,100 |
Native spp. |
|
Malaysia |
15% |
15,600 |
Dipterocarpus and other native spp. |
|
Mali |
40% |
11,200 |
Native spp. |
|
Morocco |
16% |
90,000 |
|
|
Myanmar |
38% |
126,000 |
Xylia dolabriformis (9%), Pterocarpus macrocarpus (2%), C. siamea, Albizia lebbek, A. indica, Leucaena leucocephala and others |
|
Nepal |
30% |
25,500 |
Alnus nepalensis, A. lebbek, Artocarpus spp., Ficus spp., Michelia champaca and others |
|
Niger |
45% |
18,900 |
A. indica, Zyzyphus mauritiana, Bauhinia spp. and other natives |
|
Nigeria |
22% |
30,800 |
A. indica (7%) and other native spp. |
|
Pakistan |
30% |
153,600 |
Bombax ceiba, Morus alba, Populus spp. , Prosopis spp. Ailenthus spp. and others |
|
Peru |
5% |
15,000 |
Native spp. |
|
Philippines |
32% |
51,700 |
P. facataria (25%), Enthocephalus spp., Pterocarpus spp., Endospermum spp., L. leucocephala and others |
|
South Africa |
|
10,000 |
Native spp. |
|
Rwanda |
10% |
17,300 |
|
|
Senegal |
48% |
72,500 |
P. juliflora (24%), P. aculeata (4%), A. indica (2%), L. leucocephala and others |
|
Sri Lanka |
13% |
12,500 |
C. siamea, Callindra spp., A. indica, Albizia spp., L. leucocephala and others |
|
Tanzania |
50% |
70,000 |
C. siamea, A. indica, L. leucocephala, and Grivellia robusta |
|
Thailand |
20% |
106,000 |
M. azaderach, A. indica, Hopea odorata, Pterocarpus spp., Chukrasia spp. and others |
|
Tunisia |
4% |
12,800 |
|
|
Uruguay |
5% |
17,400 |
|
|
Venezuela |
5% |
24,500 |
C. odorata, L. leucocephala, Tabebia rosea and others |
|
Vietnam |
36% |
552,400 |
Styrax tonkinensis (3%), Manglieta glauca (5%), Mangroves (6%), Melia azaderach and others |
|
[1] China is not
included |