One of the functions of the Wuxi Centre according to the document, “Outline Research Programmes for the Regional Aquaculture Lead Centres in Asia - Part III”, will be to conduct experimental investigations to elucidate the ways in which the various integrated fish farming activities function.
It is recommended that experimentation be conducted largely in a three tier system of “water containers” of increasing size:
Small tanks which would enable a rapid experimental assessment of many hypotheses. Treatments should be in triplicate.
Experimental earth ponds to further test promising results obtained from the tank experiments. The ponds should be small enough to enable the testing of several treatments in duplicate or preferably in triplicate, but large enough so that the results obtained may be extrapolated to commercial sized fish ponds.
Commercial fish ponds to field test, under actual farm conditions, those techniques which appear to hold real promise of increasing farming efficiency, based on the results of experimentation in systems (i) & (ii).
This section consists of two parts, the description of a preliminary tank experiment which was set up during the Consultancy, and the outlines of thirteen experimental designs suitable for small tanks.
(a) Preliminary Tank Experiment
This experiment was designed, prepared and set up during the Consultancy. Fish were stocked on 14 November, 1981. Although growth conditions were far from ideal at the time with the approach of winter, it was felt that the exercise of initiating an experiment would be a useful experience.
The experiment was set up in a series of ten concrete tanks at the Wuxi Fish Farm, Li Yuan People's Commune.
The experiment was designed to provide the following information:
Will grass carp grow when pig manure is the only pond input?
Is vegetable matter as good a fertilizer as pig manure?
What is the fertilizing effect of grass carp faecal matter on the growth of silver carp and bighead carp with vegetable matter for grass carp as the only pond input?
The ten ponds were used for five treatments, in duplicate. Ponds received either pig manure, vegetable matter, or pig manure and vegetable matter together. A limited polyculture of three species was used, silver carp, bighead carp, and grass carp. Common carp was not included because it would consume vegetable matter in the absence of sufficient benthic animals. Some treatments did not receive grass carp as follows:
| Treatment 1 | Treatment 2 | Treatment 3 | Treatment 4 | Treatment 5 |
| Pig manure | Pig manure | Pig manure | - | - |
| Vegetable | - | - | Vegetable | Vegetable |
| Bighead carp | Bighead carp | Bighead carp | Bighead carp | Bighead carp |
| Silver carp | Silver carp | Silver carp | Silver carp | Silver carp |
| Grass carp | - | Grass carp | - | Grass carp |
Although two stocking densities were recommended in the “Outline Research Programmes…”, 10,000 fish per ha and 1,000 fish per mu (= 15,000 fish per ha) it was decided to use the latter figure as the standardized stocking weight since it gives a higher initial fish biomass.
The limited polyculture recommended above in the above report was: 5 silver carp, 1 bighead carp, 2 grass carp, and 1 common carp. However, this is incorrect according to Chinese practice in the Wuxi area since grass carp should be 50% of silver and bighead carp combined. Thus, the number of grass carp individuals was increased to 3. The standardized stocking stocking ratio for experimentation was thus: 5 silver carp, 1 bighead carp, 3 grass carp, and 1 common carp.
The tanks were 15 m2 × 1 m deep. Soil from a nearby hillside, infertile since it had never been cultivated, was homogenized and placed in the tanks to a depth of 5 cm. Water from the lake was pumped into the tanks and filtered through fine mesh net. The stocking density was calculated as follows: standard stocking density, for a typical Chinese pond of 2 m depth, as recommended is 15,000 fish per ha; thus, stocking density for a 15 m2, 0.75 m deep pond
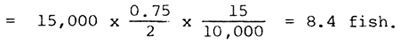
The number of fish stocked to conform to the recommended ratio was: 5 silver carp, 1 bighead carp, and 3 grass carp. The size of the fish stocked were silver carp 100 g, bighead carp 100 g, and grass carp 175 g. The fish were fed once a day, with the same dry weight of material, either pig manure and vegetable alone or in combination. The initial feeding weight was 3% of the body weight of the grass carp per day.
(b) Experimental Design Outlines
It is recommended that the initial experiments in small tanks be based on the following suggestions for experimental design.
(i) A repeat of the preliminary experiment described above but with the 6 possible treatments in triplicate. Standard stocking density, and amount of feed, based on body weight of grass carp. Total 18 tanks.
| Treatment 1 | Treatment 2 | Treatment 3 | Treatment 4 | Treatment 5 | Treatment 6 |
| Pig manure | Pig manure | Pig manure | Pig manure | - | - |
| Vegetable matter | Vegetable matter | - | - | Vegetable matter | Vegetable matter |
| Bighead carp | Bighead carp | Bighead carp | Bighead carp | Bighead carp | Bighead carp |
| Silver carp | Silver carp | Silver carp | Silver carp | Silver carp | Silver carp |
| Grass Carp | - | - | Grass carp | Grass carp | - |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
(ii) Different types of fresh manure - Standard stocking density; standard species ratio; dry weight of manure inputs the same; manure added at regular 3 day intervals. Four treatments in triplicate, a total of 12 tanks.
| Treatment 1 | Treatment 2 | Treatment 3 | Treatment 4 |
| Pig manure | duck manure | chicken manure | cow manure |
 |  |  |  |
(iii) Different qualities of manures - Standard stocking density; standard species ratio; manures from animals receiving low grade feed and high grade feed. Eight treatments in triplicate, a total of 24 tanks.
| Pig | Duck | Chicken | Cow | ||||
 |  |  |  | ||||
| Treatment 1 | Treatment 2 | Treatment 3 | Treatment 4 | Treatment 5 | Treatment 6 | Treatment 7 | Treatment 8 |
| low grade | high grade | low grade | high grade | low grade | high grade | low grade | high grade |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
(iv) Manuring frequency - Standard stocking density; standard species ratio; two rates of manuring time frequencies. Because of the unpredictability of manure effects on phytoplankton, it may not be possible to continue loading at regular specified time intervals due to poor water quality. Then manuring should be suspended until water quality improves; and then continued at regular intervals as specified by the given experimental treatment. Experiments of this type should enable criteria to be developed for manure loading. It is suggested that pig manure be used initially, but the experiment could be repeated with other types of manure. Six treatments in triplicate, a total of 18 tanks.
| Treatment 1 | Treatment 2 | Treatment 3 | Treatment 4 | Treatment 5 | Treatment 6 |
| Low loading | High loading | Low loading | High loading | Low loading | High loading |
| Daily | Daily | 3 days | 3 days | 10 days | 10 days |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
(v) Fish versus fermented manure - Standard stocking density; standard species ratio; manure fresh or fermented for 15 days; manure added on dry weight basis at same frequency, say every 3 days. Six treatments in triplicate, a total of 18 tanks.
| Treatment 1 | Treatment 2 | Treatment 3 | Treatment 4 | Treatment 5 | Treatment 6 |
| Pig manure | Pig manure | Duck manure | Duck manure | Cow manure | Cow manure |
| Fresh | Fermented | Fresh | Fermented | Fresh | Fermented |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
(vi) Different types of green fodder or vegetable matter - Standard stocking density; standard species ratio; same dry weight of inputs based on 3% body weight of grass carp per day. Five treatments in triplicate, a total of 15 tanks.
| Treatment 1 | Treatment 2 | Treatment 3 | Treatment 4 | Treatment 5 |
| English rye grass | Sudan grass | Vegetable | Lake Taihu macrophyte e.g. Potamogeton | Macerated water hyacinth |
 |  |  |  |  |
(vii) Fresh versus aerobic composted green fodder - Standard stocking density; standard species ratio plus Tilapia nilotica which can digest compost; same dry weight of inputs based on 3% of body weight of grass carp per day. Six treatments in triplicate, a total of 18 tanks.
| Treatment 1 | Treatment 2 | Treatment 3 | Treatment 4 | Treatment 5 | Treatment 6 |
| Land grass Fresh | Land grass Composted | Potamogeton Fresh | Potamogeton Composted | Macerated Water hyacinth Fresh | Water hyacinth Composted |
 |  |  |  |  |  |
(viii) Fresh versus anaerobic composted green fodder - As for experimental design (vii) but with the compost done anaerobically in a sealed pit for 3 months.
(ix) Role of pond mud - Standard stocking density; standard species ratio; pig manure plus green fodder i.e., a standard fertilizer/feed input. Four treatments in triplicate, a total of 12 tanks.
| Treatment 1 | Treatment 2 | Treatment 3 | Treatment 4 |
| Pond mud | Pond mud | - | - |
| Fish | - | Fish | - |
 |  |  |  |
(x) Straw - Standard stocking density; standard species ratio plus Tilapia nilotica which may be able to digest straw; same dry weight inputs based on 3% of body weight of grass carp per day as in other experimental designs. The straw should be cut into 0.25 – 1.00 cm pieces. Five treatments in triplicate, a total of 15 tanks.
| Treatment 1 | Treatment 2 | Treatment 3 | Treatment 4 | Treatment 5 |
Untreated straw | Untreated plus N:P chemical fertilizer to give C:N:P, 20:1:0.2 | N:P chemical fertilizer | Treated with 1% NaoH for 4 days | Treated with 1% NaoH for 4 days plus N:P chemical fertilizer to give C:N:P, 20:1:0.2 |
(xi) Various species ratios - Standard stocking density; standard fertilizer/feed input of pig manure and green fodder at 3% of body weight of grass carp per day on a dry weight basis; in treatments 7, 8,, and 9 in which various fish are left out, the remaining species are stocked in their standard ratios. Total 27 tanks since each of the 9 treatments is in triplicate.
| Treatment | Fish stocking ratios | Comments | |||
| Grass carp | Silver carp | Bighead carp | Common carp | ||
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 1 | Standard stocking density |
| 2 | 10 | - | - | - | Monoculture |
| 3 | - | 10 | - | - | " |
| 4 | - | - | 10 | - | " |
| 5 | - | - | - | 10 | " |
| 6 | - | 7.1 | 1.4 | 1.4 | Eliminate grass carp |
| 7 | 6 | - | 2 | 2 | Eliminate silver carp |
| 8 | 3.3 | 5.5 | - | 1.1 | Eliminate bighead carp |
| 9 | 3.3 | 5.5 | 1.1 | - | Eliminate common carp |
(xii) Conventional pelleted feed - Use the standard pellet from Wuxi City Fishery Pellet Processing Factory with the same treatments as in experimental design (xi) above. Total 27 tanks since each of the 9 treatments is in triplicate.
(xiii) High protein pelleted feed - Test pellets suitable for monoculture of high market value carnivorous species e.g. mandarin fish and black carp. A possible source of high quality animal protein suitable for incorporating into pellets is the earthworm cultivated on animal manure, nightsoil and agricultural residues such as rice and wheat straw. Six suggested treatments are pellets of varying protein content 10, 20, 30, 40 and 50% including comparison with the Wuxi pellet factory standard pellet i.e., 6 treatments, in triplicate, or 18 tanks per species. Should the preliminary tests in tanks prove promising, further experimentation in floating cages in Lake Taihu is recommended.
(i) Varying pond depth (a) - Standard stocking density; standard species ratio; standard fertilizer/feed regime of pig manure and green fodder based on 3% body weight of grass carp per day. Five treatments in triplicate, a total of 15 ponds.
| Treatment 1 | Treatment 2 | Treatment 3 | Treatment 4 | Treatment 5 |
| 1.0 m | 1.5 m | 2.0 m | 2.5 m | 3.0 m |
 |  |  |  |  |
(ii) Varying pond depth (b) - As for experimental design (i) above, but the fish stocking densities and fertilizer/feed inputs to the pond should be based on volume rather than surface area. Thus, in design (ii) the amount of fish and fertilizer/feed would increase with depth.
(iii) Optimum number of livestock per unit pond area - Standard species ratio; manure from pigs added according to the design, water quality permitting. Should the water quality not allow the daily addition of manure then fertilizing should be suspended until the water quality improves, when the fertilization should be continued according to the design on a daily basis. Factorial experiment requiring 16 ponds.
| Fish stocking density per ha | Number of pigs per ha | ||||
| 25 | 75 | 100 | 125 | ||
| 25,000 | |||||
| 20,000 | |||||
| 15,000 | |||||
| 10,000 | |||||
The experiment could be repeated with manure from different livestock.
(iv) Monoculture versus polyculture - A monoculture of Tilapia nilotica, the standard limited polyculture of 4 species, and a typical Chinese polyculture of 8 species; standard fertilizer/feed inputs of pig manure and fertilizer based on the body weight of grass carp. A factorial experiment requiring 15 ponds.
| Fish stocking density per ha | |||
| monoculture | limited polyculture | Chinese polyculture | |
| 30,000 | |||
| 25,000 | |||
| 20,000 | |||
| 15,000 | |||
| 10,000 |
(v) Aerators and pelleted feed - A high stocking density, perhaps 1,500 per mu (22,500 per ha) with standard fertilizer/feed inputs. Four treatments in triplicate, a total of 12 ponds.
| Treatment 1 | Treatment 2 | Treatment 3 | Treatment 4 |
| Aerator | Aerator | - | - |
| Pellets | - | Pellets | - |
 |  |  |  |
(vi) Aquatic macrophytes in fish ponds - 1 m deep ponds to allow benthic macrophytes to grow in ponds with low fertility and light penetrating to the bottom; standard stocking density; standard stocking ratio except 2 treatments without grass carp. Four treatments in triplicate, a total of 12 ponds.
| Treatment 1 | Treatment 2 | Treatment 3 | Treatment 4 |
| Low pig manure | Low pig manure | Medium pig manure | High pig manure |
| Grass carp | - | Grass carp | Grass carp |
 |  |  |  |
With the exception of testing various manure distribution techniques, it will be possible to test only those methods which show great promise for increasing existing fish yields on Commune fish farms. This is because commercial fish farms are concerned with achieving high yields of fish and not experimentation.
(i) Different methods of manure application - A series of 9 ponds with identical water area, depth, stocking densities, stocking ratios, and supplementary feeding regimes. Ideally one type of manure should be used, and since these are commercial ponds it will be added as required and not at regular, specified time intervals which may not be feasible.
| Treatment 1 | Treatment 2 | Treatment 3 |
| 1 location | Several locations along one dike | Spray evenly over pond surface |
 |  |  |
The above experiment may be carried out at Wuxi Fish Farm or Holei People's Commune Fish Farm. At the former fish farm, a series of five ponds of varying sizes are available for experimentation, These ponds provide a great opportunity for resolving some of the controverses in fish culture. The experiments should run for the duration of the growing season.
The following five factors are of interest:
Pond area - 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 mu area (fixed)
Pond water depth - 1.5 and 3 m (two treatments)
Species ratio - Tilapia monoculture, limited polyculture (4 spp), Chinese polyculture (8 spp) (three treatments)
Fertilizer/feed inputs - fertilizer, fertilizer plus green fodder, fertilizer plus green fodder plus pellets (three treatments)
Pond input computation - input per unit area, input per unit volume (two treatments)
Total number of permutations = 1 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 2 = 36.
Thus to test all the above factors in various combinations would take 36 years. Clearly, this is not feasible so the following three experiments are recommended:
Wuxi Fish Farm Experimental Design 1
Depth 1.5 m; limited polyculture with standard stocking density;
standard fertilizer/feed regime.
Compute inputs on an area basis.
Wuxi Fish Farm Experimental Design 2
As for (i) but pond depth 3.0 m
Compute inputs on an area basis.
Wuxi Fish Farm Experimental Design 3
as for (ii) but compute inputs on a volume basis i.e., increase the
stocking density and fertilizer/feed inputs by a factor of two.